![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
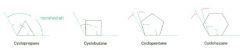
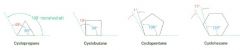
angle strain
|
the strain induced in a molecule when bond angles are forced to deviate from the ideal 109 degree tetrahedral value
This is destabilizing |
|
|
|
|
|
The more energy (strain) the compound contains, the more the _____ is released on _______
|
energy (heat); combustion
|
|
|
angle strain
|
the strain due to expansion or compression of bond angles
|
|
|
torsional strain
|
the strain due to eclipsing of bonds on neighboring atoms
|
|
|
steric strain
|
strain due to repulsive interaction when atoms approach each other too closely
|
|
|
What cycloalkane is the most strained of all the rings? Why?
|
Cyclopropane; primarily because of the angle strain caused by its 60 degree C--C--C bond angles
|
|
|
What are the most common cycloalkanes?
|
substituted cyclohexanes, which occur widely in nature
|
|
|
chain conformation
|
a strain-free, three dimensional shape (e.g., in cycyclohexane)
|
|
|
twist-boast conformation
|
nearly free of strain (does have steric strain and torsional strait, however)
|
|
|
Two hydrogens on the same face of a ring are always
|
cis
regardless of whether they're axial or equatorial and regardless of whether they're adjacent |
|
|
Two hydrogens on opposite faces of a ring are always
|
trans
|
|
|
Draw cyclohexane with its hydrogen bonds as a chair
|
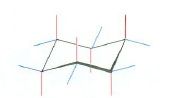
|
|
|
ring-flip
|
interconversions
e.g., different chair conformations readily interconvert, exchanging axial and equatorial positions |
|
|
The energy difference between axial and equatorial conformations is due to steric strain caused by:
|
1,3-diaxial interactions
|
|
|
decalin
|
two fused cyclohexane rings joined to share wo carbon atoms
|
|
|
Draw norbornane
|
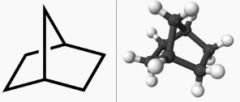
|
|
|
E(total) =
|
E(bond stretching) + E(angle strain) + E(torsional strain) + E(van der Waals)
|

