![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Show the hydrogen bonding which occurs when adenine and thymine form a base pair.
|
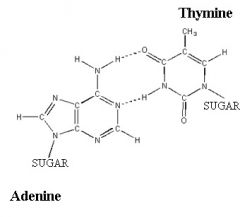
|
|
|
Provide the structure of adenosine monophosphate
|
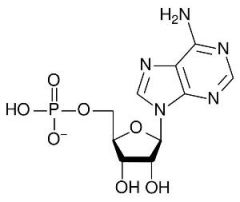
|
|
|
Which of the following can NOT be found in a nucleotide of RNA?
a. purine b. deoxyribose c. phosphate d. pyrimidine e. ribose |
b. deoxyribose
|
|
|
When DNA duplicates itself, the correct placement of the nucleotides is accomplished by
a. polymerase b. enzyme matching c. base matching d. transcription e. complementary base pairing |
e. complementary base pairing
|
|
|
In transcription
a. the mRNA produced is identical to the parent DNA b. the mRNA produced is complementary to one strand of the DNA c. a double helix containing one parent strand and one daughter strand is produced d. both strands of the DNA are copied e. uracil pairs with thymine |
b. the mRNA produced is complementary to one strand of the DNA
|
|
|
A DNA template having the base sequence 3'A-G-A-T-G-A-5' would produce a mRNA with a base sequence of
|
5'-U-C-U-A-C-U-3'
|
|
|
Codons are base pair sequences that
a. signal the end of DNA synthesis b. signal the start of RNA synthesis c. signal the start of the DNA synthesis d. code for amino acid e. code for one or more bases in mRNA |
d. code for amino acid
|
|
|
The codon is found on _____, and the anticodon is found on _____.
|
rNA; tRNA
|
|
|
The anticodon is
a. identical to the codon on mRNA b. identical to the codon in DNA c. complementary to the codon on DNA d. complementary to the codon on tRNA e. complementary to the codon on mRNA |
e. complementary to the codon on mRNA
|
|
|
The insertion of new DNA into the plasmid DNA of a bacterium produces
a. DNA fingerprints b. viral DNA c. ribosomes d. recombinant DNA e. restriction enzymes |
d. recombinant DNA
|
|
|
The result of a defective enzyme caused by mutation in the DNA nucleotide sequence is
a. AIDS b. recombinant DNA c. a genetic disease d. translocation e. HIV |
c. a genetic disease
|
|
|
A virus that contains RNA as its genetic material is a
a. recombinant DNA b. retrovirus c. bacteria d. genetically engineered virus e. vaccine |
b. retrovirus
|
|
|
When a mutation occurs by elimination of one base in the DNA sequence, this mutation is called a
a. translocation mutation b. frame-shift mutation c. viral mutation d. retrovirus mutation e. substitution mutation |
b. frame-shift mutation
|
|
|
Which of the following is a secondary amine?
a. 3-pentanamine b. N-ethyl-1-propanamine c. N,N-dimethylaniline d. methylamine e. cyclohexylamine |
b. N-ethyl-1-propanamine
|
|
|
What is the reaction of N-ethylformamide?
|
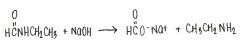
|
|
|
Draw the structure of N-ethyl-N-methyl-hexanamine
|
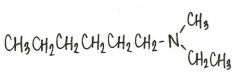
|
|
|
A plot of enzyme activity (y-axis) versus pH (x-axis) with other variables constant is a
a. line with an upward slope and a long flat top b. line with an upward slope followed by a downward slope c. straight horizontal line d. straight line with an upward slope |
b. line with an upward slope followed by a downward slope
|
|
|
A plot of enzyme activity (y-axis) versus substrate concentration (x-axis) with other variables constant is a
a. straight horizontal line b. line with an upward slope followed by a downward slope c. line with an upward slope and a long flat top d. straight line with an upward slope |
c. line with an upward slope and a long flat top
|
|
|
Which of the following statements concerning a competitive enzyme inhibitor is correct?
