![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Tectonic plates
|
Tectonic plates the size of continents and oceans move at rates of a few centimeters per year in response to movement in the mantle.
|
size of continents...at rate...mantle
|
|
|
Theory of Plate Tectonics
|
The Earth's lithosphere is divided up into tectonic plates that slowly move around the top of the athenosphere.
|
tectonic plates...move...athenosphere
|
|
|
Boundary
|
Where plates meet. 3 types of boundaries classified by how the plates move in relationship to each other
|
meet...classified...relationship to each other
|
|
|
Convergent boundary
|
Plates collide. Continental continental plates collide makes mountains. Continental and oceanic collide oceanic crust which is denser some subducts under the continental crust and forms volcanic chains such as Mt. St. Helens. Oceanic and oceanic collides then the denser crust subducts and creates an island arch.
|
|
|
|
Divergent Boundaries
|
Plates separate. Most are on the ocean floor. MOR!
|
|
|
|
Transform boundaries
|
Slide past each other. San Andreas Fault.
|
|
|
|
What Causes Tectonic Motions?
|

The motion is the result of the difference in the density caused by the flow of heat within the earth. Convection currents!!!
|
|
|
|
Ridge push
|
O.C. is higher at MOR slides down because of gravity
|
higher at... slides...gravity
|
|
|
Slab pull
|
As O.C., it pulls the rest of the plate with it. Most plates move between 2.5 and 15 centimeters per year.
|
|
|
|
Deformation
|
Deformation causes rock layers to bend and break and causes mountains to form. It is the process in which the shape of rock changes in response to stress. Rock layers can bend and break with enough stress.
|
rock layers...break...mountains
|
|
|
Stress
|
The amount of force per unit area on a given material.
|
force...area...material
|
|
|
Fault
|
The surface along which rocks break and slide past each other. They are classified according to how the fault blocks move in relation to each other.
|
|
|
|
Normal Fault
|
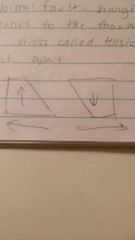
A normal fault has a hanging wall that moves down in relative to the footwall. This is caused by a stress called tension. Stress that pulls Rock apart.
|
|
|
|
Reverse fault
|

A reverse fault is a hanging wall that moves up on relation to the footwall. This is caused by a stress that is called compression,stress that pushes rock together.
|
|
|
|
Strike-Slip fault
|

2 blocks move horizontally
No angle! The blocks move horizontally caused by the stress shearing. It pushes rock in different directions. Found at transform boundaries. San Andreas Fault. |
|
|
|
How Are Mountains Formed?
|

1. Folded mountains. When rock layers are squeezed together and pushed up. Form at convergent boundaries. Appalachians.
2. Fault block Mts. Tension causes the crust ti break into normal faults-large blocks of crust drop in relation to other blocks. 3. Volcanic Mt. When molten rock erupts onto Earth's surface. Most volcanic mts. are located at convergent boundaries. Ring of Fire |
|
|
|
Random 6.4 Facts
|

|
|
|
|
North American,Farralon, and Pacific Plate
|

All that is left of the Farralon plate is the Juan de Fuca plate. Farralon plate subducting. There is a convergent boundary between the Farralon plate and the N.A. plate.
|
|
|
|
Batholic
|
A large mass of igneous rock that forms deep below the surface. It means deep rock.
|
|
|
|
Subduction and Volcanism
|

Subduction of the F.P. had 2 major results.
1. Sierra Nevada Batholic Magma solidified 210-100 mya to create this granite mass. |
|
|
|
Plate tectonics Tectonic plates
|
Plate tectonics are the theory that explains how the continents move anstectonic plates are the continental and oceania pieces of crust that move and change shape.
|
|
|

Chapter Review
|

|
|

