![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Cell cycle |
Cells reproduction, the way cells work throughout life. |
1.) reproduction 2.) reproduction is a big part in the cell cycle |
|
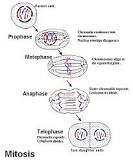
Mitosis |
A part of the cell cycle process by which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. |
1.) daughter cells 2.) daughter cells are two identical cells which is an example of mitosis |
|
|
Interphase |
The period between divisions. |
1.) gaps between division 2.) gaps between division is when cells go through interphase |
|
|
G1/G0 |
Prereplication/nondividing cells |
1.) gap 1 and gap 0 2.) gaps between cell division labeled G1/G0 |
|
|
s |
DNA synthesis |
1.) composing DNA 2.) during S DNA I'd being composed |
|
|
G2 |
Pre-mitosis |
1.) the stage before mitosis 2.) the stage before mitosis is G2 |
|
|
M |
stands for mitosis |
1.) cell division 2.) M (mitosis) helps with cell division |
|
|
Restriction point |
When a cell in G0 or G1 receives a signal to divide, it passes through the restriction point. |
1.) dividing point 2.) the restriction point is the dividing point |
|
|
Cytokinesis |
When the cell itself divides. |
1.) dividing of the cell 2.) cytokinesis is dividing of the cell |
|
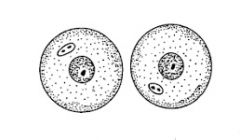
Daughter cell |
A cell made that is identical to the parent cell. |
1.) identical cell 2.) a daughter cell is an identical cell |
|
|
Cyclins |
A family of proteins that control the progression of cells through the cell cycle by activating enzymes. |
1.) proteins 2.) cyclins are groups of proteins |
|
|
Kinases |
An enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to a specified molecule. |
1.) ATP transfers 2.) kinases makes ATP transfers faster and easier |
|
|
Cell-cycle arrest |
The process by which the cell cycle is halted during one of the normal phases (G1, S, G2, M). |
1.) pausing 2.) cell-cycle arrest is a pause in the cell-cycle stages |
|
|
Cancer |
The disease caused by an uncontrolled division of abnormal cells in a part of the body. |
1.) over division 1.) when cells are over divised it causes cancer |