a. its effect can be overcome by decreasing the substrate concentration b. binds at a site other than the active site c. its effect is never reversible d. resembles the substrate in structure |
b. binds at a site other than the active site
|
|
|
The final product of a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions causes the enzyme that catalyzes the first reaction of the series to be inhibited. This is an example of
a. positive regulator control b. substrate control c. feedback control d. competitive control |
c. feedback control
|
|
|
The major function for B vitamins within the human body is as
a. components of coenzymes b. regulators of calcium ion and phosphate ion concentrations in blood c. regulators of cell differentiation d. antioxidants |
a. components of coenzymes
|
|
|
Which of the following would be the name for an enzyme?
a. pepsin b. succinate dehydrogenase c. pyruvate d. more that one correct answer e. no correct answer |
d. more that one correct answer
|
|
|
Which of the following binds to an enzyme at its active site?
a. irreversible inhibitor b. reversible noncompetitive inhibitor c. reversible competitive inhibitor d. more that one correct answer e. no correct answer |
d. more that one correct answer
|
|
|
Vitamins C and K are important, respectively, in
a. blood clotting and mucous membrane integrity b. bone formation and mucous membrane integrity c. vision and bone formation d. bone formation and blood clotting |
d. bone formation and blood clotting
|
|
|
In a solution that is highly acidic (low pH), which of the following forms the amino acid alanine (Ala) would predominate?
|
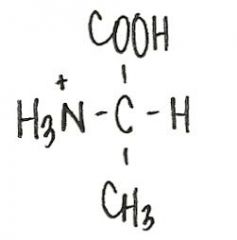
|
|
|
Interactions between amino acid R groups is responsible for which of the following levels of protein structure?
a. tertiary b. both secondary and tertiary c. secondary d. primary |
a. tertiary
|
|
|
Quaternary structure is possible for a protein only when
a. two or more protein chains are present b. a protein chain bends back upon itself c. all amino acids have nonpolar R groups d. the amino acid cystine is present |
a. two or more protein chains are present
|
|
|
The complete hydrolysis of a protein produces a mixture of
a. dipeptides b. free amino acids c. polypeptides and free amino acids d. polypeptides |
b. free amino acids
|
|
|
Which of the following statement concerning protein structure is correct?
a. amino acids are connected to each other through peptide bonds b. more than one chain of amino acids may be present c. at least one unit of each of the 20 standard amino acids must be present d. more that one correct answer e. no correct answer |
d. more that one correct answer
|
|
|
Which of the following tripeptides is a possible product from the partial hydrolysis of Ala-Val-Gly-Gly-Ala-Val?
a. Ala-Val-Val b. Ala-Val-Ala c. Gly-Gly-Ala d. more that one correct answer e. no correct answer |
c. Gly-Gly-Ala
|
|
|
Parallel polypeptide chains in a beta-pleated sheet conformation are held together by
a. hydrogen bonding b. R-group interactions c. covalent bonding d. more that one correct answer e. no correct answer |
a. hydrogen bonding
|
|
|
Which of the following types of interactions contributes to protein tertiary structure?
a. hydrogen bonds between C=O and N-H groups b. hydrogen bonds between polar neutral R groups c. hydrophobic interactions between nonpolar R groups d. more that one correct answer e. no correct answer |
d. more that one correct answer
|
|
|
The amine salt produced from the reaction of ethyl amine with HCl would have the formula _______.
|
CH₃-CH₂-NH₃-Cl
|
|
|
Which of the following is not an alkaloid?
a. caffeine b. histamine c. cocaine d. nicotine |
b. histamine
|
|
|
The organic products from the basic hydrolysis of an amide are
a. an amide salt and an amide b. a carboxylic acid salt and an amine c. a carboxylic acid and an amine salt d. a carboxylic acid and an amine |
b. a carboxylic acid salt and an amine
|
|
|
Which of the following statements concerning proteins is incorrect?
a. adjacent amino acids in a protein chain cannot be identical b. next to water, proteins are the most abundant molecules in the human body c. more that one amino acid chain may be present in a protein d. all proteins contain the elements C, H, O and N |
a. adjacent amino acids in a protein chain cannot be identical
|
|
|
What is the zwitterion form of the amino acid alanine (Ala)?
