![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why do we pay taxes 1)
|
Raise Revenue to finance spending on goods and services
|
|
|
Why do we pay taxes 2)
|
So gov't can control AD
|
|
|
Why do we pay taxes 3)
|
Redistribute Income
|
|
|
Why do we pay taxes 4)
|
Correcting Externalitites
|
|
|
Why do we pay taxes 5)
|
Control Balance of Payments and Imports
|
|
|
What is the effect of Indirect Taxes
|
Regressive Taxes and proportion of income paid decreases as income rises
|
|
|
What is the effect of Direct Taxes
|
Progressive Taxes and proportion of income paid increases as income rises
|
|
|
What is the effect of Proportional Taxes
|
Proportion of Income stays constant as income changes
|
|
|
What are Direct Taxes
|
Direct Taxes are typically on income divided for certain expense like (Insurance, Corporate Tax, Peteroleum Tax, Inheritance Tax, Capital Gains Tax)
|
|
|
What is Fiscal Drag
|
Earnings rise faster than prices
|
|
|
What are Excise Duties
|
Specific taxes levied on a certain good or service. Measurable in units per good
|
|
|
What is Value Added Tax
|
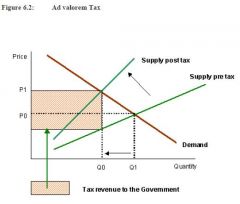
Tax as a proportion of Price - Raises Prices and Reduces Demand
|
|
|
Whats the advantage of Indirect Taxes to Direct Taxes
|
Income and Corporate Taxes get lowered. Incentive to work is increased, increasing productivity and AS, pushing prices down. More Flexible and can be used by Gov't to meet policy objectives
|
|
|
What is the Substitution Effect
|
Income Taxes are cut, and working more earns more. Opportunity Cost of leisure time is higher
|
|
|
What is the Income Effect
|
Income Taxes are cut, and people can work fewer hours to get the same amount of income
|
|
|
Which types of taxes increase Saving
|
Indirect Taxes reduce consumption and in effect increase saving
|
|
|
How are Indirect Taxes used for the environment
|
Indirect Taxes correct for Market Failure and/or externalities
|
|
|
What are Externalities
|
Occur when Social Costs of Production exceed Private Costs of Production
|
|
|
What is easier to Administer from Gov't standpoint Direct or Indirect Taxes
|
Indirect Taxes because collection only comes from Businesses
|
|
|
Reasons for Gov't Spending 1)
|
Providing Public and Merit Goods
|
|
|
Reasons for Gov't Spending 2)
|
Redistributing Wealth and Income
|
|
|
Reasons for Gov't Spending 3)
|
Regulating Economic Activities
|
|
|
Reasons for Gov't Spending 4)
|
Influence Resource Allocation and Industrial Efficiencies
|
|
|
Reasons for Gov't Spending 5)
|
Influencing Macro Level Activities
|
|
|
What does the Private Finance Initiative do?
|
Long-Term Leases and/or Financing Projects for Public Goods.
|
|
|
What is PSNCR or PBNR
|
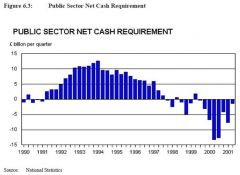
Public Sector Net Cash Requirement (Public Sector Borrowing Requirement) - Combined Financial deficit of Central Gov't, Local Govt, and Public Capital
|
|
|
Three Ways to Measure PSNCR: 1)
|
Nominal PSNCR - Money Terms, not adjusted for economic variables
|
|
|
Three Ways to Measure PSNCR: 2)
|
PSNCR as % of GDP - Measures Debt Problem Well
|
|
|
Three Ways to Measure PSNCR: 3)
|
Cyclically Adjusted PSNCR - Allows for adjustments of Economic Variables
|
|
|
How is National Debt Different than PSNCR
|
This is the Unpaid Portion of Borrowing or the Sum of all Central Gov't Debt
|
|
|
What are the Risks of a High Level of Borrowing 1)
|
Interest Rates could rise and crowd out Private Investment
|
|
|
What are the Risks of a High Level of Borrowing 2)
|
Increase of Tax Burden
|
|
|
What are the Risks of a High Level of Borrowing 3)
|
Interest Payments are higher
|
|
|
Reasons for Govt Spending
P R R E M |
1)Providing Public / Merit Goods
2) Redistribution of income and Wealth 3) Regulation 4) Influencing Economic Efficiency 5) Influencing Macro Activity |

