![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
176 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are saccharides?
|
monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides
|
|
|
|
What are the classifications of carbs?
|
stereoisomers, saccharides, aldoses, ketoses
|
|
|
|
What are the classifications of stereoisomers?
|
enantiomers, diastereoisomers, chiral molecules, chiral carbon or center, anomers, epimers
|
|
|
|
What are the types of monosaccharides?
|
glucose, fructose and galactose
|
|
|
|
What are the types of disaccharides?
|
maltose, lactose, and sucrose
|
|
|
|
What are the types of polysaccharides?
|
starch → amypectin, amylose
cellulose glycogen |
|
|
|
What are carbohydrates?
|
compounds containing CO₂ + H₂O
carbon + hydrate = carbohydrate |
|
|
|
What is the formula for cellular respiration?
|
6CO₂ + 6H₂O ⇌ C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
|
|
|
|
What are aldoses?
|
compounds containing C as an aldehyde (-CHO)
|
|
|
|
What are ketoses?
|
compounds containing a keto group (C=O)
|
|
|
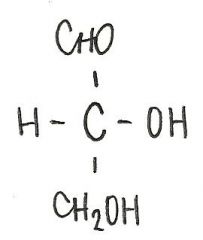
Identify the molecule
|
d-glyceraldehyde
aldotriose |
|
|
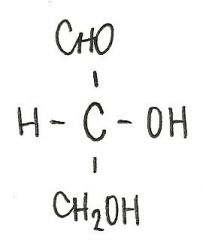
Identify the molecule
|
d-threose
aldotetrose |
|
|
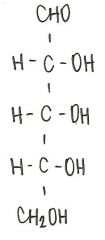
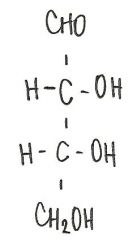
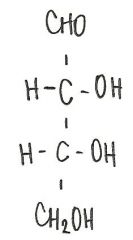
Identify the molecule
|
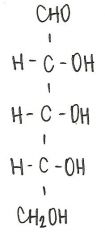
d-ribose
aldopentose |
|
|
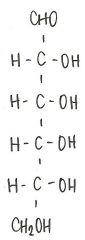
Identify the molecule
|
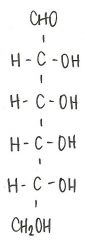
d-glucose
aldohexose |
|
|
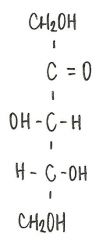
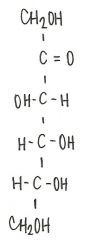
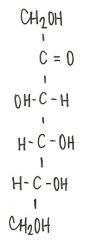
Identify the molecule
|
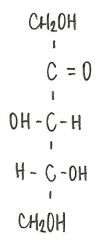
d-ribulose
ketopentose |
|
|
Identify the molecule
|
d-fructose
ketohexose |
|
|
|
Define: stereoisomers
|
isomers in which the atoms are arranged in the same sequence but differ in the spatial arrangement (three-dimensional arrangement)
|
|
|
|
Define: enatomers
|
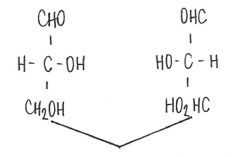
stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other but not super imposable, and they are chiral molecules containing chiral carbons
|
|
|
|
Define: diastereoisomers
|

molecules which are not mirror images of each other
|
|
|
|
Define: chiral molecule
|
carbon attached to 4 different groups is a chiral carbon
|
|
|
|
Define: epimer
|
compounds differ from each other in only one chiral carbon or chiral centers (MF = C₆H₁₂O₆)
|
|
|
|
What is a D (dextro) isomer?
|
when the hydroxyl group on the chiral carbon (center) farthest removed from the aldehyde (-CHO) or keto group (C=O) is on the right side it is a "D" isomer of configuration
|
|
|
|
What is a L-isomer?
|
when the hydroxyl group is on the left and the molecule is the mirror images it is an "L" isomer
|
|
|
|
Naturally occurring carbohydrates have only _____ and no ______
|
Naturally occurring carbohydrates have only D-isomers and no L-isomers
d-glucose is natural dl-glucose is suynthetic (manmade) |
|
|
|
What are the three types of saccharides?
