![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Six identified Health Risk Behaviors |
1. Smoking and other forms of tobacco use 2. Eating high-fat & low-fiber foods 3. Not engaging in enough physical activity 4. Abusing alcohol or other drugs (including prescription drugs) 5. Not using proven medical methods for preventing or diagnosing disease (flu shots, practicing safe sex, Pep smears, colonoscopies, mammograms) 6. Engaging in violent behavior or behavior that may cause unintentional injuries (e.g., driving intoxicated) |
|
|
|
The Health Belief Model (HBM) |

|
|
|
|
The Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) |

|
|
|
|
The Transtheoretical Model |
▫ Maintenance > "I have been tobacco free for six months" ▫Action > "I'm actively cold turkey, and it's week two. So far, so good." ▫Preparation > "I've seen my doctor & told her I am going to quit smoking. She wrote a prescription to help reduce my cravings." ▫Contemplation > "I need to quit smoking." ▫Precontemplation > "I have no plans to quit smoking." |
Assesses a person's readiness to act on a new, healthier behavior. Identifies strategies & processes to guide the individual through these states of change to successful action and maintenance. Critiques point out that the states are not mutually exclusive, & people do not always move sequentially through discrete stages as they strive for change health behaviors. |
|
|
3 Stages of Prevention |

|
|
|
|
Health Education Programs (HEPs) |
Carefully planned HEPs that present information on several fronts& that are community-based often can promote changes that are difficult for individuals to accomplish by themselves. |
|
|
|
Precede/ Proceed Model |
The most widely used HEPs model. ▫Planning begins by identifying specific health problems in a targeted group. ▫Next, lifestyle & environmental elements that contribute to the targeted health problem are identified. ▫Then background factors that predispose, enable, & reinforce the lifestyle & environmental factors are analyzed. ▫Finally, health education programs are designed, initiated, & evaluated. |
|
|
|
Behavioral Interventions |
Focus on the conditions that elicit health behavior's and the factors that help to maintain & reinforce them. Many programs use self-monitoring as the initial step in promoting behavior. |
|
|
|
Aversion therapy |
Based on classical conditioning of respondent behaviors. |
|
|
|
Contingency contracting, modeling, & use of tokens economies are based on... |
Operant conditioning principles |
|
|
|
Research shows (2005) that when we adversity, whether psychological or physical, there are at least 4 possible outcomes: |
1. A continued downside 2. Survival with diminished capacity or impairment, 3. A gradual or rapid return to the pre-adversity level of functioning, 4. The emergence of a quality that makes the person somehow better of than beforehand, referred to as thriving. |
|
|
|
Allostatic load |
According to neuroscientists Bruce McEwen, who introduced the concept, "Under the conditions of stress, one would expect a physically weakened system, but psychological changes can occur - often in the context of psychological thriving. In psychological terms, this transfers into greater restorative processes than destructive processes at work." |
|
|
|
Environmental/ Psychological stressors in adulthood |
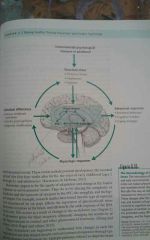
|
|

