![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
8 things that make something living I. All living organisms are comprised of cells. There are two main categories of cells:____________________ and ____________________. |
growth metabolism reproduction adapt responsiveness movement homeostasis comprised of cells prokaryotic arcaebacteria eubacteria and eukaryotic-protist algae fungi plants animals |
|
|
There are some ____________________ between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells including: |
similarities |
|
|
The parts of the cells are comprised of the same basic chemicals...the four ____________________. |
macromolecules protein lipids carbohydrates nucleic acids |
|
|
All living organisms utilize their ______________ as “instructions” for building ____________________. The process in which DNA is converted to RNA iscalled ____________________and the process in which RNA molecules areconverted into proteins is called ____________________. |
DNA/nucleic acids proteins transcription translation |
|
|
There are also ____________________ between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cellsincluding: |
differences |
|
|
The structure of the ____________________... The chromosomes of prokaryotic organisms are _________________ and ____________________. They are also contained within thecytoplasm in a general region called the ____________________region. |
nucleus circular haploid (1 copy per chromosome) most bacteria have 1 chromosome nucleiod region |
|
|
The chromosomes of eukaryotic organisms are _________________and ____________________ or polyploidy. They are also containedwithin a membrane bound organelle called the __________________. |
linear diploid ) 2 copies ) polyploid ( 3 or more ) - in plants the nucleus |
|
|
The process of cell ____________________ and/or organismal____________________. |
replication reproduction |
|
|
Prokaryotic organisms replicate or reproduce through a process called____________________ ____________________. |
binary fission the reason why mitosis is not possible is bc mitosis is a form of nuclear division |
|
|
Eukaryotic organisms which reproduce ____________________utilize a process called ____________________ which is also utilized to for cell replication in multicellular organisms. Organisms whichreproduce ____________________ utilize a process called____________________ to generate sex or germ cells. |
asexually mitosis or sexually meiosis binary fission and mitosis have daughter cells identical to parent bacterial cells reproduce much more quickly, which increases the likelihood or cell mutations |
|
|
The ____________________ or ____________________ of membrane-bound organelles... |
present or absence |
|
|
Prokaryotic organisms _____________ membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic organisms ______________ membrane-bound organelles. endosymbiont theory - supporting theory ( |
lack have mitochondria is the same size as a prokaryotic cell supporting theory mitochondria have they're own DNA, which is circular mitochondrial DNA is from your mom because you do not get mitochondria from your dad mitochondria divide through binary fission during mitosis same is true for chloroplast REVIEW FUNCTIONS OF CELL ORGANELLES |
|
|
The structure of ____________________... Prokaryotic organisms have ____________________ ribosomeswhich are comprised of a 50S large subunit and 30S small subunit.The ribosomes of prokaryotic organisms are a common target formany ____________________. |
ribosomes 70s ribosome numbers refer to what speed they spin out in a centrifuge antibiotics -ribosomes are necessary for translation, which means that proteins will never be formed , can not affect eukaryotic because eukaryotic have 80s ribosomes |
|
|
Eukaryotic organisms have ____________________ ribosomeswhich are comprised of a 60S large subunit and 40S small subunit. a. The 70S ribosome is found in the ____________________ ofeukaryotic organisms. |
80s ribosome, mitochondria |
|
|
The location and timing of transcription and translation is different... In prokaryotic organisms, transcription and translation occur ____________________ within the cytoplasm. In eukaryotic organisms, transcription occurs in the ______________ during interphase and translation occurs in the cytoplasm. |
simultaneously sometimes the dna is not even completely transcribed before the translation of proteins occurs 45 mins for a prokaryotic cell to divide and 4 and 8 hours for eukaryotic nucleus interphase is most metabolic phase in cell division |
|
|