|
monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides
|
|
|
|
monosaccharides contain _____
|
only one sugar unit
(MF = C₆H₁₂O₆) |
|
|
|
disaccharides contains _____
|
two monosaccharides
(MF = C₁₂H₂O₁₁) |
|
|
|
polysaccharides are ____
|
a polymer of monosaccharides
(MF = (C₆H₁₂O₆)n |
|
|
|
monosaccharides cannot further be _______
|
monosaccharides cannot further be hydrolyzed into simpler saccharides
α-D-glucse α,β - D- Glucose DL-glucose (don't buy) |
|
|
|
An open chain structure of carbohydrates is known as
|
Fischer Projection Formula
|
|
|
|
Identify the molecule
|
d-glucose
|
|
|
|
Identify the molecule
|
d-galactose
|
|
|
|
Identify the molecule
|
d-fructose
|
|
|
|
Haworth (cyclic) structure of monosaccharides
1. In solutions, the hydroxyl groups on the 5th carbon adds onto the carbonyl group to result a stable molecule known as a _______. |
Haworth (cyclic) structure of monosaccharides
1. In solutions, the hydroxyl groups on the 5th carbon adds onto the carbonyl group to result a stable molecule known as a hemiacetal. |
|
|
|
Haworth (cyclic) structure of monosaccharides
2. The newly formed acetal contain the newly created chiral center of chiral carbon (#1); and it is known as an _______. |
Haworth (cyclic) structure of monosaccharides
2. The newly formed acetal contain the newly created chiral center of chiral carbon (#1); and it is known as an "anomeric" center carbon. |
|
|
|
Haworth (cyclic) structure of monosaccharides
3. The hemiacetal (ring structure of carbohydrates is known as ______. |
Haworth (cyclic) structure of monosaccharides
3. The hemiacetal (ring structure of carbohydrates is known as Haworth structure. |
|
|
|
Haworth (cyclic) structure of monosaccharides
4. In the Haworth structure of aldoses and ketoses the 6th carbon is ________. |
Haworth (cyclic) structure of monosaccharides
4. In the Haworth structure of aldoses and ketoses the 6th carbon is always pointing up |
|
|
|
Haworth (cyclic) structure of monosaccharides
5. When the -OH group on the newly created chiral center [anomeric carbon] is pointing down; it is an ___ form. |
Haworth (cyclic) structure of monosaccharides
5. When the -OH group on the newly created chiral center [anomeric carbon] is pointing down; it is an α form. |
|
|
|
Haworth (cyclic) structure of monosaccharides
5. When the -OH group on the newly created chiral center [anomeric carbon] is pointing up; it is an ___ form. |
Haworth (cyclic) structure of monosaccharides
5. When the -OH group on the newly created chiral center [anomeric carbon] is pointing up; it is an β form. |
|
|
|
Haworth structure of d-fructose
|
add picture here
|
|
|
|
cereal grains including legumes, barley and fruits contain _____.
|
Preparation and Properties of monosaccharides
cereal grains including legumes, barley and fruits contain monosaccharides. |
|
|
|
Fruits contain d-fructose; therefore _______
|
Preparation and Properties of monosaccharides
Fruits contain d-fructose; therefore it is a fruit sugar |
|
|
|
Fructose is _____ more sweet than d-glucose.
|
Preparation and Properties of monosaccharides
Fructose is 100% more sweet than d-glucose. |
|
|
|
Grape sugars including fructose and glucose on fermentation results in ______.
|
Preparation and Properties of monosaccharides
Grape sugars including fructose and glucose on fermentation results in drinking alcohol. |
|
|
|
d-glucose undergoes Tollens oxidation results in _____ and _____
|
Preparation and Properties of monosaccharides
d-glucose undergoes Tollens oxidation results in d-glucomic acid and silver mirror |
|
|
|
d-glucose undergoes Benedicts oxidation results in _____ and _____
|
Preparation and Properties of monosaccharides
d-glucose undergoes Benedicts oxidation results in d-glucomic acid and Cu₂O |
|
|
|
d-glucse on hydrogenation [addition of H₂] in the presence of Pt or Pd results in _________
|
Preparation and Properties of monosaccharides
d-glucse on hydrogenation [addition of H₂] in the presence of Pt or Pd results in a sugar known as "d-glucitol" |
|
|
|
________ on hydrolysis results in two monosaccharides
|
Disaccharides on hydrolysis results in two monosaccharides
(C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁) |
|
|
|
monosaccharides _____ be hydrolyzed
|
monosaccharides can't be hydrolyzed
|
|
|
|
What is the source of maltose?
|
grains (soybeans, barley, maize, legumes, beans)
|
|
|
|
What is the MF of maltose?
