![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the use of the first-hop? |
- the first hop is considered the default gateway of the network; the name of the device that the packet is sent to when it needs to leave the local subnet of the network that it is on |
|
|
What happens if the host cannot reach the default gateway? |
- the host will no longer be able of reach destinations out side of its own subnet |
|
|
What is the first hop redundancy? |
- a set of routers or layer 3 switches that work together to present the illusion of a single router to hosts on the LAN |
|
|
How are the layer 3 devices addressed in FHRP? |
- these layer 3 devices share a virtual IP address and a virtual MAC address
|
|
|
How does FHRP work in basic terms? |
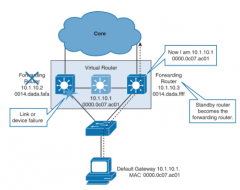
- one of the devices is the forwarding device and forwards traffic destined for the virtual router - the other device is a standby device, and will take over forwarding traffic if the original fails |
|
|
How can we set up FHRP and waht are the options to make it work in basic terms? |
- devices need to talk to each other using the FHRP The options for the FHRP are: HSRP VRRP GLBP |
|
|
What is the Hot-Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) in basic terms? |
- FHRP Cisco-proprietary specified in the RFC 2281 - participating routers tlak to each other and agree on a virtual router configuration, with a virtual IP address and a virtual MAC address which end systems use as a default gateway |
|
|
How do HSRP router communicate and what needs to be set up to let them communicate? |
- HSRP routers communicate using the multicast address 224.0.0.2 (HSRPv1) or 224.0.0.102 (HSRPv2), on UDP port 1985 - hello messages are used to communicate configuration information and act as a keepalive mechanism between HSRP routers - all HSRP routers need to be layer 2 adjacent so that the hello packets can be exchanged |
|
|
what are the roles available for the HSRP group? |
the roles are: virtual router Active router standby router other routers (remember as VASO) |
|
|
what is the role of the virtual router? |
- an IP and MAC address pair that end devices have configured as their default gateway; the virtual router will process no physical frames |
|
|
What is the role of the active router? |
- within the HSRP group, one router is elected to be the acitve router; the acitve router physically forwards paclets sent to the MAC address of the virtual router - there is only one active router in the HSRP group |
|
|
What is the role of the standby router? |
- listens for periodic hello messages - when the active fails and stops sending hello messages the standby router will assume the role of the active - there is only one standby in the HSRP group |
|
|
What is the role of other routers? |
- all other routers (other than the acitve and the standby) listen and if both the active and the standby fail, all routers will contend for active and standby roles |
|
|
List and define the HSRP states. |
Initial - the beginning state - this state indicates that HSRP does not run - entered via a configuraiton change or when an interface first comes up Listen - the router knows the virtual IP address; the router is neither the acitve nor the standby - it listens for hello messges from those routers Speak - the router will send periodic hello messages and actively participates in the election of the active or standby router - a router cannot enter speak state unless the router has the virtual IP address Standby - this router will become the next active and sends hello messages - with the exception of transient conditions, there is, at most one router in the group on standby Active - processes physical packets to the group virtual MAC address - the router sends periodic hello messages - with the exclusion of transient conditions there is at most one active router |
|
|
Give an example of the HSRP state transition. |
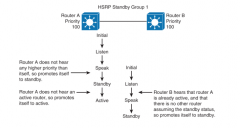
|
|
|
Describe the HSRP election process? |
- when two routers enter the paritcipation process, a priority can be configured to determine which router should become active - during the election process the router with the hihgest prioroty in a gorup will become the active router - if a tie occurs the router wiht th ehihgest IP will become the acitve - the priority value ranges from 0 to 255 and the default is 100 - when HSRP starts the rotuers will start their acitve and standby timers (10 seconds default) - if the rouer does not hear from a stnadby router before the standby epxires; the router will become the standby - if the router does not hear form the acitve router before any active timer expires, the router will take the acitve role |
|
|
What is HSRP preemption and why is it used? |
- regardless of other router priorities or IP addresses an acitve router will stay acitve by default - this means that a router that boots up significantly faster thatn the others in the standby group becomes the acitve router, regardless of configured priority - you can override this default behavior by configuringt he HSRP preemption - with preemption configured, if a router with a hihger priority comes online, it will send an HSRP coup message telling the current active to step down and allow the new router to become the acitve |
