![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
If an atom is electrically neutral, how many electrons does it contain? |
The electrons equal the number of protons |
|
|
Protons and neutrons are found where? |
The atomic nucleus |
|
|
Element |
Consists of a certain kind of atom that is different from those of other elements and cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. |
|
|
Valence electrons Valence shell |
Outermost electrons Outermost shell |
|
|
How many elements make up 96% of living matter? What are they? |
4 Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen |
|
|
Radioactive isotope |
Nucleus decays (loses subatomic particles) spontaneously giving off particles and energy |
|
|
Subatomic particles |
Neutrons Electrons Protons |
|
|
Lewis dot structure (for 2 hydrogen |
H:H |
|
|
Atomic Nucleus |
Dense core comprised of tightly packed protons and neutrons |
|
|
Mass |
Amount of matter in an object |
|
|
Orbital |
Three dimensional space where an electron is found 90% of the time |
|
|
Chemical Bonds |
Attractions between atoms in incomplete valence shells |
|
|
An electron's state of potential energy |
Energy level (electron shell) |
|
|
Matter exists in _______ available state of potential energy |
Lowest (fills shells inner to outer) |
|
|
Electronegativity |
The attraction of a particular atom for the electrons of a covalent bond |
|
|
Organisms are composed of |
Matter |
|
|
2 H2 + O2 -> 2 H2O Identify the (a) Reactant(s) (b) Reaction(s) (c) Product(s) |
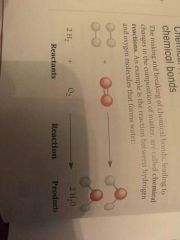
|
|
|
Weight |
How strongly the mass in an object is pulled by gravity |
|
|
Essential Elements |
Essential to an organism's needs to live a healthy life and reproduce (20-25% of all elements) |
|
|
Hydrogen bond |
Attraction between a hydrogen and an electronegative atom (caused when a hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to an electronegative atom, the hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge that allows it to be attracted to a different electronegative atom nearby) |
|
|
Mass number (atomic mass) |
Protons + Neutrons |
|
|
Isotope |
Different atomic forms of the same element (contain same number of protons but different amount of neutrons) |
|
|
What is a double bond? |
Sharing of two pairs of valence electrons |
|
|
In a Polar Covalent Bond, which element will carry a negative charge (d-) and which will carry a positive charge (d+)? |
The element with more powerful electronegativity will have a negative charge (d-) (electrons are negative and will spend more time near the more powerful electronegativity) The weaker element will have a positive charge (d+) |
|
|
Atomic number |
Protons in nuclei |
|
|
Covalent bond |
The sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms |
|
|
Define the bond H-H O=O |
Single Bond Double Bond |
|
|
True or False. All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons in their nuclei. |
True |
|
|
The row of an element on the periodic table shows |
The number of shells of the element |
|
|
What is the most accurate shape representation |
Space filling model |
|
|
Matter |
Anything that takes up space and has mass |
|
|
Ionic bonds are also known as |
Salts |
|
|
Molecular formula (for 2 hydrogen) |
H2 |
|
|
Chemical reactions |
The making and breaking of chemical bonds, leading to changes in the composition of matter |
|
|
Valence is equal to |
Usually equals the number of unpaired electrons required to complete the atom's outermost shell |
|
|
van der Waals interactions |
Ever-changing regions of positive and negative charge that enable all atoms and molecules to stick to one another (individually weak and occur only when atoms and molecules are very close together) |
|
|
Atoms with the same number of electrons in their valence shells exhibit |
Similar chemical behavior |
|
|
Structural formula (for 2 hydrogen) |
H-H |
|
|
Energy |
The capacity to cause change by doing work |
|
|
Reactivity of an atom arises from |
The presence of unpaired electrons in one or more orbitals of its valence shell |
