![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Carboxylic acids boil at considerably higher temperatures than do alcohols, ketones, or aldehydes of similar molecular weights. This is because they:
a. form stable hydrogen-bonded dimers b. are hydrophobic c. are more acidic d. have a greater oxygen content e. none of the above |
a form stable hydrogen-bonded dimers
|
|
|
1-hexanol reacts with chromic acid to yield what product?
|
hexanoic acid
|
|
|
The first mechanistic step in the direct reaction of an amine with carboxylic acid to produce an amide is:
a. nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon b. loss of N₂ c. loss of CO₂ d. loss of H₂O e. an acid-base reaction |
e. an acid-base reaction
|
|
|
Provide the structure of succinic acid.
|
HO₂CCH₂CH₂CO₂H
|
|
|
Provide the IUPAC name for HO₂CCH₂C(CH₃)₂CH₂CH₂CO₂H
|
aa
|
|
|
Provide the IUPAC name for the compound shown below
add pic |
o-hydrobenzoic acid
|
|
|
Provide the IUPAC name for the compound shown below
add pic |
aa
|
|
|
Provide the IUPAC name for the compound shown below.
|
3-hydroxyhexanoic acid
|
|
|
Provide the structure of 3,3-dimethylheptanoic acid
|
add pic
|
|
|
Provide the major organic product of the following reaction.
add pic |
add pic
|
|
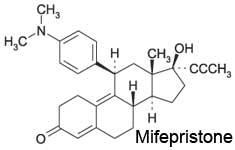
Choose the functional group which is not represented in the structure of RU-486
a. alkyne b. alcohol c. ketone d. amine e. ether |
e. ether
|
|
|
Which of the following molecules below is an ester?
a. CH₃CH₂CH(CH₃)₂ b. CH₃OCH₂CH₂CH₃ c. CH₃COOH d. CH₃COOCH₃ e. HC=CCH₃ |
d. CH₃COOCH₃
|
|
|
Which of the following molecules below has the higher boiling point?
a. CH₃CH₂CH₂OH b. CH₃CH₂OCH₃ |
a. CH₃CH₂CH₂OH
|
|
|
Which of the molecules below has the higher boiling point?
a. (CH₃)₃N b. CH₃CH₂CH₂NH₂ |
b. CH₃CH₂CH₂NH₂
|
|
|
Which of the molecules below has the higher boiling point?
a. CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂CH₃ b. (CH₃)₂CHCH₂CH₃ |
a. CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂CH₃
|
|
|
Which of the molecules below can be properly called an amine?
a. CH₃CN b. CH₃COOH c. CH₃CH₂CH₂OH d. CH₃CH₂NHCH₃ e. CH₃CH₂CH₂NO₂ |
d. CH₃CH₂NHCH₃
|
|
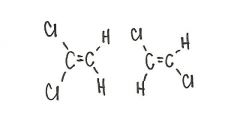
Are the two compounds shown below best described as cis-trans isomers, constitutional isomers, or not isomeric?
|
constitutional isomers
|
|
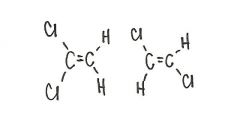
Are the two compounds shown below best described as cis-trans isomers, constitutional isomers, or not isomeric?
|
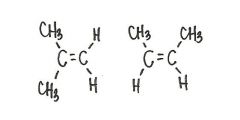
constitutional isomers
|
|
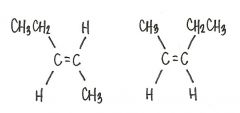
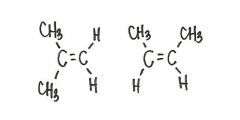
Are the two compounds shown below best described as cis-trans isomers, constitutional isomers, or not isomeric?
|
cis-trans isomers
|
|
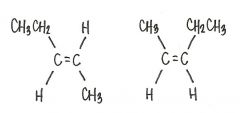
Are the two compounds shown below best described as cis-trans isomers, constitutional isomers, or not isomeric?
|
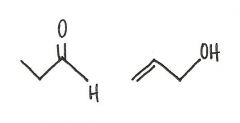
constitutional isomers
|
|
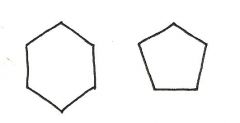
Are the two compounds shown below best described as cis-trans isomers, constitutional isomers, or not isomeric?
|
not isomeric
|
|
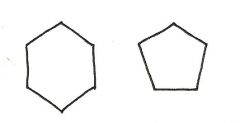
Are the two compounds shown below best described as cis-trans isomers, constitutional isomers, or not isomeric?
|
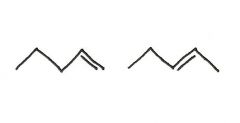
constitutional isomers
|
|
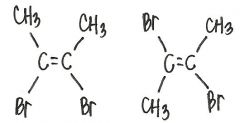
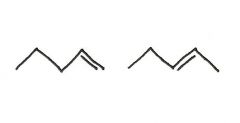
Are the two compounds shown below best described as cis-trans isomers, constitutional isomers, or not isomeric?
|
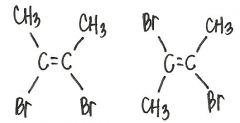
cis-trans isomers
|
|
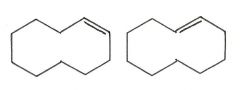
Are the two compounds shown below best described as cis-trans isomers, constitutional isomers, or not isomeric?
|
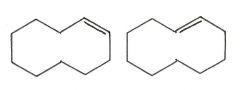
cis-trans isomers
|
|
|
Which of the functional groups below indicate the presences of two atoms connected by a triple bond?
a. alkyne b. alkene c. nitrile d. ester e. both A and C |
e. both A and C
|
|
|
Which of the class of organic compound below contains a carbonyl group as a part of its structure?
a. aldehyde b. ketone c. carboxylic acid d. ester e. all of the above |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
Which of the functional groups below contain a hydroxyl group as a part of their structure?
a. aldehyde b. alcohol c. carboxylic acid d. amine e. B and C only |
e. B and C only
|
|
|
Which of the following molecules below can hydrogen bond to another of the same compound?
a. CH₃CH₂OCH₂CH₃ b. CH₃CH₂COOCH₃ c. (CH₃CH₂)₂CHOH d. CH₃CH₂COCH₂CH₃ e. all of the above |
c. (CH₃CH₂)₂CHOH
|
|
|
What is the name of the characteristic functional group found in the molecule CH₃CH₂COOH?
|
carboxylic acid
|
|
|
What is the name given to a hydrocarbon that contains a carbon-carbon triple bond?
a. alkane b. alkene c. alkyne d. aromatic e. none of the above |
c. alkyne
|
|
|
Anisole, the compound shown below, is an example of _____.
add pic a. an ester b. an ether c. an alcohol d. an aldehyde e. a ketone |
b. an ether
|
|
|
Which of the following does not contain a carbonyl group?
a. aldehyde b. ketone c. carboxylic acid d. ester e. ether |
e. ether
|
|
|
Which of the following functional groups is not present in the HIV protease inhibitor drug called Saquinavir?
a. alcohol b. amine c. aromatic d. amine e. ketone |
number 95
|
|
|
Which functional group occurs more than two times in the structure of the HIV protease inhibitor?
add pic a. ketone b. carboxylic acid c. amine d. amide e. alkene |
96
|

