![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mirror image is not superposable on the original, therefore the stickman is ______. |
chiral |
|
|
Mirror image is superposable on the original, therefore the stickmanis ______. Also, if there is an axis of symmetry, an object is ______. |
achiral |
|
|
Define enantiomers |
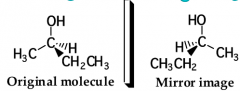
nonsuperposable mirror images |
|
|
If an object and its mirror image are superposable, they are __________ and there is no possibility of enantiomerism |
identical/same |
|
|
the R,S system is a way to distinguish between _____________ without having to draw them and point to one or the other |
enantiomers |
|
|
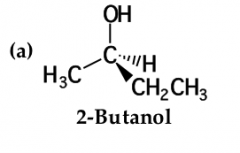
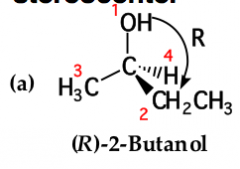
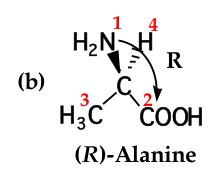
The first step in assigning an R or S configuration to a stereocenter is to: |
arrange the groups on the stereocenter in order of priority. priority is based on atomic number. the higher the atomic number, the higher the priority |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For a molecule with n stereocenters, the maximum number of stereoisomers possible is ____ |
2n |
|
|
Define diastereomers: |
stereoisomers that are not mirror images |
|
|
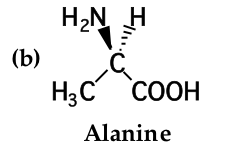
The most common cause of enantiomerism in organic molecules is the presence of a carbon with _____ different groups bonded to it. a carbon with ______ different groups bonded to it is called a _____________. |
four; stereocenter |
|
|
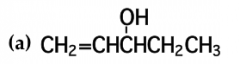
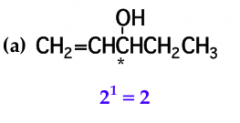
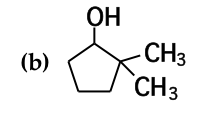
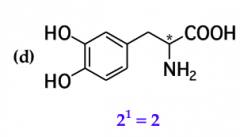
mark all stereocenters in each molecule and tell how many stereoisomers are possible for each |
*BLANK* |
|
|
|
|
|
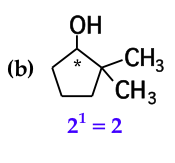
|
|
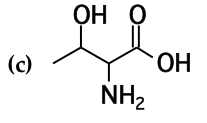
|
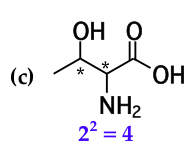
|
|
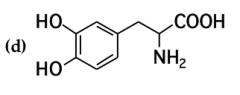
|
|

