![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the main function of the respiratory stystem?
|
Gas Exchange - To move oxygen in and move CO2 out.
|
|
|
Define Ventilation
|
Ventilation: Movement of air into and out of lungs
|
|
|
Define External respiration
|
External respiration: Gas exchange between air in lungs and blood
Transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood |
|
|
Define internal respiration
|
Internal respiration: Gas exchange between the blood and tissues
|
|
|
If the pH of the blood is acidic, then breaths get __________.
|
faster
|
|
|
If blood pH is basic, then breaths get ___________
|
slower
|
|
|
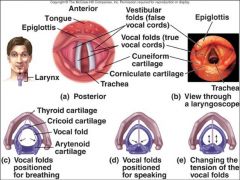
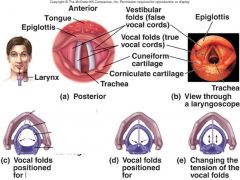
Describe voice production
|
Movement of air past vocal folds in the larynx makes sound and speech
|
|
|
Describe how the respiratory system functions to protect
|
Protection: Against microorganisms by preventing entry and removing them. (Clean the air before it gets to the alveoli.)
|
|
|
what structures are in the upper respiratory tract?
|
Nasal cavity, nose, pharynx (throat)
|
|
|
what structures are in the lower respiratory tract?
|
Larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs
|
|
|
what are the five functions of the respiratory system?
|
gas exchange
regulation of blood pH Voice production olfaction protection |
|
|
what does the upper respiratory tract do?
|
purifies air
|
|
|
Why does the upper respiratory tract need to purify the air?
|
Because the lower tract is where pathogens and contaminants can enter the body's blood stream
|
|
|
Describe the function of the concha.
|
The superior, middle and inferior concha (also called turbinates) case the air to stay in the nasal cavity longer, allowing for more purification of the air before it enters the lower tract
|
|
|
which bone forms the concha?
|
the ethmoid bone
|
|
|
What are the functions of the nasal cavity?
|
cleaning the air and humidifying the air.
|
|
|
why is it important to humidify the air in the nasal cavity?
|
humidity slows down air movement - a mucosal layer of epithelial cells moistens the air so the air stays int the nose longer, giving a change to be cleaned further before moving to lower respiratory tract
|
|
|
why do women have higher pitched voices then men typically?
|
because women have shorter vocal folds, and men have longer.
|
|
|
what is the pharynx?
|
Common opening for digestive and respiratory systems
|
|
|
what are the three regions of the pharynx? What moves through these regions?
|
Nasopharynx - strictly for air
Oropharynx - air & food Laryngopharynx - air & food |
|
|
|
|
|
When speaking, the arytenoid cartilage moves ___________
|
medially
|
|
|
What does the trachea do?
Describe |
connects larynx to the bronchi
Windpipe Divides to form Primary bronchi Carina: Cough reflex |
|
|
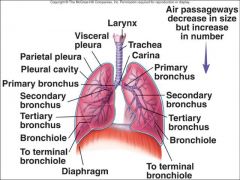
Describe the conducting zone of the tracheobronchial tree
|
No gas exchange - ventilation only
Trachea to terminal bronchioles which is ciliated for removal of debris Passageway for air movement Cartilage holds tube system open and smooth muscle controls tube diameter |
|
|
Describe Respiratory zone
|
Respiratory bronchioles to alveoli
Site for gas exchange |
|
|
|
|
|
Does the terminal bronchiole contain alveoli?
|
No
|
|
|
Do respiratory bronchioles contain alveoli?
|
yes
|
|
|
why do lungs change shape with muscle contraction?
|
serosa membranes secrete a fluid to lubricate and to create a fluid seal between lungs and thoracic cavity. The lungs are attached to the thoracic cavity by the fluid seal.
|
|
|
During exercise, which intercostal muscles contract for forceful inhalation?
|
external intercostal muscles
|
|
|
During exercise, which intercostal muscles contract for forceful expiration?
|
internal intercostal muscles
|
|
|
compare and contrast inspiration
|
inspiration = diaphragm contracts, leading to increase in volume, which leads to lowering in pressure inside the lungs. The external air has higher pressure and thus moves into area of lower pressure inside the lungs.
|
|
|
compare and contrast
expiration |
expiration = diaphragm relaxes, leading to decrease in volume, which leads to raising in pressure inside the lungs. The external air has lower pressure and thus air moves into area of lower pressure outside the lungs.
|
|
|
Pressure is _________ related to volume
|
inversely
|
|
|
what is a pneumothorax?
|
Pneumothorax is an opening between pleural cavity and air that causes a loss of pleural pressure
|
|
|
__________ pressure can cause alveoli to expand
|
Negative
|
|
|
What is compliance?
