![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The common structural feature of all aldehydes and ketones is?
|
The common structural feature of all aldehydes and ketones is the carbonyl functional group.
|
|
|
The common structural feature of all aldehydes and ketones is?
|
The common structural feature of all aldehydes and ketones is the carbonyl functional group.
|
|
|
Show me the funtional groups of aldehydes and ketones and the the carboxyl group.
|
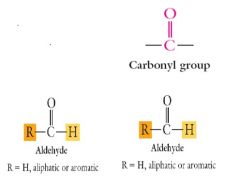
|
|
|
Other families containing the carbonyl group contain a heteroatom—What is an heteroatom?
|
Other families containing the carbonyl group contain a heteroatom—an oxygen in carboxylic acids and esters, and a nitrogen in amides.
|
|
|
Give pictoral examples of heteroatoms?
|
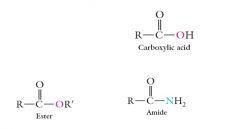
|
|
|
What are other examples of families containing carbonyl groups?
|
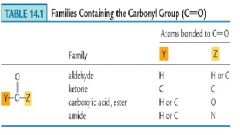
|
|
|
Aldehydes and ketones are related to alcohols in the same way that alkenes are related to alkanes: the loss of two hydrogen atoms: Show me?
|

|
|
|
The C=O double bond in aldehydes and ketones acts like the C=C double bond in alkenes: the molecular formula of an aldehyde or ketone contains two fewer hydrogen atoms than the parent alcohol.
|
|
|
|
Both the carbon and oxygen atoms in the carbonyl group are sp2 hybridized. What do they contain?
|
Both the carbon and oxygen atoms in the carbonyl group are sp2 hybridized. The carbonyl group contains one strong σ-bond and a weaker π-bond.
|
|
|
The bonds angles about the carbonyl group are close to 120°. Show me?
|
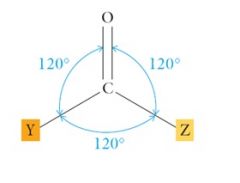
|
|
|
Aldehydes and ketones can have different constitutional isomers based on what?
|
Aldehydes and ketones can have different constitutional isomers based on different carbon skeletons, and on the placement of the carbonyl group.
|
|
|
Both compounds have the same formula C3H6O: Show me how?
|
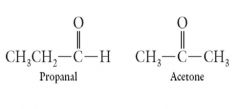
|
|
|
The IUPAC naming system for aldehydes and ketones is a variation of the naming system for alkanes: Show me how?
|

|
|
|
Show me IUPAC and common names of Aldehydes and Ketones.
|
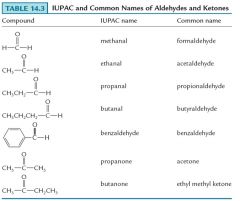
|
|
|
Show me the physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones?
|
The physical properties of aldehydes and ketones depend upon the polar nature of their carbonyl group.
Higher boiling and melting points than those of the corresponding hydrocarbons but lower than those of the corresponding alcohols. Almost the same water solubility as that of alcohols. |
|
|
The carbonyl group is highly polarized: Show me?
|
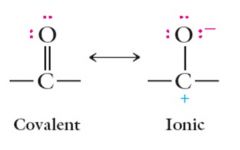
|
|
|
The true structure is between these two extremes, or a blend of the two structures. The carbonyl carbon possesses a partial positive charge and the carbonyl oxygen a partial negative charge. Show me
|
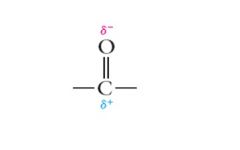
|
|
|
Show me examples of boiling points and ketones?
|
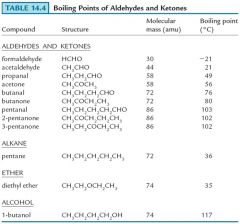
|
|
|
Show me the relation of secondary attraction forces and boiling point.
|
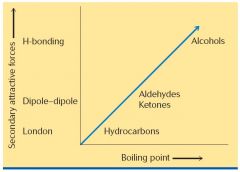
|
|
|
What are some of the relations between boiling points of alcohols, aldehydes, and alkanes with molecular mass?
|
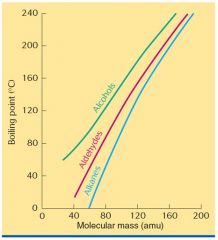
|
|
|
What are some physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones?
|
Aldehydes and ketones have boiling points considerably lower than those of alcohols, however, they all have about the same water solubility.
