![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
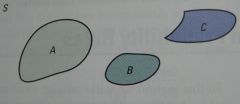
Addition Rule for Disjoint Events
|
If events A, B, and C are disjoint in the sense that no two have any outcomes in common, then
P(A or B or C)=P(A)+P(B)+P(C) |
|
|
|
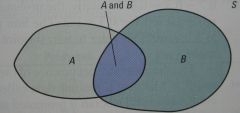
General Addition Rule for Unions of Two Events
|
For any two events A and B,
P(A or B)=P(A)+P(B)-P(A and B) |
|
|
|
Simulation
|
Imitation of chance behavior, based on a moedl that accurately reflects the phenomenon under consideration
|
|
|
|
Randint Function
|
randint(x,y,z)
x=minimum y=maximum z=number of digits to generate |
|
|
|
Simulation Steps
|
State problem or describe random phenomenon
state assumptions assign digits simulate many repetitions state conclusions |
|
|
|
Empirical
|
Based on observation, not theory
|
|
|
|
Probability Models
|
Sample space S of a random phenomenon is set of all possible outomes
event is any outcome or set of outcomes of a random phenomenon probability model is mathematical description of a random phenomenon, consisting of a sample space and a way of assigning probabilities to events |
|
|
|
Tree Diagram
|
A handy way to depict all possible outcomes
|
|
|
|
Multiplication Principle
|
if you can do something n ways and another m ways, the total number of ways to do both is n x m
|
|
|
|
Sampling with replacement
|
Put the things back after drawing
|
|
|
|
Sampling without replacement
|
Not putting things back after drawing them
|
|
|
|
probability rules
|
any probability is between 0 and 1
the sum of all probablities of all possible outcomes must equal 1 if 2 events have no outcomes in common, the probability that one or the other occurs is the sum of the two individuals the probability that an event does not happen is 1 minus the probability that the event does occur |
|
|
|
Mickey Rat
|
RATS
|

|
|
|
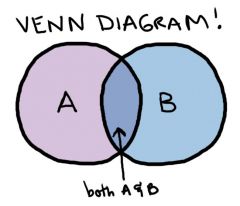
Venn Diagram
|
diagram to find probability of union of two events or joint probability
|
|
|
|
Disjoint events
|
probability of A and B is 0
|
|
|
|
Conditional Probability
|
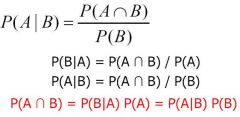
|
|
|
|
Complement (A^c)
|
i.e. complement of Event A is all outcomes that are not in A
|
|
|
|
Random Phenomenon
|
Outcomes that we cannot predict but that nonetheless have a regular distribution in very many repetitions.
|
|
|
|
Total Probability
|
All of the probabilities must add up to 1.
|
P(S) = 1
|
|
|
Joint Probability
|
The probability of two events occurring together.
|
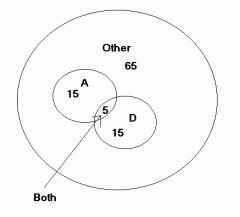
|

