![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Identify the 2 types of organic nitrogen-containing compounds.
|
Amines and amides
|
|
|
The elements in amines include the following: _________.
|
Carbon
Hydrogen Nitrogen |
|
|
The elements in amides include the following: _________.
|
Carbon
Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen |
|
|
Nitrogen has ____ valence e- and can form _____ covalent bonds.
|
Nitrogen has 5 valence e- and can form 3 covalent bonds.
|
|
|
Identify and illustrate ammonia.
|
NH3
PIC |
|
|
Identify the 3 common classifications for amines.
|
Primary amines (1o): Nitrogen with one R group
Secondary amines (2o): Nitrogen with two R groups Tertiary amines (3o): Nitrogen with three R groups |
|
|
amine
|
Organic derivative of ammonia (NH3) in which one or more alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl groups are attached to the nitrogen atom
|
|
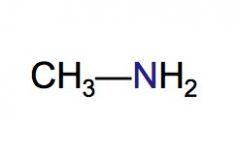
Classify the following HC as a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
|
primary amine
|
|
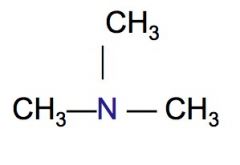
Classify the following HC as a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
|
tertiary amine
|
|
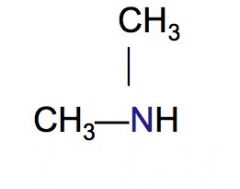
Classify the following HC as a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
|
secondary amine
|
|
|
Identify the general formula for the following:
Primary amine Secondary amine Tertiary amine |
Primary amine - R-NH2
Secondary amine - R2-NH Tertiary amine - R3-N |
|
|
Identify the fxn group present in a primary amine.
|
amino fxn group
|
|
|
Illustrate the amino fxn group.
|
--NH2
PIC |
|
|
Identify and illustrate the 2 classifications of amino fxn groups.
|
Monosubstituted fxn groups
Disubstituted fxn groups |
|
|
Identify another classification of amines that is not so common.
|
4° salt or quaternary salt
PIC |
|
|
Identify the general formula and charge (if any) of a 4° salt.
|
R4N+
+, positive charge |
|
|
Cyclic amines are always classified as either _________ or _______ amines.
|
secondary or tertiary
|
|
|
heterocylic compound
|
cyclic organic compound in which one or more of the carbon atoms in the ring have been replaced with atoms of other elements
|
|
|
heterocyclic amine
|
organic compound in which nitrogen atoms (of an amino group) are part of either an aromatic or a nonaromatic ring system
|
|
|
Identify the following hydrocarbon.
|
2-butanamine
|
|
|
Identify the following hydrocarbon.
|
3-methyl-1-butanamine
|
|
|
Identify the following hydrocarbon.
|
1,4-butanediamine
Note: There are 2 amino groups. |
|
|
Identify the following hydrocarbon.
|
N-methyl-2-butanamine
|
|
|
Identify the following hydrocarbon.
|
N, N- dimethyl-1-propanamine
|
|
|
Identify the following hydrocarbon.
|
3-aminopetanoic acid
Note: Amine group is used as substituent, -amino, with carboxylic acid |
|
|
Identify the following hydrocarbon.
|
4-amino-2-pentanone
Note: Amine group is used as substituent, -amino, with ketone |
|
|
Identify the following hydrocarbon. [common]
|
aniline
|
|
|
Identify the following hydrocarbon.
|
m-chloro aniline
|
|
|
Identify the following hydrocarbon.
|
N-ethylaniline
|
|
|
Identify the following hydrocarbon.
|
N,N-dimethylaniline
|
|
|
1-2 carbon amines are ____ at room temperature.
|
gas
|
|
|
3-8 carbon amines are ____ at room temperature.
|
liquid
|
|
|
Do amines have an odor?
|
Yes. They either smell like ammonia or raw, decaying fish.
|
|
|
Foul smell from dead fish and decaying flesh is due to _________.
|
diamines released by the bacterial decomposition of protein.
|
|
|
3° Amines have ____ B. P. than 1° and 2° amines
|
lower
|
|
|
B. P. is _______ alkanes and alcohols.
A) Above B) Below C) Inbetween |
Inbetween
alkanes < amines < alcohols |
|
|
N-H bond has ____ H-bonding than O-H.
A) stronger B) weaker C) same |
weaker
|
|
|
Amines with fewer than six carbon atoms are _____(solubility)_____ in water.
|
infinitely soluble
|
|
|
Solubility of amines results from _______ between the amines and water.
|
H-bonding
|
|
|
Amines are
A) acidic B) basic C) neutral |
basic
Note: They behave like NH3. |