|
Measure of the ease with which lungs and thorax expand
The greater the compliance, the easier it is for a change in pressure to cause expansion A lower-than-normal compliance means the lungs and thorax are harder to expand |
|
|
Conditions that decrease compliance
|
Pulmonary fibrosis
Pulmonary edema Respiratory distress syndrome |
|
|
Define tidal volume
|
Volume of air inspired or expired during a normal inspiration or expiration
|
|
|
Define inspiratory reserve volume
|
Amount of air inspired forcefully after inspiration of normal tidal volume
|
|
|
define expiratory reserve volume
|
Amount of air forcefully expired after expiration of normal tidal volume
|
|
|
define residual volume
|
Volume of air remaining in respiratory passages and lungs after the most forceful expiration
|
|
|
define inspiratory capacity
|
Tidal volume plus inspiratory reserve volume
|
|
|
define functional residual capacity
|
Expiratory reserve volume plus the residual volume
|
|
|
define vital capacity
|
The maximum amount of air that can be ventilated by the lungs. Sum of inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and expiratory reserve volume
|
|
|
define total lung capacity
|
Sum of inspiratory and expiratory reserve volumes plus the tidal volume and residual volume
|
|
|
define anatomic dead space
|
Anatomic dead space: Part of respiratory system where gas exchange does not take place
|
|
|
define diffusion coefficient
|
how easily gas moves across a membrane
|
|
|
what four things effect the diffusion coeffecient?
|
membrane’s thickness, the diffusion coefficient of gas, surface areas of membrane, partial pressure of gases in alveoli and blood
|
|
|
if there is a high diffusion coefficient, then there will be _________ gas exchange
|
higher
|
|
|
if the membrane is thicker, then there will be __________ gas exchange
|
lower
|
|
|
CO2 has a ________ diffusion coefficient, therefore it moves across the membrane ________
|
high
easily |
|
|
O2 has a ________ diffusion coefficient, therefore it is ________ to move across a membrane
|
low
more difficult than CO2 |
|
|
in the lungs, the inspired air has a ___1_____ pressure of O2 and a __2_______ pressure of CO2
The capillary pressure of O2 at the lung level is __3______ and the pressure of CO2 is ____4______ Therefore, O2 moves ____5___ and CO2 moves _____6____ |
1.high
2. low 3. low 4. high 5. from the alveoli into the capillaries 6. out of the capillaries and into the alveoli |
|
|
At the tissue level, the capillary blood has a ___1_____ pressure of O2 and a __2_______ pressure of CO2
The pressure of O2 in the actual tissues is __3______ and the pressure of CO2 is ____4______ Therefore, O2 moves ____5___ and CO2 moves _____6____ |
1. high
2. low 3. low 4. high 5. out of the capillaries and into the tissues 6. out of the tissues into the capillaries |
|
|
What would cause a shift to the left in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve?
|
an increase in pH, a decrease in carbon dioxide, or a decrease in temperature results in an increase in the ability of hemoglobin to hold oxygen
|
|
|
What would cause a shift to the right in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve?
|
EXCERCISE!!! = Decrease in pH, an increase in carbon dioxide, or an increase in temperature results in a decrease in the ability of hemoglobin to hold oxygen
|
|
|
what happens during exercise?
|
increase in temperature, increase in CO2 which causes an increase in acidity of the blood (lowering pH)
|
|
|
high CO2 causes more _______ blood, which causes __________ respiration rate
|
acidic
higher |
|
|
Most Carbon dioxide is transported as ____________(70%) in combination with blood proteins (23%) and in solution with plasma (7%)
|
bicarbonate ions
|
|
|
During exercise, O2 hemoglobin saturation _________________
|
decreases as O2 is freed up to enter the tissues more easily
|
|
|
In tissue capillaries, carbon dioxide combines with _______ inside RBCs to form _____________ which dissociates to form __________ and _______ ions
|
water
carbonic acid bicarbonate ions hydrogen |
|
|
In lung capillaries, ___________ and ________ ions move into RBCs and _______ ions move out. __________ ions combine with _________ions to form carbonic acid. The carbonic acid is converted to ________ and water. The _________ diffuses out of the RBCs.
|
bicarbonate ions
hydrogen chloride Bicarbonate hydrogen carbon dioxide carbon dioxide |
|
|
what is H2CO3?
|
Carbonic Acid
|
|
|
What is HCO3?
|
Bicarbonate
|
|
|
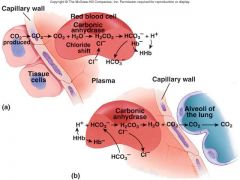
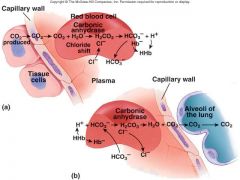
Explain in the tissues capillaries:
CO2 + H2O === H2CO3 === HCO3 + H |
In tissue capillaries, carbon dioxide combines with water inside RBCs to form carbonic acid which dissociates to form bicarbonate ions and hydrogen ions
|
|
|
Explain in the lung capillaries:
CO2 + H2O === H2CO3 === HCO3 + H |
In lung capillaries, bicarbonate ions and hydrogen ions move into RBCs and chloride ions move out. Bicarbonate ions combine with hydrogen ions to form carbonic acid. The carbonic acid is converted to carbon dioxide and water. The carbon dioxide diffuses out of the RBCs
|
|
|
|
|
|
Carbon dioxide is a major regulator of the
|
speed of ventilation
|
|
|
O2 levels in blood affect respiration when a _______ decrease from normal levels exist
|
50% or greater
|
|
|
If Blood pH is alkaline, then there's too little _____ and too much _____
|
CO2
O2 |
|
|
what happens when blood pH is alkaline?
|
causes a decrease in ventilation and respiration, which decreases gas exchange, which causes and increase of CO2 in the blood, causing pH to drop.
|
|
|
If Blood pH is acidic, then there's too little _____ and too much _____
|
O2
CO2 |
|
|
what happens when blood pH is acidic?
|
causes and increase in ventilation and respiration, which causes an increase in gas exchange, which allows more CO2 to be removed, then blood pH raises.
|

