![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Reactant |
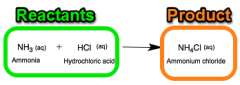
A substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction. |
|
|
Product |
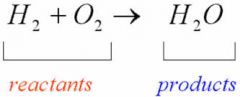
A substance produced during a natural, chemical, or manufacturing process |
|
|
Catalyst |
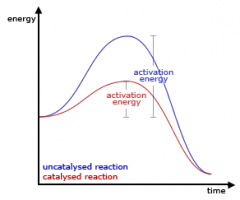
A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change. |
|
|
Inhibitor |
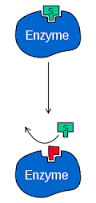
A substance that slows down or prevents a particular chemical reaction or other process, or that reduces the activity of a particular reactant, catalyst, or enzyme. |
|
|
Rate of Reaction |
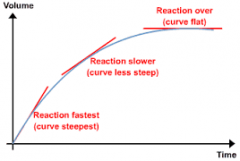
The reaction rate or speed of reaction for a reactant or product in a particular reaction is intuitively defined as how quickly or slowly a reaction takes place |
|
|
Chemical Reaction |

A process that involves rearrangement of the molecular or ionic structure of a substance, as opposed to a change in physical form or a nuclear reaction. |
|
|
Decomposition (Chemical Reaction) |
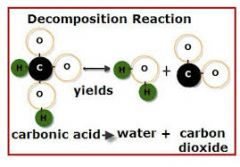
A decomposition reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which a single compound breaks down into two or more elements or new compounds. |
|
|
Precipitation (Chemical Reaction) |
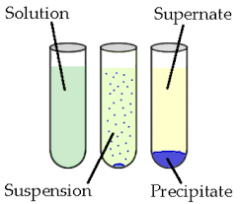
A precipitate is an insoluble solid that emerges from a liquid solution. The emergence of the insoluble solid from solution is called precipitation. |
|
|
Synthesis (Chemical Reaction) |
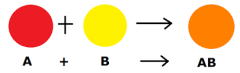
A synthesis reaction or direct combination reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two or more simple substances combine to form a more complex product. |
|
|
Single Displacement (Chemical Reaction) |
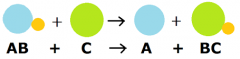
A single replacement reaction, also known as a substitution reaction, is a type of chemical reaction where one element replaces another element in a compound. |
|
|
Double-Displacement (Chemical Reaction) |

A chemical reaction is where two compounds react, and the positive ions and the negative ions of the two reactants switch places, forming two new compounds or products. |
|
|
Exothermic Reaction |
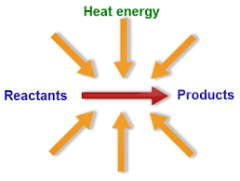
An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that releases energy by light or heat. It is the opposite of an endothermic reaction. |
|
|
Endothermic Reaction |
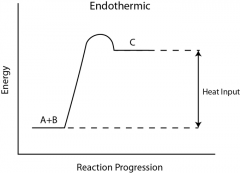
The term endothermic process describes a process or reaction in which the system absorbs energy from its surroundings; usually, but not always, in the form of heat. |
|
|
Chemical Equation |
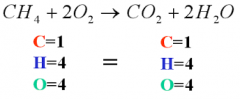
A chemical reaction in the form of symbols and formulae, where in the reactant entities are given on the left-hand side and the product entities on the right-hand side. |
|
|
Conservation Of Mass |
A principle stating that mass cannot be created or destroyed. |