|
|
How is HSRP preemption configured? |
Standy [gorup-number] preempt [delay {minimum seconds reload seconds sybc seconds}] |
|
|
How do HSRP and spanning tree interact? |
- spanning tree has no awareness about the HSRP configuration - there is no automatic relationship between the acitve router election process and the root bridge election - when configuring both spanning tree and HSRP (or any other FHRP) you must make sure that the active router is the same as the root bridge for the corresponding VLAN - when the root bridge is different form the HSRP active router, a suboptimal path can be created |
|
|
How do we configure HSRP? |
- we do it on the interface: standby group-number ip virtual-ip-address - the group number is optional and indicates the HSRP group to which the interface belongs - specifying a unique group number in the standby commands enables the creation of multiple HSRP groups (default is 0) - the IP address is that of the virtual router IP address for the HSRP group NOTE: the group numbers must all match on all HSRP routers in the group |
|
|
What will happen if you leave the default HSRP priority values? |
- a single layer 2 swithc will likely become an active gateway for both VLANs - you are effectively utilizing one uplink toward the core of the network - the link to switch 2 will only be used in the event of a failure on switch 1 |
|
|
How can we enable load balancing on HSRP and how does it work? |
- to use both paths toward the core network, configure HSRP with mulit group HSRP (MHSRP) - essentially when we have two end devices connected to a layer 2 device which are consequently connected to a layer 3 device and the end devices have two VLANs then one switch will becom the acitve for one VLAN and standby for the other and vice versa for the second switch - we should also ensure that the spanning tree route for the VLANs are on the same switch as the HSRP gateway for that VLAN |
|
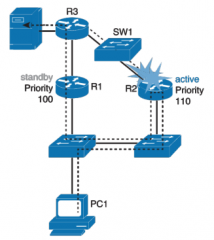
In the given scenario what will happen if R2's uplink fails? |
- the iplink interface is not HSRP enabled so the failure does not affect HSRP; r2 is still the defualt gateway - all of the traffic form PC1 to the server now goes through the second router then to router 1 and forwarded to the server resulting in inefficient traffic - solution: HSRP interface tracking |
|
|
Describe the purpose of HSRP interface tracking and how it works. |
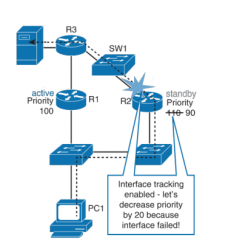
- this allows you to specify another interface on the router for the HSRP process to monitor - if the specified interface's line protocol goes down, the HSRP priority of this router is reduced, allowing another HSRP router with a higher priority to become the active router -preemption must be enabled - looking at the example the failed interface causes R2 to lower its priority and R1 will become acitve (preemption configured) |
|
|
How is interface tracking enabled? |
- configure interface mode: standby group-number track intf-type/number interface-priority - the group number is the HSRP group this tracking is applied to - specify the interface that should be tracked - the interface priority indicates what amount the HSRP priority determines if the interface fails - this is optional however because the default decremented is 0 |
|
|
In what case would HSRP interface tracking fail? What would be the solution? |
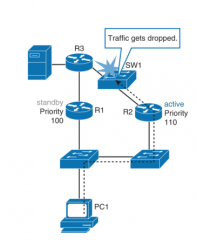
- interface tracking cannot always provide the optimal path even if the up link ports are up - ex. if a device is not directly connected to the HSRP router fails, interface tracking would not be able to discover this - the router would remain the active gateway and would be forwarding traffic that would be eventually dropped elsewhere in the network - solution: object tracking |
|
|
What is object tracking and how does it work? |
- with HSRP object tracking, the router can monitor an object, such as IP SLA and react according to the state of an object - in the example an IP SLA object is created to monitor connectivity to R3 (ICMP echo) - R2 is tracking the object and if it fails then HSRP decrements its priority by 20 - this leads R1 to taking over as the active gateway - traffic flows through R1, bypassing the failed switch |
|
|
How is HSRP object tracking configured? |
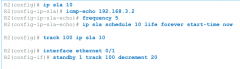
- first we determine an IP SLA ICMP echo test - next we create an object and track the IP SLA instance - next we configure HSRP to track an object and decrement if the test fails |
|
|
What is HSRP authentication and what type does it use? |
- HSRP authenticaiton prevent rogue layer 3 devices on the network from joining the HSRP gorup - a rogue deivce may claim the active role and can prevent hosts form communication with the rest of the network (DoS attack), or capture traffic from the hosts (man in the middle attack) - HSRP provides the following types of authentication: plain text MD5 |