Aldehydes and ketones are hydrogen bond acceptors and thus can interact with the hydrogen bond donors of water molecules. Aldehydes and ketones cannot hydrogen bond with each other, however, because they lack hydrogen bond donating groups. |
|
|
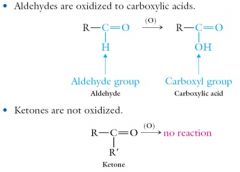
Aldehydes and ketones undergo combustion reactions with oxygen to carbon dioxide and water.Selective oxidations using permanganate (MnO4-) or dichromate (Cr2O72-) yield: Show me?
|
|
|
|
The selective oxidation of aldehydes is used commercially for the synthesis of what?
|
The selective oxidation of aldehydes is used commercially for the synthesis of carboxylic acids.
|
|
|
The oxidation of aldehydes also takes place slowly upon exposure to air. Ketones are what?
|
The oxidation of aldehydes also takes place slowly upon exposure to air. Ketones are not affected.
|
|
|
Dichromate and permanganate oxidations are useful tests for distinguishing aldehydes from what? They cannot distinguish aldehydes from primary and secondary alcohols and alkenes, however.
|
Dichromate and permanganate oxidations are useful tests for distinguishing aldehydes from ketones. They cannot distinguish aldehydes from primary and secondary alcohols and alkenes, however.
|
|
|
Reagents such as Tollens's reagent can distinguish from what to what?
|
Reagents such as Tollens's reagent can distinguish aldehydes from ketones, primary and secondary alcohols and alkenes.
|
|
|
What is Tollens's reagent and properties?
|
Tollens's reagent is colorless alkaline solution of a silver-ammonia complex ion, [Ag(NH3)2]+, which reacts with aldehydes to form a shiny gray precipitate of silver metal. The silver usually coats the surface of the test tube, giving the appearance of a silver mirror.
|
|
|
What is Benedict’s reagent and its properties?
|
Benedict’s reagent is a blue, alkaline solution of copper (II) ion stabilized as its polyatomic ion with citrate anion.
|
|
|
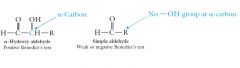
In the presence of an -hydroxy aldehyde, the blue color disappears and is replaced by a red precipitate of what?
|
In the presence of an -hydroxy aldehyde, the blue color disappears and is replaced by a red precipitate of Cu2O.
|
|
|
Simple aldehydes such as acetaldehyde and benzaldehyde do not give what with Benedict’s reagent?
|
Simple aldehydes such as acetaldehyde and benzaldehyde do not give positive tests with Benedict’s reagent.
|
|
|
Only alpha-hydroxy aldehydes give what with Benedict’s reagent?
|
Only alpha-hydroxy aldehydes give a positive test with Benedict’s reagent.
|
|
|
Show me the relation of test with hydroxy aldehydes and test?
|
|
|
|
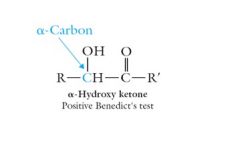
The alpha-hydroxy ketones are the only ketones which give a positive test with Benedict’s reagent.
|
|
|
|
Benedict’s reagent detects glucose and certain other carbohydrates and thus can distinguish them from what?
|
Benedict’s reagent detects glucose and certain other carbohydrates and thus can distinguish them from simple aldehydes and ketones, alcohols, and other compounds.
|
|
|
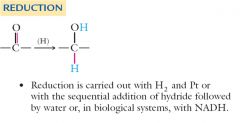
Aldehydes can be reduced to primary alcohols and ketones to secondary alcohols. The reduction process is the reverse of the oxidation process already described.
|
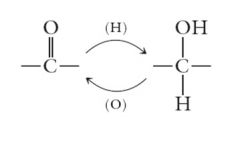
|
|
|
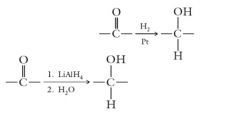
Two methods of reduction are useful for aldehydes and ketones.