Chemical composition of the cell wall... The cell wall of prokaryotic organisms contains _________________. The cell wall of eukaryotic organisms contains __________________ and is only present in ____________________ cells and some fungiand protists. |
peptidoglycan (part protein part sugar) cellulose (polysaccharide of glucose) plant |
|
|
vii. The average size of the cell... Prokaryotic cells are generally between ____________________. Eukaryotic cells are generally between ____________________. |
0.5 microns and up to 5 microns 5 microns to 100 microns |
|
|
Many bacterial cells have specialized structures which occur external to the cell... The ____________________ is a gelatinous, sticky substance that may surround the outside of the cell. The chemical composition of the capsule varies among different species, but most are made of ____________________ and/or ____________________. A glycocalyx composed of repeating units firmly attached to the cell surface is called a ____________________. A loose, water-soluble glycocalyx is called a ___________________ |
glycocalyx "sugarcup" gooey layer prevents the phagocytes from recognizing the bacteria, polysaccharides and or polypeptides greater adherence capsule slime layer |
|
|
The function of the glycocalyx includes... Protection from ___________________ and ___________________. Enhancing the ____________________ factor. Allow for ____________________ to surfaces. Causes inhibition of ____________________ absorption. |
dessication phagocytosis virulence(harmfulness of a disease) factor attachement phage negative stain shows a capsule |
|
|
____________________ are long structures which originate from the cytoplasmicmembrane and extend beyond the surface of the cell and its glycocalyx. |
flagella kamikaze sperm have more than one flagellum and will kill sperm from a different donor |
|
|
Flagella are composed of three parts...the ____________________, a hook,and a basal body. |
filament |
|
|
. The filament extends into the cell’s environment and is composed ofmany identical subunits of a protein called ____________________. |
flagellin flagellin is sensitive to pH and temp. since it is composed of a protein, heat fixing causes flagellum to disappear. hook is in charge of movement basil body is the anchor. |
|
|
Bacteria may have one of several flagellar ____________________... ____________________ have single flagellum at one pole. ____________________ have single flagellum at each pole. ____________________ have two or more flagellum at one or bothpoles.____________________ have flagella evenly distributed over theentire surface of the cell. |
arrangments monotrichous -vibrio chlorea amphitrichous lophotricous peritrichous 670 mph |
|
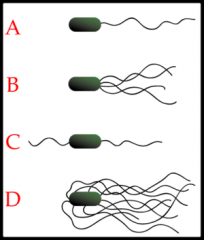
|
a. monotrichous b. lophotricous c. amphitrichous d. peritrichous |
|
|
Flagella provide the bacteria with ____________________...bacteria canmove towards favorable or away from unfavorable environmental conditions. 1. Movement in response to a stimulus is called ___________________. movement toward favorable unfavorable |
motility taxis runs tumbles |
|
|
____________________ refers to response to chemical attractants, nutrients, or toxic materials. |
cheomotaxis |
|
|
____________________ refers to movement towards optimal concentrations of dissolved ____________________. |
aerotaxis oxygen |
|
|
____________________ refers to movement towards optimal ____________________ intensity and quality. |
phototaxis light |
|
|
____________________ refers to movement along lines of____________________ forces...often within sediments of marine or fresh water systems. |
magnetotaxis magnetic |
|
|
__________________ are internalized flagella which form _______________ filaments which run lengthwise between the cytoplasmic membrane and anouter membrane. They are found in ____________________ like Treponema pallidum(syphillus) and Borrelia burgdorferi. (lyme disease) instead of tumbles and runs it moves like a corkscrew allowing it of move in deeper tissues |
endoflagella axial spirochetes |
|
|
____________________ and ____________________ are sticky, bristle-likeprojections. |
fimbriae and pili |
|
|
Fimbriae, which are much more ____________________ and shorter thanflagella, allow the bacterial cell to adhere to one another and to substances inthe environment. |
numerous specific to tissue ex gonorrgea can attach to the eye rectum or throat |
|
|
Pili, a special type of fimbriae, are longer and less abundant.1. A ____________________ pili mediates the transfer of ______________ from one cell to another cell. |
conjugation ( fertility ) DNA or genetic info F positive , usually plasmids |
|
|