|
|
How is HSRP authentication configured? |
- to configure as plain text: (on interface mode) standby group authentication string - to configure MD5: (on interface mode) standby group authentication md5 key-string [ 0 | 7 ] string |
|
|
Define hello time and hold-time. |
- a hello message contains the priority of the router, the hello time, and hold-time - the hello time parameter value indicates the interval between the hello messages that the router sends (3 seconds by default) - the hold time parameter value indicates how long the current hello message is considered valid (10 seconds by default) - the hold-time value must be greater than the value of the hello time an should be at least three times the hello time |
|
|
How are the HSRP timers configured? |
You can adjust the HSRP timers to tune the performance fo HSRP: standby group timers [msec] hellotime [msec] haldtime - the msec timer allows you to configure sub-second failover times - NOTE: lower hello times lead to an increase in HSRP traffic and processing overhead |
|
|
What are the differences between the versions of HSRPv1 and HSRPv2 |
- HSRPv2 allows group numbers up to 4095 (as opposed to 255 for HSRPv1); the benefit is that the group number can be configured to match the VLAN number (VLAN 100 and group number 1000) - HSRPv2 is the only version of HSRP that supports IPv6, and it must be enabled on an interface before you can configure HSRP for IPv6 - HSRPv2 uses the multicast address 224.0.0.102 (as opposed to 224.0.0.2 for v1) - this is the all routers multi cast address, and using it for HSRP can cause issues with other features, essentially the cisco group multi cast protocol (CGMP); the unique address used by HSRPv2 avoids this problem - HSRPv2 has a different packet format, includes a 6 byte identifier that is used to identify the sender of an HSRP message. it is usually set to the MAC address of the sender NOTE: HSRPv2 is not backwards compatible with HSRPv1 |
|
|
Explain the difference between HSRP and VRRP standards? |
HSRP -Cisco proprietary - created in 1994 and formalized with the RFC 2281 in march 1998 VRRP - IEEE standard for router redundancy - (RFC 2338 in 1998; then RFC 3768 in 2005; then RFC 5798 in 2010) |
|
|
Explain the difference between HSRP and VRRP groups allowed? |
HSRP - 16 groups VRRP - 255 groups |
|
|
Explain the difference between HSRP and VRRP routers? |
HSRP - 1 active, 1 standby, several candidates VRRP - 1 active and several backups |
|
|
Explain the difference between HSRP and VRRP IP addressing? |
HSRP - virtual IP is different from active and standby real IP addresses VRRP - virtual IP can be the same as one of the group members real IP address |
|
|
Explain the difference between HSRP and VRRP address for hello packets? |
HSRP - uses 224.0.0.2 for hello packets VRRP - uses 224.0.0.18 for hello packets |
|
|
Explain the difference between HSRP and VRRP default timers? |
HSRP - defualt timers: hello 3s, holdtime 10s VRRP - the default timers are shorter; this gave the reputation of it being faster |
|
|
Explain the difference between HSRP and VRRP object tracking? |
HSRP - can track interfaces and objects VRRP - can track objects |
|
|
Explain the difference between HSRP and VRRP authentication? |
HSRP - uses authenitcation within each group by default - when the authenticaiton is not configured a default password using "cisco" is used VRRP - supports plain text and HMAC/MD5 authentication methods (RFC 2338) - the new VRRP RFC (RFC 3768) removes the support for these methods - the new consequnces is that VRRP does not support VRRP anymore - it still supports RFC 2338 authentication methods |
|
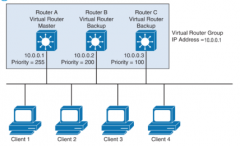
Describe this VRRP scenario. |
- routers A, B and C are members of a VRRP gorup; the IP address of the virtual router is the same as that of the LAN interface of router A (10.0.0.1); Router A is responsible for forwarding packets sent to this IP address - the clients have a gateway address of 10.0.0.1. Routers B and C are backup routers. If the master router fails, the backup router with the highest priority becomes the master router. When router A recovers, it resumes the role of the master router. |
|
|
What is the first step to configuring the VRRP router? |
- to enable VRRP on an interface - this makes the interface a member of the virtual gorup with the virtual IP virtual address: vrrp group-number ip virtual-gateway-address |
|
|
What is the second step to configuring the VRRP router? |
- to set a VRRP priority number for this router for this VRRP group; highest value wins election as active router. - Default is 100 - if routers have the same VRRP priority, the gateway with the highest real IP address is elected to become the master virtual router vrrp group-number priority priority-value |
|
|
What is the third step to configuring the VRRP router? |
- to change timer and indicate if it should advertise for master or just learn the backup routers vrrp group-number timers advertise timer-value vrrp group-number timers learn |

