![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What happens to the red bone marrow when you get older and where do adults make red bone marrow |
Most red bone marrow other child turns to yellow bone marrow Adult red bone marrow is found in the E flat bone of the skull, vertebra, rib, sternum, hip, proximal end of humerus and femur |
|
|
Types of tissue in the skeletal system and some functions |
Mostly connective tissue but smooth muscle to push blood Supports weight, produces movement, mineral storage |
|
|
Two main minerals stored in Bones and what they're used for |
90% of minerals of calcium and phosphate are stored in the bone Calcium is used for muscle contraction, blood clotting, nerve impulse transmission Phosphate need to atp utilisation |
|
|
What happens when there is either calcium or phosphate and isolation |
Bone formation occurs make a kidney stones |
|
|
What is in cartilage and what are three functions |
Semi rigid with chondroblasts
Three functions are supportsoft issue, gliding surface of articulating joints, provide model for formation for most bones in body AKA rough draft |
|
|
Difference between chondroblasts and chondrocytes |
Chondroblasts produce The Matrix and when they are done that building cartilage they turn into chondrocytes Aka the chondrocytes are the retired form |
|
|
Difference between tendon, ligaments, aponeurosis |
Tendon is bone Ligament is bone to bone Both are chords with dense regular tissue
Aponeurosis is muscle muscle and it's a sheet |
|
|
Four types of bone description |

|
|
|
Cortex vs. Medulla |
Cortex is outside manoulas inside |
|
|
Endosteum versus periosteum |
Periosteum is the outside layer of the surface and endosteum is the cellular membrane that covers the internal surface |
|
|
What's a osteoprogenitor |
Is the stem cell of the bone in makes the new osteoblasts when you break bone |
|
|
Osteoblast vs. Osteoclast |
Osteoblast make the new bone and become osteocytes Osteoclast break down bone and I multi new healer |
|
|
Description of ostyeclasts |
Break down bone, multi nuclear, they secrete HCL to dissolve bone mineral, it's a resorption, lysosomes in osteoclast secrete enzymes to dissolve organic compounds AKA collagen
Not the bad guy |
|
|
Describe flat bone layers Haversian canals Valkmanns canal |

|
|
|
What is bone ossification and 2 kinds/ where does it occur |
It is the creation of bone Intramembraneous happens within the membrane of flat bone, cranial Endochondral: cartilage gets replaced by bone. |
|
|
Two different ways bone grow |
Diameter increase called apposition New bone lamella Endochondral growth - increase length, within cartilage |
|
|
Two different modes of opposition |
Bone deposited by osteoblasts, bone resorbed by osteoclasts (shape bone) |
|
|
Six steps of endochondral ossification |
Fetal hyaline cartilage model develops Diaphysis outside becomes bony and more chondrocytes Blood vessels penetrate diaphysis inform primary ossification site Blood vessels go to proximal and distal ends two create secondary office acacian sites Middle cartilage turns to Bone completely but ends are still cartilage AKA growth plates AKA leaves articulating cartilage Epiphyseal plate forms bone stops growing blood can flow through the hole bone now |
|
|
What are the irregular bones? |
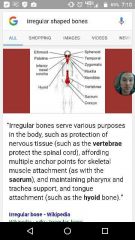
|
|
|
What is sesamoid bone |
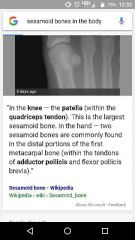
|
|
|
Flat bones |
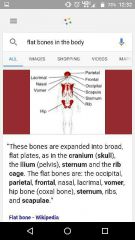
|
|
|
Long bones |

|
|
|
Short bones |
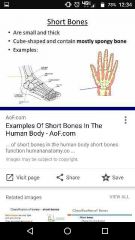
Carpals! |

