![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Ptolemy |
Claudius Ptolemy was a Greco-Egyptian writer, known as a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer, and poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology.
|
|

Copernicus |
Nicolas Copernicus was a Renaissance mathematician and astronomer who formulated a model of the universe that placed the Sun rather than the Earth at the center of the universe, possibly independently.
|
|

Kepler |
Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician, astronomer, and astrologer. A key figure in the 17th century scientific revolution, he is best known for his laws of planetary motion.
|
|

Galileo Galilei |
Galileo Galilei was an Italian astronomer, physicist, engineer, philosopher, and mathematician who played a major role in the scientific revolution of the seventeenth century. |
|

Francis Bacon |
Francis Bacon, 1st Viscount St Alban PC KC was an English philosopher, statesman, scientist, jurist, orator, and author. He served both as Attorney General and as Lord Chancellor of England. |
|

Descartes |
René Descartes was a French philosopher, mathematician, and scientist. Dubbed the father of modern western philosophy, much of subsequent Western philosophy is a response to his writings, which are studied closely to this day. |
|

Newton |
The newton (symbol: N) is the International System of Units (SI) derived unit of force. It is named after Isaac Newton in recognition of his work on classical mechanics, specifically Newton's second law of motion. Sir Isaac Newton FRS was an English physicist and mathematician who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and a key figure in the scientific revolution. |
|

Revolution |
A forcible overthrow of a government or social order in favor of a new system. |
|

Geocentric |
A Geocentric theory is an astronomical theory which describes the universe as a Geocentric system, i.e., a system which puts the Earth in the center of the universe, and describes other objects from the point of view of the Earth. |
|

Astronomer |
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who concentrates their studies on a specific question or field outside of the scope of Earth. |
|

Heliocentric |
Having or representing the sun as the center, as in the accepted astronomical model of the solar system. Measured from or considered in relation to the center of the sun. |
|

Excommunication |
Excommunication is an institutional act of religious censure used to deprive, suspend, or limit membership in a religious community or to restrict certain rights within it, in particular receiving of the sacraments. Some Protestants practice an alternate form of excusing congregants from the church. |
|
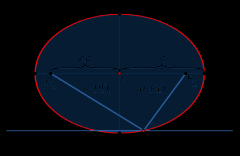
Ellipses |
a regular oval shape, traced by a point moving in a plane so that the sum of its distances from two other points (the foci) is constant, or resulting when a cone is cut by an oblique plane that does not intersect the base. |
|

Heresy |
Belief or opinion contrary to orthodox religious (especially Christian) doctrine. Opinion profoundly at odds with what is generally accepted. |
|
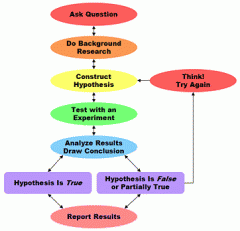
Scientific Method |
A method of procedure that has characterized natural science since the 17th century, consisting in systematic observation, measurement, and experiment, and the formulation, testing, and modification of hypotheses. |
|

Hypothesis |
A supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation. A proposition made as a basis for reasoning, without any assumption of its truth.
|