Catalytic hydrogenation: Hydride reduction: Show me? |
|
|
|
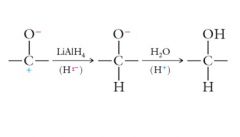
In hydride reduction, a metal hydride is employed. Metal hydrides are a source of H- ions: Show me?
|

|
|
|
The actual mechanism of the hydride reduction involves an initial transfer of a hydride ion to the carbonyl carbon, followed by a transfer of H+ from water to the carbonyl oxygen: Show me?
|
|
|
|
The reagents must be added sequentially because water is more reactive to the hydride than is the carbonyl group. Show me?
|
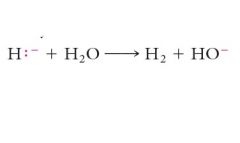
|
|
|
Catalytic hydrogenation reduces both carbon-carbon and carbon-oxygen double bonds. Hydride reduction is more selective and reduces only carbon-oxygen double bonds.
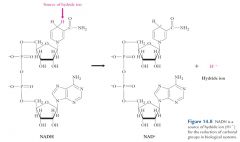
Hydride reductions in biological systems are accomplished by an organic compound called nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Show me? |

|
|
|
Nadh is the source of Hydride ions. Show me?
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
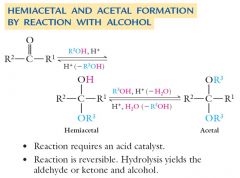
Aldehydes and ketones react with alcohols to form hemiacetals and acetals. Show me?
|
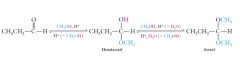
|
|
|
Hemiacetals and acetals are important structures what?
|
Hemiacetals and acetals are important structures in carbohydrates.
|
|
|
What are some of the properties of hemiacetals?
|
The products formed from ketones were previously called hemiketals and ketals to distinguish them from the products formed from aldehydes.
Most hemiacetals are unstable and cannot be isolated. The equilibrium forming a hemiacetal lies far to the left, or to the reactant side of the reaction. The equilibrium forming an acetal from a hemiacetal lies far to the right, or to the product side of the reaction. |
|
|
Acetals can be isolated if excess alcohol is present, in which case Le Chatelier’s principle applies, and the favorable second reaction shifts the first reaction to the right. Show me?
|
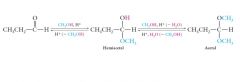
|
|
|
Both hemiacetals and acetals have two different oxygens bonded to the same carbon. In acetals, both oxygens are in –OR groups; in hemiacetals, one oxygen is in an –OH group and the other is in an –OR group. Show me?
|
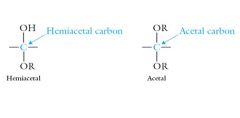
|
|
|
Hemiacetal and acetal formations are reversible reactions: How?
|
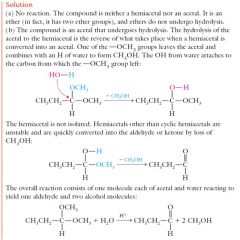
Hemiacetal and acetal formations are reversible reactions:
In the presence of excess water and an acid catalyst, an acetal is converted into its parent aldehyde or ketone. In the presence of excess alcohol and an acid catalyst, an aldehyde or ketone is converted into its corresponding acetal. |
|
|
The reaction of an acetal with water is an example of a hydrolysis reaction. How?
|
The reaction of an acetal with water is an example of a hydrolysis reaction: an organic molecule reacting with water and splitting into two parts, one of which combines with the H+ from a water molecule and the other with the OH- from the water molecule.
|
|
|
In animals, the hydrolysis of acetal groups is the first step in what?
|
In animals, the hydrolysis of acetal groups is the first step in the digestive breakdown of starch and other carbohydrates in the digestive tract.
|
|

|
|
|
|
Structural Features of Aldehydes and Ketones
• Aldehydes and ketones contain the what group? |
Structural Features of Aldehydes and Ketones
• Aldehydes and ketones contain the carbonyl group (C=O). |
|
|
An aldehyde has at least one what directly attached to the carbon of the carbonyl group?