|
C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁
|
|
|
|
Maltose on hydrolysis using an enzyme known as _____ present in the saliva is converted into two molecules of _______.
|
Maltose on hydrolysis using an enzyme known as maltase present in the saliva is converted into two molecules of α-d-glucose.
|
|
|
|
Maltose contains ______ glycosidic link
|
Maltose contains α-1, 4 - glycosidic link
|
|
|
|
The enzyme lactase in saliva hydrolyzes lactose into ______ and ______
|
The enzyme lactase in saliva hydrolyzes lactose into β-d-galactose and α-d-galactose
|
|
|
|
Lactose contains ____ glycosidic link.
|
Lactose contains β-1,4 glycosidic link.
|
|
|
|
Mother's milk contains ___ lactose; whereas cow's contains ___ lactose.
|
Mother's milk contains 8% lactose; whereas cow's contains 4% lactose.
|
|
|
|
If you lack the necessary enzyme to breakdown the β-1,4 glycosidic link present in lactose resulting in a condition known as _____.
|
If you lack the necessary enzyme to breakdown the β-1,4 glycosidic link present in lactose resulting in a condition known as lactose intolerance; resulting in stomach cramp and diarrhea
|
|
|
|
Lack of enzyme known as "β-d-galactose" necessary to convert β-d-galactose from lactose, into d-glucose results in a condition known as _____.
|
Lack of enzyme known as "β-d-galactose" necessary to convert β-d-galactose from lactose, into d-glucose results in a condition known as galactosemia leaving the β-d-galactose in the blood causing "cataract, cirrhosis, mental retardation & eventually death"
|
|
|
|
Sucrose on hydrolysis by an enzyme "sucrase" in saliva results in _____ & _____.
|
Sucrose on hydrolysis by an enzyme "sucrase" in saliva results in α-d-glucose & β-d-fructose
|
|
|
|
Sucrose contains ___, ___ glycosidic link
|
Sucrose contains α-1, β-2 glycosidic link
|
|
|
|
What is the MF for sucrose?
|
C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁
|
|
|
|
Sugar cane contains ___ sucrose; whereas sugar beet contains ___ sucrose.
|
Sugar cane contains 25% sucrose; whereas sugar beet contains 15% sucrose.
|
|
|
|
What is glucosamine?
|
for alleviating inflammatory swelling due to rheumatoid arthritis
|
|
|
|
What is galactosamine?
|
antigen for blood analysis
|
|
|
|
Maltose and lactose have a free hemiacetal group in the molecules; whereas sucrose has both anomeric carbons are tied up or linked therefore, sucrose is ________.
|
Maltose and lactose have a free hemiacetal group in the molecules; whereas sucrose has both anomeric carbons are tied up or linked therefore, sucrose is not a reducing sugar. (i.e. it does not undergo oxidation)
|
|
|
|
α-d-glucose and β-d-glucose are in equilibrium in solution thru their open, and it is known as ______
|
α-d-glucose and β-d-glucose are in equilibrium in solution thru their open, and it is known as mutarotation
|
|
|
|
What are the two types of starch?
|
amylose and amylopectin
|
|
|
|
What is starch present in?
|
grains, barley, legumes, carrots, potatoes, yams, wtc
|
|
|
|
What is a simple starch?
|
amylose
|
|
|
|
List characteristics of amylose
|
(simple starch)
-20% of starch -250-4000 glucose units -present in cereal grains, legumes, soy beans -grown over ground |
|
|
|
List characteristics of amylopectic
|
(complex starch)
-80% of starch -potatoes, carrots yams, taro, etc. -grown under ground |
|
|
|
What is the structure of amylose?
|
therefore amylose contains α-1,4 glycosidic link
|
|
|
|
amylose + amylopectin →"amylase"→
|
dextrins
|
|
|
|
dextrins →"amylase"→
|
maltose
|
|
|
|
maltose →maltase in saliva→
|
α-d-glucose
|
|
|
|
Efficacy
Fermentation followed by distilled maltose yield ______ |
Efficacy
Fermentation followed by distilled maltose yield CH₃CH₂OH (whiskey) |
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
amylopectic
|
|
|
|
Amylopectin contains a _____ glycosidic link and _______ glycosidic link every ____ units
|
Amylopectin contains an α-1,4 glycosidic link and α-1,6 glycosidic link every 25 units
|
|
|
|
Cellulose on hydrolysis results in _____ which on further hydrolysis results in _____
|
Cellulose on hydrolysis results in cellulose (C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁) which on further hydrolysis results in β-d-glucose
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
cellulose
|
|
|
|
Cellulose contains _____ glycosidic link containing _____
|
Cellulose containsβ-1,4 glycosidic link containing β-d-glucose
|
|
|
|
Humans do not have the necessary enzyme to metabolize ____; whereas animals do.
