![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Glacier formations |
100s to 1000s years to form
accumulation, compaction and recrystallization of snow
important record of time |
|
|
Types of Glaciers (2 types to know for exam) |
Continental/Ice sheets (only Greenland and Antarctica)
Alpine or Valley Glaciers (Alps, Alaska, Northern Rockies, Southern Andes, Himalayas) |
|
|
Erosion and Landforms |
1. Plucking and Abrasion
2. Glacial Trough - U shaped valley
3. Glacial Striations |
|
|
Plucking |
Occurs when melt water penetrates the cracks and joints along the rock floor of the glacier and freezes |
|
|
Abrasion |
As the ice and its load of rock fragments slide over bedrock, they function like sandpaper to smooth and polish the surface below. |
|
|
Glacial Trough |
The result during glaciation, narrow valleys undergo a transformation as the glacier widens and deepens them creating a U-shaped glacial trough |
|
|
Glacial Striations |
scratches and grooves made when ice contains large rock fragments |
|
|
Glacial Deposits |
Glacial Drift - sediments of glacial origin no mater how where or what form they were deposited (Till or Stratified Drift)
Moraines - Layers or ridges of till |
|
|
Glacial Drift - two distinct types |
Till and Stratified Drift |
|
|
Till |
Materials deposited directly by the glacier. Till is deposited as glacial ice melts and drops its load of rock debris |
|
|
Stratified Drift |
Sediments laid down by glacial meltwater. It is sorted according to the size and weight of the fragments. |
|
|
Effects of Glaciation |
1. Lithospheric Subsidence - Greenland
2. Lowering of Sea Level
3. Pluvial Lakes and Drainage Basins
4. Climate |
|
|
Causes of Glaciation |
1. Plate Tectonics
2. Variations of Earth's orbit |
|
|
Three types of Variations to Earth's orbit |
1. Eccentricity- elliptical orbit
2. Obliquity- 22.5 - 24.5 degrees
3. Precession - wobble of axis rotation |
|
|
How much of Earth's surface is desert? |
30% |
|
|
What are some misconceptions of deserts? |
1. Deserts are lifeless
2. Deserts are always hot (snow in Sonoran desert and Antarctica is a desert)
3. Deserts are vast expanses of sand
4. Desert erosion is caused by wind ~ it's caused mostly by water. |
|
|
How do climatologists define "dry climate" |
A climate in which yearly precipitation is less than the potential loss of water by evaporation. |
|
|
Ephemeral Streams |
Streams in response to specific episodes of rainfall. May only flow for a few days or hours |
|
|
Interior Drainage |
A discontinuous pattern of ephemeral streams that do not flow out of the desert to the ocean. |
|
|
Alluvial Fans |

A cone of debris at the mouth of a canyon |
|
|
Bajada |

Over time Alluvial fans enlarge and connect with fans from adjacent canyons to produce an apron of sediment along the mountain foot. |
|
|
Playa Lakes |
Streams may flow across the alluvial fans to the center of the basin converting the basin floor into a shallow lake lasting only a few days or weeks before evaporation and infiltration remove the water. |
|
|
Desert pavement and deflation |
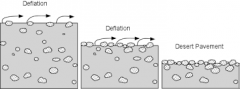
Over time, deflation lowers the surface and coarse particles become concentrated |
|
|
Saltation |
Sediment moving appears to jump or skip along |
|
|
Abraison |
Windblown sand cuts and polishes exposed rock surfaces. |