Cells of most prokaryotes are surrounded by a ______________________________... |
cell wall |
|
|
Functionally the cell wall... Provides the characteristic ____________________ of the organism...the three basic shapes are... ____________________, ____________________, and ____________________. ____________________ are slightly curved rods. ____________________ are intermediate between cocci and bacillus. |
shape cocci spherical bacilli rod and spirals includes spirilla and spirochetes bribes are slightly curved rods coccobacillus |
|
|
Assists in ____________________ to other cells. Protects the cell against ____________________ chemicals including bile salts in digestive tract, antibiotics, disinfectants, and antiseptics. Assists in ____________________ regulation. |
attaching antimicrobial osmotic |
|
|
Chemically the cell wall is composed of ____________________. Peptidoglycan is composed of two types of regularly alternating sugar molecules called, N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid(NAM), which are covkalently linked to form long chains which make up the“____________________” portion. |
peptidoglycan glycan |
|
|
Chains of NAG and NAM are attached to other chains by____________________ of four amino acids or the “___________________”portion. This portion varies among bacterial species, but the most commonfour amino acids are... 1. L-alanine 2. D-glutamic acid 3. Diaminopinelioacid (DAP) or L-lysine 4. D-alanine |
crossbridges peptido |
|
|
Bacteria can be categorized into one of two categories based on the structure of their cell wall... i. Gram-positive bacteria... 1. Cell walls have relatively ____________________ layer ofpeptidoglycan along with unique chemicals... ____________________ acids and ____________________acids anchor the peptidoglycan to the cytoplasmic membrane. ____________________ acid is a waxy lipid which helps thecell survive desiccation. |
thick teichoic lipoteichoic mycolic |
|
|
Gram-negative bacteria... 1. Cell walls have only a ____________________ layer of peptidoglycan, but outside the cell wall is an asymmetric____________________ membrane called the __________________membrane. The ____________________ layer of the outer membrane iscomprised of ____________________ and proteins. The ____________________ layer is made of_______________________________ (LPS) which determinethe ____________________ of the organism. i. The ____________________ portion of the LPS maytrigger fever, vasodilation, inflammation, shock, andblood clotting. |
thin bilayer membrane outer member inner phospholipids outer lipopolysaccharide virulence lipid |
|
|
Functionally the outer membrane...a. ____________________ the cell by blocking polar and nonpolar molecules from entering the cell.b. Serves as an ____________________. |
protects endotoxin gram negative are more resistant to antibiotics |
|
|
Other important structures of the outer membrane include...a. The ____________________ ____________________which occurs between the cytoplasmic membrane and the outermembrane and contains the peptidoglycan and____________________. b. ____________________ are integral proteins which formchannels through the outer membrane allowing for____________________ of nutrients. c. ____________________ assist in anchoring the outermembrane to the cell wall. |
periplasmic space periplasm porins transport lipoproteins |
|
|
A few bacteria lack cell walls entirely...the ____________________. |
mycoplasma |
|
|
Below the cell wall is the ____________________ membrane... |
cytoplasmic |
|
|
a. The cytoplasmic membrane follows the ________________________________________ model. i. The cytoplasmic membrane is composed of a ____________________ ofphospholipids and ____________________ proteins. |
fluid mosaic bilayer ( center is hydrophobic) integral |
|
|
Functionally the cytoplasmic membrane... ____________________ the contents of the cell from the outer environment. Is ____________________ permeable...controlling the passage ofsubstances into and out of the cell. There are two types of transport acrossthe membrane... |
separates semi |
|
|
____________________ transport...a. Includes diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis. ____________________ transport... a. ____________________ ____________________ is an active process in which the substance is chemically modified during transport in order to prevent it from leaving the cell. Produces molecules for energy storage and harvesting of light energy |
passive active group translocation |
|
|
