![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
DNA |
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) - A nucleic acid composed of deoxyribonucleotides that carries the genetic information of a cell. Generally occurs as two intertwined strands, but these can be separated. |
|
|
Double helix |
the secondary structure of DNA, consisting of two antiparallel DNA strands wound around each other. |
|
|
Nucleotide |
A molecule consisting of a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of several nitrogen-containing bases. DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides containing deoxyribose and ribose. |
|
|
Phosphodiester linkage / Phosphodiester bond |
chemical linkage between adjacent nucleotide residues in DNA and RNA. Forms when the phosphate group of one nucleotide condenses with the hydroxyl group on the sugar of another nucleotide. |
|
|
RNA |
ribonucleic acid - A nucleic acid composed of ribonecleotides that usually is single stranded. Functions include structural components of ribosomes (rRNA), transporters of amino acids (tRNA), and messages of DNA code required for protein synthesis (mRNA). |
|
|
Label the three main parts of a nucleotide. |
1. a phosphate group 2. a 5-carbon sugar 3. a nitrogenous (nitrogen-containing) base. |
|
|
Know how to number the carbons on a pentose sugar and know what is attached to each carbon. |
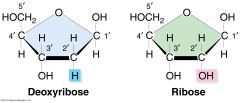
|
|
|
Compare and contrast ribose and deoxyribose: |
deoxy means containing less oxygen. Deoxyribose is ribose but without the oxygen in the 2' position. |
|
|
List the four nitrogenous bases that make up DNA: |
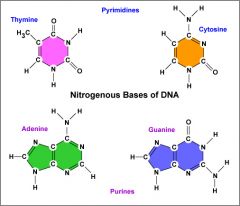
Thymine |
|
|
List the four nitrogenous bases that make up RNA. |
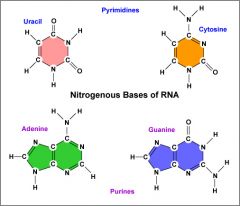
Uracil |
|
|
Daughter strand |
the strand of DNA that is newly replicated from an existing template strand of DNA |
|
|
dNTP (deoxynucleoside triphosphate) |
A monomer used by DNA polymerase to polymerize DNA. Consists of the sugar deoxyribose, a base (A, T, G, or C) and three phosphate groups. |
|
|
Okazaki fragment |
Short segment of DNA produced during replication of the lagging strand template. Many Okazaki fragments make up the lagging strand in newly synthesized DNA. |
|
|
Origin of replication |
The site on a chromosome at which DNA replication begins. |
|
|
Parental strand |
A strand of DNA that is used as a template during DNA synthesis. |
|
|
Primer |
A short, single-stranded RNA molecule that base-pairs with a DNA template strand and is elongated by DNA polymerase during DNA replication. |
|
|
Replication bubble |
a portion of the DNA molecule that has opened, providing a site for two replication forks. Multiple replication bubbles along the DNA molecule speed up the process of replication. |
|
|
Replication fork |
One half of a replication bubble; a y-shaped structure on the DNA molecule along which replication takes place. |
|
|
Telomere |
The end of a linear chromosome that contains a repeated sequence of DNA. |
|
|
Describe semi-conservative DNA replication |
The way DNA replicates, in which each strand of an existing DNA molecule serves as a template to create a new complementary DNA strand. It is called semiconservative because each newly replicated DNA molecule conserves one of the parental strands and contains another, newly replicated strand. |
|
|
Identify the function of the following during DNA replication: DNA helicase |
This enzyme separates double-stranded DNA into single strands allowing each strand to be copied. |
|
|
Identify the function of the following during DNA replication: DNA ligase |
This enzyme brings together the Okazaki fragments. |
|
|
Identify the function of the following during DNA replication: DNA polymerase |
This enzyme catalyzes the synthesis of the mRNA strand during transcription. |
|
|
Identify the function of the following during DNA replication: Primase |
(RNA polymerase) - This enzyme synthesizes short RNA sequences called primers. These primers serve as a starting point for DNA synthesis. |
|
|
Identify the function of the following during DNA replication: Single-stranded binding proteins (SSBP) |
They proven annealing, or the DNA from snapping back to the other strands while it is being copied. |
|
|
Identify the function of the following during DNA replication: Topoisomerase |
This enzyme regulates the overwinding or under winding of DNA. |