|
|
Cation Anion |
Positively charged ion Negatively charged ion |
|
|
Ions |
Oppositely charged atoms (or molecules) that result when two atoms are so unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that the more electronegative atom strips an electron completely away from its partner |
|
|
How many elements are known |
92 |
|
|
What elements account for the remaining 4% of an organism's mass (non-CHON)? |
Calcium Potassium Phosphorus Sulfer A few other elements |
|
|
Valence |
Bonding capacity (corresponding to the number of covalent bonds the atom can form) |
|
|
Dalton |
Unit of measurement equivalent to the atomic mass unit (AMU) |
|
|
Atom |
The smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element |
|
|
Orbital Shape 1st Shell 2nd Shell 3rd Shell and up |
One spherical s orbital (1s) Four orbitals: one large spherical s orbital (2s) and three dumbbell-shaped p orbitals (2p) s and p orbitals of more complex shapes |
|
|
How is potential energy of an electron measured? |
The more distance from the nucleus, the greater the potential energy. |
|
|
The mass of an electron is? |
1/200th of a neutron or proton |
|
|
Ionic bond |
Opposite attraction of ions resulting in a bond (any opposite ions can form a bond) (can form from a transfer of electrons or simply from opposite attraction) |
|
|
Orbital is a component of |
electron shell |
|
|
Nonpolar covalent bond |
Electrons are shared equally because the two atoms have the same electronegativity (tug-of-war standoff). (seen in a covalent bond between two atoms of the same element) |
|
|
Max number of electrons First Shell Second Shell Third Shell |
Max 2 electrons Max 8 electrons Max 8 electrons |
|
|
How many electrons can occupy a single orbital? |
No more than 2 |
|
|
Potential energy |
Energy that matter possesses because of its location or structure (not yet used) |
|
|
Ionic compounds |
Compounds formed by ionic bonds (does not consist of molecules |
|
|
An atom with a completed valence shell |
Unreactive (inert) atom |
|
|
Protons and neutrons are _____ dalton(s) |
These subatomic particles are each 1 dalton (mass = 1.7 x 10^24 g/particle) |
|
|
Charge of Proton Electron Neutron |
Positively charged subatomic particle Negatively charged subatomic particle Neutral charged subatomic particle |
|
|
Compound |
Substance consisting of two or more different elements (in a fixed ratio) |
|
|
True or Flase. All chemical actions are reversible |
True |
|
|
Trace elements |
Elements required by an organism in only minute quantities |
|
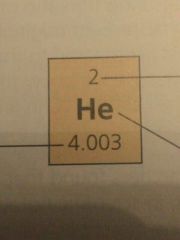
Label the parts |
Atomic number Elemental symbol Atomic Mass |
|
|
Chemical equilibrium |
The point at which the reactions (forward and reverse) offset one another |
|
|
Why is molecular shape crucial? |
It determines how biological molecules recognize and respond to one another with specificity |
|
|
Strongest kinds of chemical bonds |
Covalent bonds Ionic bonds |
|
|
Polar covalent bond |
When an atom is bounded to a more electronegative atom and the electrons of the bond are not shared equally |
|
|
Electron distribution diagram (for 2 hydrogen) |

|
|
|
What is the difference between covelent and ionic bonds? |
Covalent bonds share electrons between atoms Ionic bonds have an electric attraction beteen atoms |
|
|
What is a strong acid that ionizes completely in an aqueous solution and is condisedered a strong base? |
NaOH (Sodium Hydroxide) |
|
|
what can one expect to see if the pH of blood drops? |
A decrease in concentration of H2CO3 and an increase in concentration of HCO3 |
|
|
What 2 functional groups are always in amino acids? |
Carboxyl and amino |
|
|
O2 has an atomic number of 8 and a mass of 16. What is the atomic mass of an O2 atom? |
16 Daltons |
|
|
Each element is unique and has different chemical properties due to? |
Unique number of protons |
|
|
Flourine has an atomic number of 9 and a mass of 19, it requires how many electrons to complete its valence shell? |
1 (atomic number equals 9, 2 electrons on inner shell, 7 of 8 on valence shell) |

