![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Metabolism |
All chemical reactions that happen in the body |
|
|
Metabolic pathways |
Specific molecule is altered in a series of defined steps, resulting in a product. Each step of the pathway is catalyzed by a specific enzyme |
|
|
What does Metabolism as a whole manage? |
Manages material and energy resources of the cell |
|
|
Catabolic pathways |
Release energy by breaking things down |
|
|
A major pathway of catabolism |
Cellular respiration, in which the sugar glucose and other organic feels are broken down in the presence of oxygen to carbon dioxide and water. Energy stored in the organic molecules becomes available to do work for this cell, such as ciliary beating or membrane support |
|
|
Anabolic pathways |
Consume energy and build molecules |
|
|
Examples of anabolism |
Synthesis of an amino acid from simpler molecules and the synthesis of a protein from amino acids |
|
|
Bioenergetics |
Study of how energy flows through living organisms |
|
|
What is energy? |
Energy is the capacity to cause change You cannot see or hold energy |
|
|
what is kinetic energy? |
Energy associated with the relative motion of objects |
|
|
What is thermal energy? |
The kinetic energy associated with the random movement of atoms or molecules |
|
|
What is heat? |
Thermal energy in transfer from one object to another |
|
|
What is potential energy? |
Energy that matter possesses because of its location or structure |
|
|
What is chemical energy? |
Potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction |
|
|
What is thermodynamics? |
Study of the energy transformations that occur in a collection of matter |
|
|
What is an isolated system? |
A closed system that doesn't exchange energy or matter with its surroundings |
|
|
What is an open system? |
A system in which energy and matter can be transferred between the system and its environment, organisms have open systems |
|
|
What is the first law of thermodynamics? (principle of conservation energy) |
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed |
|
|
During every energy transfer or transformation some energy is? |
Converted into thermal energy and release Dad heat becoming unavailable to do work |
|
|
What is entropy? |
Measure of disorder, or randomness. |
|
|
What is the second law of thermodynamics? |
Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy, or disorder, of the universe |
|
|
What is a spontaneous process? |
A process that can occur without any input of energy |
|
|
What is free-energy? |
Free energy is the amount of energy that is available to do work |
|

If Delta G is negative the reaction will be |
Spontaneous |
|
|
Exergonic reaction |
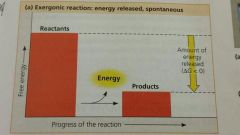
Precedes with the net release of energy, it is spontaneous |
|
|
Endergonic reaction |
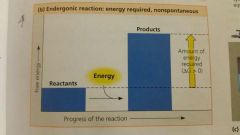
Absorbs free energy from its surroundings, needs energy, nonspontaneous |
|
|
How much work does it isolated system do when it reaches equilibrium? |
Does no work |
|
|
Metabolic equilibrium equals |
Death in organism |
|
|
Three main type of work that cells do |
Chemical work, transport work, mechanical work |
|
|
What is chemical work? |
Pushing of endergonic reactions that would not occur spontaneously |
|
|
What is transport work? |
The pumping of substances across the membrane |
|
|
What is mechanical work? |
Beating of the cilia, the contraction of muscle cells, and the movement of chromosomes during cellular reproduction |
|
|
What is energy coupling? |
The use of an exergonic process to drive an endergonic one |
|
|
The structure of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) |
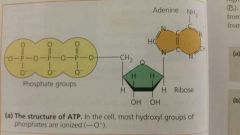
Contains the sugar ribose, with the nitrogenous base admin and a chain of three phosphate groups bonded to it |
|
|
ATP is also used to make? |
RNA |
|
|
Bonds between phosphate groups of ATP can be broken by |
Hydrolysis |
|
|
ATP to ADP |
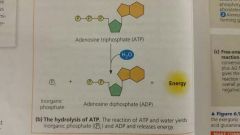
|
|
|
What is a phosphorylated intermediate |
the recipient of a phosphate group from ATP that is covalently bonded |
|
|
Transport and mechanical work in this Cell are nearly always powered by |
Hydrolysis of ATP |
|
|
Hydrolysis of ATP and transport work |
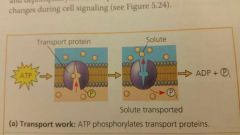
|
|
|
Hydrolysis of ATP and mechanical work |

|
|
|
ATP is a renewable resource that can be regenerated by the addition of what |
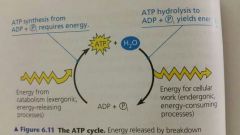
Addition of phosphate to ADP |

