![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
96 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
define chemical reaction |
where matter changes to produce new substances with the properties different from the original materials |
|
|
define a group |
vertical group that has similar properties |
|
|
define period |
horizontal, chemical properties repeat themselves |
|
|
define metalloids |
along the staircase |
|
|
define metals |
left of the stair case |
|
|
define non metals |
to the right of the staircase |
|
|
define alkali metals |
first group, react violently, silver coloured metals |
|
|
define alkaline earth metals |
group two, lightly reactive not as much much as alkali, oxidizing metals |
|
|
define noble gases |
group 18 low reactivity |
|
|
define halogens |
group 17, extremely reactive, combined with H makes an acid |
|
|
define transition metals |
group 3-12 |
|
|
define lanthinides |
outside table period 6 |
|
|
define actinides |
outside table period 7 |
|
|
define atom |
basic unit that can enter a chemical formula |
|
|
whats an amu |
atomic mass unit |
|
|
whats the symbol of carbon |
C |
|
|
define atomic number |
number of protons |
|
|
define mass number |
# of protons + # of neutrons |
|
|
define isotopes |
same atomic # but different mass # |
|
|
define atomic mass |
average mass based on percent abundances |
|
|
define neutral atoms |
same number of protons and neutrons |
|
|
how do you calculate the number of neutrons |
mass # - atomic # |
|
|
whats the isotope symbol of silicon -28 |
28 Si 14 |
|
|
what is all matter made of |
tiny particles called atoms |
|
|
what did thomson discover |
that the atoms sometimes ejects a smaller negatively charged particle called an electron |
|
|
what was thomsons model called |
plum pudding |
|
|
who invented the cloud model and what is it |
heiseberg, imagined an atom surrounded by a cloud of electrons |
|
|
what is the smallest atom |
hydrogen |
|
|
define covalent bond |
sharing of electrons |
|
|
what does the shape of crystals depend on |
radiation of the ion shape |
|
|
draw a bohr diagram for lithium it has 3pt |
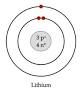
|
|
|
draw the energy level diagram for carbon it has 6 pt |

|
|
|
define an ion |
charged atom |
|
|
describe charged atom |
postive or negative charge |
|
|
what causes an ion |
loss of gain of electrons |
|
|
define cations |
a metallic ion with a positive charge |
|
|
define anion |
a nonmetallic ion with a negative charge |
|
|
naming ions how do you name a anion and cation |
anion ends with ide cation is full name of the metal |
|
|
draw the energy level diagram for nitride ion it has 7 pt and a -3 charge |
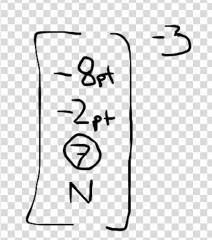
|
|
|
describe daltons model |
atoms are like small spheres, they vary in size, mass, colour |
|
|
describe J.J thomsons model |
beams of particles made in vacuum tube |
|
|
describe ernst rutherfords model |
discovered nucleus |
|
|
describe neils bohr model |
electrons surrounded the nucleus in different energy levels |
|
|
describe the quantum mechanical model of the atom |
electron cloud surrounding the nucleus |
|
|
what is an isotope |
a atom with the same atomic number different atomic mass |
|
|
describe ionic naming |
change end to ide and do not use prefixes and use roman numerals |
|
|
describe molecular naming |
use prefixes and change end to ide don't use prefixes of mono on the first atom |
|
|
what are the prefixes 1-10 |
mono di tri tetra penta hexa hepta octa nona deca |
|
|
define ionic compound |
contains one metal and one nonmetal |
|
|
define molecular compound |
only non metals |
|
|
what are the sayings for acid naming |
hide a hickey ate an icky bite a delicious |
|
|
whats the IUPAC chemical name for H3PO4 |
aqueous hydrogen phosphate |
|
|
whats the classical chemical name for H3PO4 |
phosphic acid |
|
|
define exothermic |
a rection in which more heat energy is released then absorbed, and energy is in the product |
|
|
define endothermic |
a reaction where more energy is absorbed then released, energy is in the reactants |
|
|
what are evidence for an ionic compound |
high melting point retention of crystal shape solubility in water conducts in a solution |
|
|
define electrolyte |
any solution that conducts electricity |
|
|
draw the changes of state |
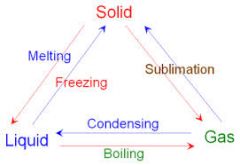
|
|
|
evidence of chemical change |
something new is formed change is colour, smell |
|
|
what change is a tire going flat |
physical |
|
|
what change is a burning,or food going bad |
chemical |
|
|
define products |
on the right side of the arrow |
|
|
define reactants |
on the left side of the arrow and they go into the reaction |
|
|
when do ionic compounds form |
when electrons transfer from one atom to another |
|
|
what is the formula unit |
the lowest whole number ratio |
|
|
what is the formula unit of Ba2F4 |
BaF4 |
|
|
in ionic naming what comes first |
cation |
|
|
what is the cation |
metal |
|
|
what is the anion |
nonmetal |
|
|
define polyatomic ions |
group of atoms covalently bonded together that have lost or gain an electron as a group |
|
|
what is multivalent |
atom with more then one charge |
|
|
define monoatiomic diatomic polyatomic |
one atom two atoms more then two atoms |
|
|
what is the law of conservation of mass |
matter cannot be created or destroyed |
|
|
what states can molecular be at room temp |
solid, liquid, gas |
|
|
what states can ionic be at room temp |
solid |
|
|
balance N2 + O2 -> NO2 |
N2 + 2O2 -> 2NO2 |
|
|
what is an unbalanced equation called |
skeleton |
|
|
what are the types of reactions |
composition decomposition single replacement double replacement neutralization hydocarbon combustion |
|
|
define composition
|
reactants combine to form product |
|
|
define decomposition |
reactants break up to form product |
|
|
define single replacement |
one atom switches places with another in a compound |
|
|
define double replacement |
two atoms switch to form new compounds |
|
|
define neutralization |
reaction occurs where salt ad water are made |
|
|
define hydrocarbon combustion |
burning of oxygen to produce CO2 and H2O |
|
|
what is avogadros number |
6.022 times 1023 |
|
|
define atomic molar mass |
atomic mass of one mole of an element |
|
|
what are the units for molar mass |
g/mol |
|
|
calculate the molar mass of Ca(NO3)2 |
1 mol - Ca =40.08 2 mol - N = 28.02 6 mol - O = 96 = 164.10g/mol |
|
|
practice molar mass calculations |
. |
|
|
what is all matter split into |
mixtures and pure substances |
|
|
what are the types of mixtures |
homogeneous and heterogenous |
|
|
what are the types of our substances |
elements and compounds |
|
|
define homogenous |
looks like one thing transparent |
|
|
define heterogenous |
can see different parts can be separated |
|
|
what re types of heterogenous mixtures |
colloids emulsions mechanical mixtures suspensions |
|
|
give an example for all the types of heterogenous mixtures |
colloids - milk emulsions - mayo mechanical mixtures - salad dressing suspensions - dirt and water |

