![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Methane
|
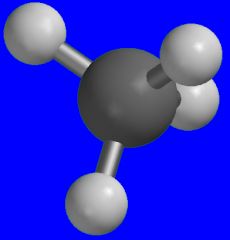
What is the name of this molecule?
|
It's a by-product of flatulence.
|
|
|
Ethane
|
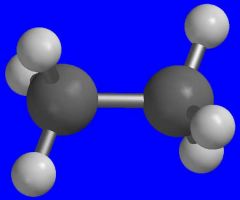
What is the name of this molecule?
|
|
|
|
Butane
|
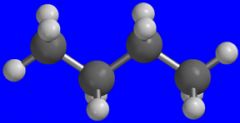
What is the name of this molecule?
|
This composes lighter fluid.
|
|
|
Propane.
|
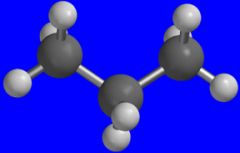
What is the name of this molecule?
|
This is what heats up your barbecue if you don't use charcoal.
|
|
|
What is the molecular formula for pentane?
|
C5 H12
|
Greek prefixes and general molecular formula.
|
|
|
What is the molecular formula for hexane?
|
C6 H14
|
Greek prefixes and general molecular formula.
|
|
|
What is the molecular formula for heptane?
|
C7 H16
|
Greek prefixes and general molecular formula.
|
|
|
What is the molecular formula for octane?
|
C8 H18
|
Greek prefixes and general molecular formula.
|
|
|
What is the molecular formula for nonane?
|
C9 H20
|
Greek prefixes and general molecular formula.
|
|
|
What is the molecular formula for decane?
|
C10 H22
|
Greek prefixes and general molecular formula.
|
|
|
What specific conformation does the prefix "iso-" refer to?
|
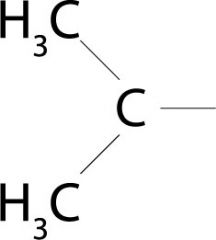
Carbon connected to two branching methyl groups
|
Think of isosceles triangles!
|
|
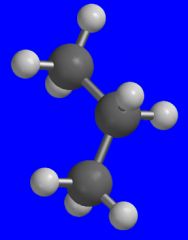
What group does this three dimensional model represent?
|
The isopropyl group.
|
That alcohol that you use to disinfect cuts.
|
|
What is the name of this molecule?
|
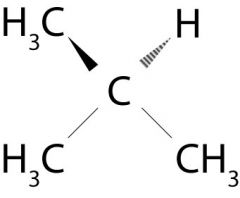
Isobutane
|
|
|
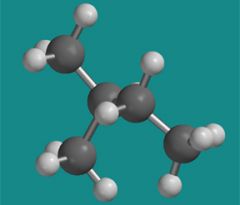
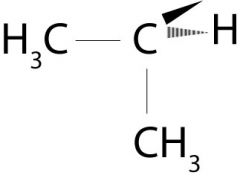
What is this molecule named?
|
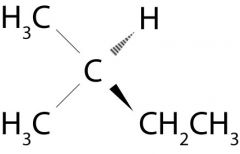
Isopentane
|
|
|
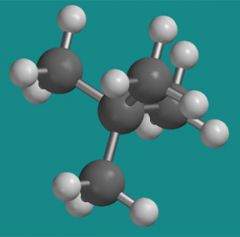
What is the name of this molecule?
|
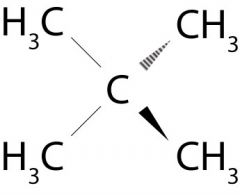
Neopentane
|
|
|
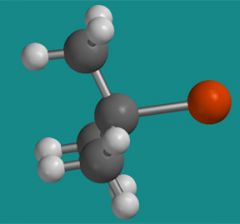
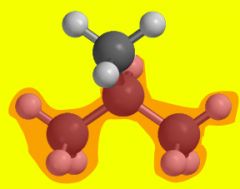
What is the name of the group attached to the bromine in this picture?
|
The tert-butyl group
|
Third cardinal number
|
|
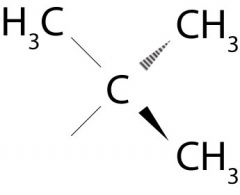
What is the name of the group attached to the benzene ring in this picture?
|
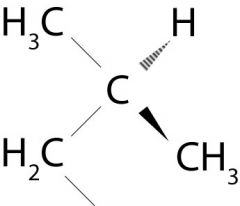
Isobutyl groups
|
Look at how the carbons are connected.
|
|
What group is attached to the cyclohexane in this picture?
|
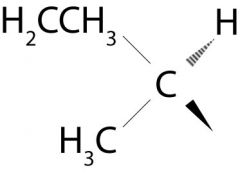
Sec-butyl group
|
Look at the carbon that is attached to the cyclohexane? If it weren't attached to the cychohexane, what kind of carbon is it?
|
|
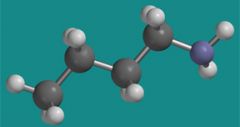
What group is attached to the amide in this picture?
|
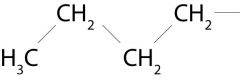
n-butyl group
|
|
|
|
What are the IUPAC rules for naming alkanes?
|
1. Find the longest continuous carbon chain and give it the name per IUPAC rules.
2. List the substituents attached to the longest continuous carbon chain in alphabetical order. 3. Use the di, tri, tetra when the same substituent appears more than once. 4. Number the chain in the direction which gives the lower locant to a substituent at the first point of difference. 5. When two different numbering directions give the same number of locants, number in the direction that gives the lowest locant to the group that appears first in the name. 6. When two chains are of equal length, choose the one with the greater number of substituents as the parent |
|
|
|
What are the IUPAC rules for naming cycloalkanes?
|
1. Count the number of carbons in the ring this is the base name of the ring.
2. Name the alkyl group and append it as a prefix to the cyclohexane. No locant is needed if it is monosubstituted. 3. When two or more different substituents are present, list them in alphabetical order, and number the ring in the direction than gives the lower number at the first point of difference. 4. Name the compound as a cycloalkyl substituted alkane if the substituent has more carbons than the ring. |
|
|
|
What are the IUPAC rules for naming alkyl groups?
|
1. Number the carbons beginning at the point of attachment, proceeding in the direction that follows the longest chain.
2. Assign a base name according to the number of carbons in the correspondinb unbranched/cycloalkane and replace the -ane ending with -yl. 3. List the substituents attached to the base group in alphabetical order using replicating prefixes when necessary. 4. Locate substituents according to the numbering of the main chain described in the rules for naming alkanes. |
|
|
|
What are sigma bonds?
|
Head on bonds, they bond on a line that connects the two nuclei.
|
|
|
|
What are pi bonds?
|
Side to side bonds, they connect above and below the line that connects the two bonding nuclei.
|
|
|
|
What are the associated characteristics of an sp3 hybridized orbital?
|
Neighboring atoms: 4
Sigma Bonds: 3 Pi Bonds: 2 VSEPR Structure: Tetrahedral |
|
|
|
What are the associated characteristics of an sp2 hybridized orbital?
|
Neighboring atoms: 3
Sigma Bonds: 2 Pi Bonds: 1 VSEPR Stucture: Trigonal Planar |
|
|
|
What are the associated characteristics of an sp hybridized orbital?
|
Neighboring atoms: 2
Sigma Bonds: 2 Pi Bonds: 2 VSEPR Structure: Linear |
|