Inside the cytoplasmic membrane is the ____________________ and other structures...a. The ____________________ is the gelatinous material inside the cell. The cytoplasm is the site of all ____________________ reactions includingthose involved in the production of energy in the form of ATP. It is composed of cytosol, nucleoid, plasmids, ribosomes, inclusions, andendospores. |
cytoplasm (2) metabolic |
|
|
____________________ is liquid portion containing water along withdissolved and suspended substances including ions, carbohydrates,proteins, lipids, and wastes. |
cytosol |
|
|
The ____________________ is a region within the cell where theDNA is located. |
necleoid |
|
|
Bacterial chromosomes are ____________________ and____________________. Some bacterial species may havemultiple circular chromosomes each with distinct genes. |
circular haploid |
|
|
____________________ are extraneous chromosomal elements(DNA) which replicate autonomously within the cytoplasm. They arenot essential for the viability of the organism unless it is placed in a____________________ environment. To ____________________a cell is to remove the plasmid. Functions of plasmids include: |
plasmids selective cure |
|
|
Capacity to mate with other cells through ________________. Confer ____________________ resistance. To code for ____________________. Confer the ability of ____________________ fixation to certain organisms. Production of plant ____________________. Code for ____________________. Used in genetic ____________________. |
conjugation antibiotic endotoxins nitrogen plant tumors bacteriocins engineering |
|
|
The number of ____________________ per bacterial cell can be up to20,000 units. The ribosomes are comprised of 60% ____________________RNA and 40% ____________________. |
ribosomes ribosomal rna protein |
|
|
The 70S ribosomes found in prokaryotic cells are made up of twosubunits... The ____________________ (30S) subunit contains the 16Sribosomal RNA which aligns the messenger RNA moleculesduring translation. The ____________________ (50S) subunit contains the 5Sand 23S ribosomal RNAs. |
small large |
|
|
The function of the ribosomes is protein synthesis or the____________________ of amino acids through the process of____________________. a. Some antibiotics function by binding to the ribosomes thusinterfering with protein synthesis. |
polymerization translatation |
|
|
____________________ ____________________are granules locatedwithin the cytoplasm which store reserves of nutrients and other molecules. |
inclusion bodies |
|
|
Store carbon and energy in molecules of ____________________ orpolyhydroxybutyrate (PHB). |
glycogen |
|
|
____________________ ____________________are inclusionswhich contain gases and allow the aquatic cyanobacteria to float inthe water column. |
gas vesicles |
|
|
____________________ are inclusions which contain pigmentsneeded for ____________________. |
chlorosomes photosynthesis |
|
|
____________________ are inclusions which contain magnetitewhich is used for ____________________. |
magnetosomes forming iron magneto taxis |
|
|
____________________ are a form of a resting cell generated underunfavorable conditions as a ____________________ mechanism by somegram-positive rods. |
endsporms survival |
|
|
Endospores are formed through a process called____________________n which may be triggered by changes to orharsh external environments including nutrient depletion,accumulation of waste products, and/or fluctuations in pH. The process through which endospores return to a vegetative state iscalled ____________________. a. Examples of organisms that form endosporesinclude...Clostridium tetani, Clostridium botulinum, Clostridiumperfringens, Bacillus anthracis. |
sporulation germination |
|
|
All prokaryotes reproduce ____________________...a. The most common method of asexual reproduction is ____________________ ____________________ which proceeds as follows...i. The cell replicates its ____________________. The cell ____________________ which requires the enlargement of thepeptidoglycan shell and moves the daughter molecules of DNA apart... ____________________ is an enzyme which breaks the crosslinksbetween the NAM and the peptides allowing for more peptidoglycanunits to be added. ____________________ reseal the breaks by adding a newpeptidoglycan monomer. a. ____________________ and related antibiotics inactivatetranspeptidases ____________________ the cell wall andcausing cell death through cell lysis. Cell forms a ____________________ ____________________, invaginatingthe cytoplasmic membrane. The cross wall completely divides the ____________________ cells whichmay or may not separate. |
asexually binary fission dna elongates autolysin transpeptidase peniclillin weakens cross wall daughter |