|
Humans do not have the necessary enzyme to metabolize β-d-glucose; whereas animals do.
|
|
|
|
Where is glycogen present in?
|
primarily in the liver and some muscle tissues
|
|
|
|
The structure of glycogen is the same as _____ except branched containing α-1,4 glycosidic link and α-1,6 glycosidic link every 10 glucose units.
|
The structure of glycogen is the same as amylopectinexcept branched containing α-1,4 glycosidic link and α-1,6 glycosidic link every 10 glucose units.
|
|
|
|
Starch with iodine result in a ____; whereas the disaccharides show _____.
|
Starch with iodine result in a deep blue color; whereas the disaccharides show brown color.
|
|
|
|
starch →H₂SO₄→
|
α-d-glucose
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure and give the IUPAC name, common name and source
H-COOH |
IUPAC: methanoic acid
Common: formic acid Source: ant, bee stings |
|
|
|
Identify the structure and give the IUPAC name, common name and source
CH₃-COOH |
IUPAC:ethanoic acid
Common: acetic acid Source: vinegar |
|
|
|
Identify the structure and give the IUPAC name, common name and source
CH₃-CH₂-COOH |
IUPAC: propanic acid
Common: propionic acid Source: milk, cottage cheese |
|
|
|
Identify the structure and give the IUPAC name, common name
CH₃-CH₂-CH₂-CH₂-COOH |
IUPAC: pentanoic acid
Common: valeroic acid |
|
|
|
Identify the structure and give the IUPAC name, common name
CH₃-CH₂-CH₂-CH₂-CH₂CH₂-COOH |
IUPAC: heptanoic acid
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure and give the IUPAC name
|
benzenoic acid
|
|
|
|
How do you name carboxylic acids?
|
1. name the alkane
2. delete the "e" 3. replace with "oic acid" |
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
lactic acid
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
succinic acid
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
citric acid
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
fumaric acid
|
|
|
|
Name the structure
|
o-hydroxybenzoic acid or salicylic acid (aspirin)
|
|
|
|
Name the structure
|
o-bromo-m-chloro-p-methoxy benzenoic acid
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
pthalic acid
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
isophatlic acid
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
terepthalic acid
|
|
|
|
Complete or strong oxidation of primary alcohols using K₂CR₂O7/H₂SO₄ or complete chromic acid oxidation results in _____.
|
Complete or strong oxidation of primary alcohols using K₂CR₂O7/H₂SO₄ or complete chromic acid oxidation results in carboxylic acid.
|
|
|
|
Oxidation of aldehydes result in a _____
|
Oxidation of aldehydes result in a carboxylic acid
|
|
|
|
Up to 4 carbons are _____ in _____
|
Up to 4 carbons are soluble in water
|
|
|
|
Carboxylic acids react with bases including sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form _____ and _____.
|
Carboxylic acids react with bases including sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form salt and water.
|
|
|
|
_____ is added to fruit juices, jams, salad dressing, etc. to prevent mold growth.
|
Sodium Benzoate is added to fruit juices, jams, salad dressing, etc. to prevent mold growth.
|
|
|
|
_____ is added to cheese, bread, and cookies (baked goods) to extend shelf life.
|
Sodium Propanate II is added to cheese, bread, and cookies (baked goods) to extend shelf life.
|
|
|
|
_____ and ____ are known as preservatives
|
Sodium Benzoate and Sodium Propanate II are known as preservatives
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
monosodiumglutamate aka MSG
|
|
|
|
Carboxylic acids have a much higher boiling point than the corresponding alcohol due to _____ resulting in a "dimer"
|
Carboxylic acids have a might higher boiling point than the corresponding alcohol due to hydrogen bonding resulting in a "dimer"
|
|
|
|
Carboxylic acid react with alcohols in presence of an acid catalyst to undergo _____ resulting in _____.
|
Carboxylic acid react with alcohols in presence of an acid catalyst to undergo dehydration resulting in "esters".
|
|
|
|
How do you name an ester?
