![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Oxidoreductase |
Catalyzes an oxidation-reduction reaction |
|
|
Transferase |
Catalyzes transfer of functional groups |
|
|
Hydrolase |
Usually with amide linkages in proteins. Catalyzes a hydrolysis reaction. Involves the addition of a water molecule |
|
|
Lysase |
Catalyzes the addition/removal of a group to form a double bind in a manner that does not involve hydrolysis or oxidation |
|
|
Isomerase |
Catalyzes isomerism or rearrangement of atoms |
|
|
Ligase |
Catalyzes formation of a bond between 2 molecules with the participation of ATP |
|
|
How are substances that react under the influence of an enzyme usually held to the enzyme? |
By side chains of amino acids in the enzyme protein |
|
|
Absolute specificity |
The enzyme will only catalyze one reaction. Not common |
|
|
Group specificity |
The enzyme will act only on molecules that have a specific functional group, such as amino, hydroxyl, or phosphate groups |
|
|
Linkage specificity |
Enzyme will act on a particular type of chemical bond, irrespective of the molecular structure. |
|
|
Stereochemical specificity |
Enzyme will act on a particular steroisomer |
|
|
Coenzyme |
When a cofactor is a small organic molecule |
|
|
B vitamins are... |
Water soluble |
|
|
The backbone of the helix of DNA is held together by... |
Sugar to phosphate bonds |
|
|
Transcription |
DNA to RNA |
|
|
What bonds link the base pairs in the DNA double helix? |
Hydrogen bonds |
|
|
mRNA |
RNA that carries instructions for protein synthesis to the sites for protein synthesis |
|
|
hnRNA |
RNA formed directly by DNA transcription |
|
|
rRNA |
RNA that combines with specific proteins to form ribosomes, the physical sites for protein synthesis |
|
|
tRNA |
RNA that delivers amino acids to the sites for protein synthesis. Activated when attached to its specific amino acid |
|
|
snRNA |
Turns hnRNA to mRNA |
|
|
Anticodon |
Complementary to codon on mRNA. Is on tRNA. |
|
|
PCR |
Polymerase chain reaction. Method for rapidly producing multiple copies of a DNA nucleotide sequence |
|
|
Due to recombinant DNA technology... |
A therapeutic product now available is human growth hormone |
|
|
Human genome project |
Purpose: to map the locations of all the genes in human DNA |
|
|
Citric acid cycle produces... |
CO2, NADH |
|
|
Flavin adenine dinucleotide |
Flavin- ribitol- phosphate- phosphate- ribose- adenine |
|
|
Carries electrons from citric acid cycle to electron transport chain: |
NADH and FADH2 |
|
|
Coenzyme A |
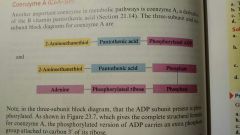
|
|
|
When combined with electron transport, one turn of the citric acid cycle produces how much ATP? |
10 |
|
|
What is both a reactant and a product in the electron transport chain? |
CoQ |
|
|
What is the "fuel" of the citric acid cycle? |
Acetyl CoA |
|
|
What steps of the citric acid cycle are molecules of carbon dioxide produced? |
Steps three and four |
|
|
Reduced means... |
NAD+ ---> NADH FADH ---> FADH2 |
|
|
What carries electrons from the citric acid cycle to the electron transport chain? |
FADH2, NADH |