|
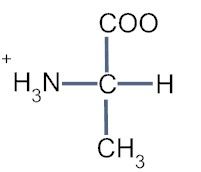
|
|
|
The joining together of two amino acids for form a dipeptide involves the reaction between
a. a carboxyl group and the hydroxyl group b. two carboxyl groups c. an amino group and a carboxyl group d. two amino groups |
c. an amino group and a carboxyl group
|
|
|
How many different tripeptides can be formed from two molecules of valine (Val) and one molecule of serene (Ser)?
a. four b. two c. three d. six |
c. three
|
|
|
To which of the following levels of protein structure is the sequence of amino acids in a protein directly related?
a. quaternary b. secondary c. tertiary d. primary |
d. primary
|
|
|
Quaternary structure is possible for a protein only when
a. the amino acid cystine is present b. all amino acids have nonpolar R groups c. a protein chain bends back upon itself d. two or more protein chains are present |
d. two or more protein chains are present
|
|
|
Which of the following types of standard amino acids exist as zwitterions in the solid state?
a. nonpolar amino groups b. polar neutral amino acids c. polar acidic amino acids d. more that one correct answer e. no correct answer |
d. more that one correct answer
|
|
|
Which of the following terms describes a protein secondary structure?
a. alpha helix b. fibrous shape c. globular shape d. more that one correct answer e. no correct answer |
a. alpha helix
|
|
|
R-group interaction between which of the following pairs of amino acids produces a disulfide bond?
a. proline-proline b. alanine-glycine c. cysteine-cysteine d. more that one correct answer e. no correct answer |
c. cysteine-cysteine
|
|
|
In which of the following is the pairing between enzyme type and enzyme function incorrect?
a. dehydrogenase - introduction of a double bond through hydrogen removal b. kinase - transfer of amino groups between substrates c. reductase - reduction of a substrate d. lipase - hydrolysis of ester linkages in lipids |
b. kinase - transfer of amino groups between substrates
|
|
|
An enzyme active site is the location in an enzyme where
a. interaction with a catalyst occurs b. catalyst molecules are generated c. substrate molecules are generated d. interaction with a substrate occurs |
d. interaction with a substrate occurs
|
|
|
Which of the following binds to an enzyme at a location other than the active site?
a. reversible noncompetitive inhibitor b. reversible competitive inhibitor c. irreversible inhibitor d. substrate |
a. reversible noncompetitive inhibitor
|
|
|
Which of the following pairing of terms is correct?
a. a synthase is a lyase b. a kinase is a transferase c. a mutase is a ligase d. more that one correct answer e. no correct answer |
b. a kinase is a transferase
|
|
|
Which of the following is not a water-soluble vitamin?
a. vitamin A b. vitamin B c. vitamin C d. more that one correct answer e. no correct answer |
d. more that one correct answer
|
|
|
Which of the following pairings of vitamins and functions is correct?
a. vitamin D; maintenance of mucous membranes b. vitamin D; an antioxidant c. vitamin C; a coenzyme d. more that one correct answer e. no correct answer |
b. vitamin D; an antioxidant
|
|
|
Bradykin, a peptide has the following condensed formula, Briefly mention of the functions of Bradykinin in humans, and show its complete (expanded) structural formula horizontally.
Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg |
Bradykinin is a pain enhancing peptide
|
|
|
Briefly describe the source and efficacy of vasopressin and oxytocin
|
Both are produced in the anterior pituitary.
Vasopressin regulates blood pressure. 9 amino acid oligopeptide Oxytocin is a 9 amino acid oligopeptide that is produced in the uterus. 1. enhancing or stimulates the uterus contraction during childbirth 2. stimulates mammary glands during lactation 3. enhances maternal characteristics |
|
|
Briefly describe the structure, source and efficacy of insulin in relation to type I and type II diabetes.
|
• Insulin is made up of peptide molecule chain A (21 amino acids) and B (30 amino acids)
• Chains A and B are intermolecullarly connected by two disulfide linkage between two cysteine amino acids • Chain A contains intramolecular disulfide linkage Efficacy 1. Insulin is essential for metabolizing glucose 2. Type I Diabetes is due to absence of inability to produce insulin 3. Type II Diabetes is due to inadequate protection of biosynthetic insulin; it is a "lifestyle disease" 4. Ingestion of insulin inhibits biosynthetic insulin Source: traditionally harvested from animal pancreas currently obtained genetic engineered insulin |