|
1. name the alcohol alkyl group (i.e. the alkyl on the oxygen)
2. name the carboxylic acid 3. delete the "ic acid" 4. replace with "ate" |
|
|
|
Esters are low boiling liquids when compared with the carboxylic acids and alcohols due to the absence of _____.
|
Esters are low boiling liquids when compared with the carboxylic acids and alcohols due to the absence of hydrogen bonding.
|
|
|
|
Esters are ____ smelling compounds and are used in the ______ industry.
|
Esters are sweet smelling compounds and are used in the perfume industry.
|
|
|
|
Esters on hydrolysis results in the _____ and the alcohols; whereas the ____ hydrolysis result in the alcohol and the ____ of the carboxylic acid
|
Esters on hydrolysis results in the carboxylic acid and the alcohols; whereas the base (NaOH) hydrolysis result in the alcohol and the sodium salt of the carboxylic acid
|
|
|
|
Saponification
|
????
|
|
|
|
What are some diseases that are linked to obesity?
|
1. cancer
2. heart disease 3. diabetes 4. stroke 5. Alzheimer's disease 6. obesity |
|
|
|
Fatty acids are a long chain of carboxylic acids that contain ____ number of carbons
|
Fatty acids are a long chain of carboxylic acids that contain an even number of carbons
|
|
|
|
Fatty acids that contain a C-C single bond are _______
|
saturated fatty acids
|
|
|
|
Fatty acids that contain at least one C-C bond is
|
unsaturated fatty acid
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure and name name it and the source
|
Name: lauric acid
Source: coconut |
|
|
|
Identify the structure and name name it and the source
|
Name: myristic acid
Source: nutmeg |
|
|
|
Identify the structure and name name it and the source
|
Name: palmitic acid
Source: palms |
|
|
|
Identify the structure and name name it and the source
|
Name: stearic acid
Source: animal fat |
|
|
|
Identify the structure and name name it and the source
|
Name: arachidic acid
Source: corn, tissues, etc. |
|
|
|
Identify the structure and name it and the source
|
Name: palmitolecic acid
Source: butter |
|
|
|
Identify the structure and name it and the source
|
Name: oleic acid
Source: olive oil |
|
|
|
Identify the structure and name it and the source
|
Name: linoleic acid
Source: vegetable oil, soy oil |
|
|
|
Identify the structure and name it and the source
|
Name: linolemic acid
Source: found in COLD WATER FISH (salmon, halibut, mackerel, walnuts, tuna |
|
|
|
How much saturated fat does Tilapia have?
|
90%
|
|
|
|
How much saturated fat does catfish have?
|
60%
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
arachadonic acid
|
|
|
|
Naturally occurring unsaturated fatty acids contain only
|
a cis double bond
|
|
|
|
A cis fatty acid has a(n) _____ shape and it does not compact into a solid (i.e. is not solidified)
|
A cis fatty acid has an irregular shape and it does not compact into a solid (i.e. is not solidified)
|
whereas a trans fatty acid is _____ in structure the same as a _____ fatty acid and easily deposited as a solid
|
|
|
Saturated fatty acid is _____ a solid; whereas an unsaturated fatty acid is a(n) _____ of _____ melting point
|
Saturated fatty acid is invariable a solid; whereas an unsaturated fatty acid is a(n) oil of low melting point
|
|
|
|
Fatty acids are ______ in water but _____ in organic solvents.
|
Fatty acids are not soluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
|
|
|
|
Fatty acids react with alcohols including glycerol to result in _____ known as _____ or _____
|
Fatty acids react with alcohols including glycerol to result in triesters known as triacyl glycerols or glyceroltriesters
|
|
|
|
Triglycerides known as ____ are present in human in the adipose tissue cells under the skin especially in the _____.
|
Triglycerides known as fats are present in human in the adipose tissue cells under the skin especially in the abdominal cavity.
|
|
|
|
Saturated triglycerides are known as _____ contain _____ molecules of the same fatty acid
|
Saturated triglycerides are known as simple triglycerides contain 3 molecules of the same fatty acid
|
|
|
|
Unsaturated triglycerides contain different fatty acids and are hence known as _____
|
Unsaturated triglycerides contain different fatty acids and are hence known as mixed triglycerides
|
|
|
|
Triglycerides are _____
|
Triglycerides are hydrophobic, not soluble in H₂O
|
|
|
|
Triglycerides on acid hydrolysis results in _____ and the fatty acid; whereas on base hydrolysis results in _____ and the _____ of the fatty acid, known as _____.
