![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Biology |
The Study of living things |
|
|
Properties of Life |
|
|
|
Scientific Method |
|
|
|
Theory |
Hypothesis or set of hypotheses, supported by a great deal of evidence, but may be revised as new evidence becomes available
|
|
|
Law |
Theory supported by so much evidence it is almost irrefutable |
|
|
Evolution |
A gradual change in a species over time |
|
|
Natural Selection |
Nature selects for survival those organisms that are most suited for their environment (Natural Selection is a mechanism for Evolution)
|
|
|
Classification Scheme For Living Things (Taxonomy) |
|
|
|
Prokaryotic (simple cells)
|
|
|
|
Eukaryotic (complex cells) |
|
|
|
Matter |
Anything that has mass & occupies space |
|
|
Mass |
The amount of matter something contains |
|
|
Element |
a pure substance that can not be broken down by ordinary chemical means |
|
|
Molecule |
2 or more atoms joined by a chemical bond |
|
|
Compound |
Substance whose molecules contain atoms of more than one element |
|
|
Atom |
smallest unit of an element that has all the properties of that element |
|
|
Atomic Number |
Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Defines the element. |
|
|
Mass Number |
The number of protons plus the number of neutrons in the nucleus |
|
|
Isotopes |
Atoms of the same element that differ only in the number of neutrons |
|
|
Radioactive Isotopes |
isotope with an unstable nucleus, the nucleus decays at a characteristic rate |
|
|
Half-Life (T1/2) |
The time it takes for 50% of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay |
|
|
Chemical Properties of an atom depend only on its outer (valence) electrons |
this is why different isotopes of the same element act the same - they only differ in their nuclei |
|
|
Chemical Bond |
Union between the electron structures of atoms |
|
|
Electrons orbit at different energy levels |
|
|
|
What are the 3 Chemical Bonds? |
|
|
|
Ionic Bond |
Formed when 2 atoms of opposite charges attract |
|
|
Covalent Bond |
Formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons.
|
|
|
Hydrogen Bond |
The weak attraction between the partially positive end of one polar molecule and the partially negative end of another.
|
|
|
Electronegativity |
attraction of an atom for the shared electrons of a covalent bond |
|
|
Water |
A polar compound |
|
|
Ions and polar compounds are? |
Hyrophilic |
|
|
Non-Polar compounds are? |
Hydrophobic |
|
|
Hydrogen bonds are responsible for all the biologically important properties of water. |
dont forget it |
|
|
Water clings to.... |
Other polar molecules |
|
|
Cohesion |
Water molecules form H bonds with other water molecules |
|
|
Adhesion |
Water molecules form H bonds with other polar molecules |
|
|
Water stores heat and... |
Modifies temperature |
|
|
Water is a good solvent for... |
For hydrophilic (polar and charged) substances |
|
|
Water organizes... |
Hydrophobic (non-polar) molecules |
|
|
Water ionizes |
basis for the pH scale. Neutral pH = 7.0 |
|
|
Acid |
any substance that add hydrogen ions to solution (pH less than 7.0) |
|
|
Base |
any substance that increases the hydroxide ions in solution (pH greater than 7.0) |
|
|
pH |
measures the concentration of free hydrogen ions in solution |
|
|
Carbon has _____ valance electrons |
4 |
|
|
Carbon can form ____ covalent bonds |
4 |
|
|
What does carbon form? |
the skeletons of all biological life |
|
|
Functional Groups |
specific groups of atoms attached to the carbon skeleton that are most often involved in chemical reactions. |
|
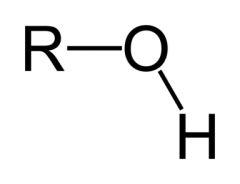
|
hydroxyl |
|
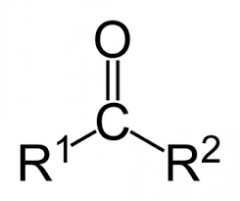
|
carbonyl |
|
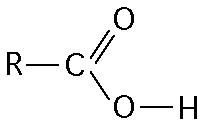
|
carboxyl |
|
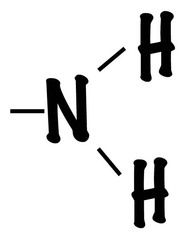
|
amino |
|
|
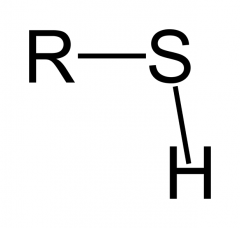
Sulfhydryl |
|
|
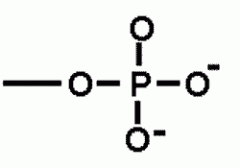
Phosphate |
|
|
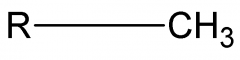
Methyl |
|
|
What are the 4 classes of biological molecules? |
|
|
|
Polymer |
large molecule made of many identical or similar subunits |
|
|
Monomer |
subunit |
|
|
Dehydration Synthesis |
synthesis of a polymer from monomers, loss of one water molecule per each bond formed |
|
|
Hydrolysis |
process of breaking down a polymer, one molecule of water added per bond broken |
|
|
Proteins |
polymers of amino acids, several levels of structure |
|
|
Primary Structure |
the linear sequence of amino acids linked by covalent peptide bonds (polypeptide chain) |
|
|
Secondary Structure |
localized regions of coiling or pleating; caused by H bonds |
|
|
Teriary Structure |
further folding of polypeptide subunits in proteins made of more than one polypeptide chain |
|
|
Quaternary Structure |
association of polypeptide subunits in proteins made of more than one polypeptide chain. |
|
|
Nucleic Acids |
DNA & RNA, and their building blocks (necleotides) |
|
|
Lipids |
many types, all hydrophobic (non-polar) to some degree |
|
|
Phospholipids |
Glycerol + 3 fatty acids + phosphate group. main component of cell membranes |
|
|
Triglyerides |
glycerol + 3 fatty acids, most abundant type of biological lipid (oils & fats) |
|
|
Terpens |
part of many biological pigments |
|
|
Steroids |
4 fused C-rings (ex. cholesterol, sex hormones, etc.) |
|
|
waxes |
the most hydrophobic lipid |
|
|
prostaglandins |
chemical messengers |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
simple sugars & their polymers |
|
|
Monosaccharides |
simple sugars, usually 5-6 carbons (ex. glucose) |
|
|
Disaccharides |
shortest polymers, 2 covalently bound monosaccharides |
|
|
Polysaccharides |
large polymers : starch(glucose storage in plants), glycongen ( glucose storage in animals), cellulose (plant cell wall), chitin (fungal cell walls, arthropod exoskeletons) |
|
|
What are the 6 lipids |
|
|
|
What are the the 3 Carbohydrates? |
|

