![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
3 main parts of a cell |
Plasma membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus |
|
|
Plasma membrane |
Outer boundary of cell that acts as a selectively permeable barrier. Separates intracellular from extracellular. Controls what enters and what leaves. |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
Intracellular fluid packed with organelles (small structures that perform specific cell functions) |
|
|
Nucleus |
An organelle that controls cell activity |
|
|
Extracellular materials |
Substances found outside cells. Extracellular fluids cellular secretions extracellular matrix |
|
|
Extracellular fluids-3 types |
Nutritious soup that cells are bathed in. Interstitial fluid Blood plasma Cerebrospinal fluid |
|
|
Cellular secretions |
Aid in digestion or produce lubrication |
|
|
Extracellular matrix |
Most abundant. Jelly like substance, "cell glue", that holds cells together. Comprised of proteins and polysaccharides. |
|
|
Plasma membrane's main structure is |
The lipid bilayer |
|
|
Lipid bilayer is composed of |
Phospholipids, glycolipids, cholesterol, and proteins. |
|
|
Phospholipid |
Lollipop shaped molecule with a polar head (hydrophilic-water loving) and a nonpolar tail made of 2 fatty acid chains (hydrophobic-fears water) 75% |
|
|
Glycolipids |
Lipids with attached sugar groups on outer membrane surface. 5 % |
|
|
Cholesterol |
Wedged between phospholipids tails to increase stability. 20% |
|
|
Glycocalyx |
Sugar coat of plasma membrane consisting of glycolipids and glycoproteins. Unique markers allow cell to be recognizable. |
|
|
Membrane proteins |
Workers! Allow cell communication. |
|
|
Integral proteins |
Inserted into lipid bilayer (transmembrane). Both hydrophilic and hydrophobic allowing interaction with lipid tails and inner and outer water. |
|
|
Peripheral proteins |
Loosely attached to integral proteins. |
|
|
Cell junctions |
Bind cells together to form tissues and organs -tight junctions -desmosomes -gap junctions |
|
|
Tight junctions |
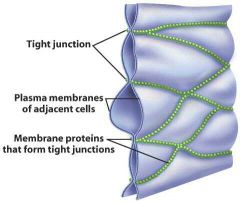
Proteins fuse together creating impermeable junction preventing molecules from passing through. Ex. Digestive/bloodstream |
|
|
Desmosomes |
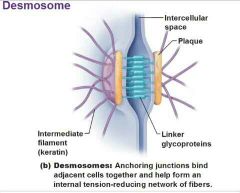
Keep tissues together. Protein velcro (cadherins). Anchored by plaques inside membrane. Keratin filaments add anchoring strength. Skin and heart muscles. Ex. Intercalated discs. |
|
|
Gap junctions |
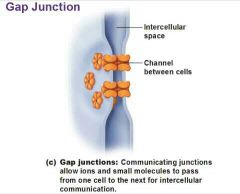
Encourages mover of material. Communicating junctions connected by hollow cylinders, called connexons, allow small molecules to pass from cell to cell. Allows electrical signals to pass quickly. Ex. Cardiac and smooth muscle. |
|
|
Substances move across membrane by: |
-Passive processes (no energy required) -active processes (ATP required) |
|
|
Types of passive membrane transport: |
No energy needed -diffusion -filtration |
|
|
Diffusion |
Molecules move from area of higher concentration to lower until evenly dispersed. Simple diffusion Facilitated diffusion Osmosis |
|
|
Simple diffusion |
Substance diffuse directly through lipid bilayer. Ex: oxygen (O), carbon dioxide (CO2). O enters CO2 exits. |
|
|
Facilitated diffusion |
Movement of molecules by means of transport. Ex: glucose, amino acids. -carrier mediated: substances bind to protein carriers -channel mediated: substances move through water filled channels. |
|
|
Polar attracts... |
Polar |
|
|
Polar and non polar.... |
Do not mix! |
|
|
Hypertonic |
Salty |
|
|
Osmosis |
diffusion of water from area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. |
|
|
Tonicity |
Ability of a solution to change shape of cells by altering the cells internal water volume. |
|
|
Isotonic solution |
Volume remains unchanged. Net is equal. |
|
|
Hypertonic solution |
Cells lose water and shrink. |
|
|
Hypotonic solution |
Cells take on water and plump or burst. |
|
|
Active membrane transport |
ATP required Active transport Vesicular transport |
|
|
Active transport |
Requires carrier, but uses ATP energy because it's going against concentration gradient |
|
|
Vesicular transport |
Involves movement of large particles and fluids |
|
|
Sodium potassium pump |
Pumps K into and Na out of cell. Common in excitable cells, netted and muscles. |
|
|
Endocytosis |
Transport into cell |
|
|
Exocytosis |
Transport out of cell |
|
|
Phagocytosis |
Large sized particles ingested. Cell eating |
|
|
Pinocytosis |
Cell drinking tiny particles. |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
All cellular material located between plasma membrane and nucleus. |
|
|
Cytosol |
Gel like solution made up of water and syllable molecules like proteins, salts, sugars, etc. |
|
|
Inclusions |
Insoluble molecules |
|
|
Organelles |
Metabolic machinery structures of cell, each with specialized function. Membranous or nonmembranous. |