|
An aldehyde has at least one hydrogen atom directly attached to the carbon of the carbonyl group.
|
|
|
A ketone has only what type of atoms, directly attached to the carbon of the carbonyl group?
|
A ketone has only carbon atoms, no hydrogen atoms, directly attached to the carbon of the carbonyl group.
|
|
|
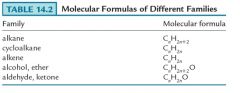
The C:H ratio for an aldehyde or ketone is what fewer than the corresponding alcohol or alkane?
|
The C:H ratio for an aldehyde or ketone is two hydrogens fewer than the corresponding alcohol or alkane.
|
|
|
Naming Aldehydes and Ketones
• In the IUPAC system, aldehydes and ketones are named by identifyingthe what chain containing the carbonyl group? |
Naming Aldehydes and Ketones
• In the IUPAC system, aldehydes and ketones are named by identifying the longest continuous carbon chain containing the carbonyl group. |
|
|
Aldehydes are named as what?
|
Aldehydes are named as alkanals.
|
|
|
Ketones are named as what?.
|
Ketones are named as alkanones.
|
|
|
For ketones, the position of the carbonyl carbon is indicated by a what in front of the name?
|
For ketones, the position of the carbonyl carbon is indicated by a number in front of the name.
|
|
|
For aldehydes, no number is needed, because the carbonyl carbon is always where?
|
For aldehydes, no number is needed, because the carbonyl carbon is always C1.
|
|
|
Prefixes preceded by numbers indicate what?
|
Prefixes preceded by numbers indicate the substituents attached to the longest chain.
|
|
|
Prefixes preceded by numbers indicate the what?
|
Prefixes preceded by numbers indicate the substituents attached to the longest chain.
|
|
|
C6H5–CHO is named what?
|
C6H5–CHO is named benzaldehyde.
|
|
|
What are used for some aldehydes and ketones?
|
Common names are used for some aldehydes and ketones.
|
|
|
Common ketone names are obtained by how?
|
Common ketone names are obtained by naming the groups attached to the carbonyl carbon, followed by the word ketone.
|
|
|
Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones
• Aldehydes and ketones have boiling and melting points intermediate between those of hydrocarbons and alcohols, a consequence of their dipole–explain? |
Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones
• Aldehydes and ketones have boiling and melting points intermediate between those of hydrocarbons and alcohols, a consequence of their dipole–dipole secondary forces being intermediate in strength between the London forces in hydrocarbons and the hydrogen-bond forces in alcohols. |
|
|
Aldehydes and ketones are only what soluble than alcohols in water?
|
Aldehydes and ketones are only slightly less soluble than alcohols in water.
|
|
|
Although aldehydes and ketones cannot hydrogen bond with themselves, they can hydrogen bond with what?
|
Although aldehydes and ketones cannot hydrogen bond with themselves, they can hydrogen bond with water.
|
|
|
Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
• Aldehydes, but not ketones, undergo oxidation with several selective oxidizing agents—what are these agents? |
Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
• Aldehydes, but not ketones, undergo oxidation with several selective oxidizing agents—dichromate, permanganate, and Tollens’s reagents. |
|
|
Dichromate and permanganate distinguish what?
|
Dichromate and permanganate distinguish aldehydes from ketones but not from primary and secondary alcohols or from alkenes, which also give positive tests.
|
|
|
Tollens’s reagent is more selective than dichromate and permanganate,and distinguishes what?
|
Tollens’s reagent is more selective than dichromate and permanganate, distinguishing aldehydes from ketones, alcohols, and alkenes.
|
|
|
Benedict’s reagent is useful for distinguishing what?
|
Benedict’s reagent is useful for distinguishing –hydroxy aldehydes and -hydroxy ketones from other compounds.
|
|
|
Aldehydes and ketones undergo addition reactions with what?
|
Aldehydes and ketones undergo addition reactions with hydrogen, hydrides, and alcohols.
|
|
|
Aldehydes and ketones are reduced to what?
|
Aldehydes and ketones are reduced to primary and secondary alcohols, respectively.
|
|
|
Explain reduction of H2 and Pt or the sequential addition of hydride followed by water with NADH?
|
|
|
|
Explain Hemiacetal and acetal formation by reaction.
|
|