|
Triglycerides on acid hydrolysis results in glyercol and the fatty acid; whereas on base hydrolysis results in glycerol and the sodium salt of the fatty acid, known as "soap".
|
|
|
|
SOAP: sodium salt of fatty acid
|
hard soap
|
soft soap
|
|
|
soap is _____ (i.e. contain polar and nonpolar domain)
|
add pic
|
|
|
|
During a bath, the _____ ends of a soap dissolves the oil and grease to form a lather; and the _____ end washes away the later in water.
|
During a bath, the nonpolar ends of a soap dissolves the oil and grease to form a lather; and the polar end washes away the later in water.
|
|
|
|
Show the formation of a triglyceride from palmitic acid
1. Name it 2. Show the saponification |
add pic
|
|
|
|
Glyceryl phospholipids "membrane lipids"
|
1 glycerol, 2 molecules of fatty acid and phosphatidyl amine
|
|
|
|
cephalin
|
components
glycerol, 2 molecules of palmitic acid, phosphate, and ethanol amine |
|
|
|
lecithins
|
components
glycerol, 2 myristi acids, phosphate, and choline |
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
choline
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
myristic acid
|
|
|
|
True/False: Glyceryl phospholipids are present in the bilayer membrane
|
true
|
|
|
|
Glyceryl phospholipids are ____
|
Glyceryl phospholipids are amphipathic (i.e. contains both nonpolar and polar domains
|
|
|
|
The _____ are known as heads are pointing towards the outer end of the bilayer membrane; whereas the _____ tail is pointing inward
|
The polar ends are known as heads are pointing towards the outer end of the bilayer membrane; whereas the nonpolar tail is pointing inward
|
|
|
|
sphingomyeline
|
contain spingosine, fatty acids, and the phospatyl choline
|
|
|
|
spingosine
|
a 18 carbon chain containing a 2° and 1° alcohol & alkene & amine group
|
|
|
|
The cermide reacts with the phosphatidyl choline to form the _____
|
sphingomyelins
|
|
|
|
sphingomyelines are present in the _____.
|
sphingomyelines are present in the myeline sheaths.
|
|
|
|
sphingoglycolipids
|
a ceramide present with β-d-galactose & β-d-glucose to result in ______.
|
glycosphingolipids
|
|
|
lack of enzyme β-d-galactidase necessary to break and metabolize the β-d-galactose present in the galactocerebroside results in a disease known as _____ disease which results in mental retardation and death.
|
lack of enzyme β-d-galactidase necessary to break and metabolize the β-d-galactose present in the galactocerebroside results in a disease known as "Krabe" disease which results in mental retardation and death.
|
|
|
|
_____ are present in the human brain
|
cerebrosides are present in the human brain
|
|
|
|
waxes
|
esters obtained by long chain carboxylic acids and long chain alcohols
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
myrissyl alcohol
|
|
|
|
cholesterol is produced in the ____
|
cholesterol is produced in the liver
|
|
|
|
Cholesterol produced in humans is known as _____
|
Cholesterol produced in humans is known as biosynthetic cholesterol
|
|
|
|
100mL of human blood contains ____mg our cholesterol and _____mg of cholesterol ester a fatty acid.
|
100mL of human blood contains 50 mg our cholesterol and 170 mg of cholesterol ester a fatty acid.
|
|
|
|
Humans produce _____mg cholesterol per day. Daily recommended intake of cholesterol is ____mg per day, in the US daily intake of cholesterol is ____mg a day.
|
Humans produce 900-1000 mg cholesterol per day. Daily recommended intake of cholesterol is 200-300 mg per day, in the US daily intake of cholesterol is 400-600 mg a day.
|
|
|
|
The biosynthetic cholesterol produced in the liver is transported in the blood to the tissue cells to covert it into _____.
|
The biosynthetic cholesterol produced in the liver is transported in the blood to the tissue cells to covert it into hormones.
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
biocholesterol (liver)
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
progesterone
|
produced in the uterus to strengthen uterus receive embryo
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
testosterone
|
(male sex hormone) enhances male sexual characteristics and builds muscle
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
estrogen
|
(ovary)
1. female sex hormone 2. enhances female sexual characteristics 3. regulates menstrual cycle 4. helps ovulation 5. stimulates mammary glands during lactation and pregnancy 6. prevents pregnancy during lactation |
|
|
Identify the structure
|
cortisol
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
norethindrone (contraceptive pills)
|
|
|
|
Identify the structure
|
RU-486
|
|

