![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
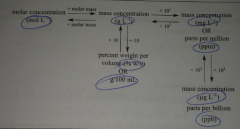
What is the table of values used to find the finding of ppm, ppb, mol/L etc.? |
|
|
|
What is adsorption? |
The process of something attaching to the surface of a solid. |
|
|
What is adsorption chromatography?
|
The more polar the compound, the more quickly they move up the mobile phase. |
|
|
What is the Rf value? |
The distance moved by the compound from the baseline divided by the distance moved by the solvent from the baseline. |
|
|
What is the retention time given as? |
A compound with a shorter retention time was adsorbed into the stationary phase less strongly than a compound with a larger retention time. It also means that the compound with a shorter retention time is less polar. |
|
|
What steps are required for a titration? |
- Preparation of solutions and glassware to be used in the titration. - Performing the titration. |
|
|
How is a standard solution created? |
A standard solution is required for a known concentration. Made by dissolving a known amount of solute (called the primary standard) in sufficient water in a volumetric flask. - The mass is measured using a balance. - Rinse the volumetric flask after washing. - Add sufficient water to the primary standard and add to the volumetric flask via a clean, dry funnel. - Rinse the funnel and beaker through. - Add distilled water until the calibration line is met. - Stopper the flask and invert to ensure constant concentration throughout. |
|
|
How is a titration performed? |
Pipette, burette and conical flask all washed with detergent, then water and then finally rinsed with: - Pipette: Solution which is to be transferred to pipette. - Burette: Solution which is to be transferred to burette. - Conical flask: Water. Tip the conical flask on its side and rest the pipette on the wall vertically. Allow the solution (which met the calibration line) to flow downwards. Let it stand for 10 seconds before removing. Add an indicator to conical flask. Use the burette until the first permanent colour change is found and record the titre value, ensuring the first time, a rough titre is recorded. |
|
|
What two phases do adsorption chromatographies use? |
Stationary phase: The material which components of a mixture pass through. (Paper for example). Mobile phase: The liquid which carries the material across the stationary phase. |
|
|
How does column chromatography work? |
Vertical glass tube which is packed with small, uniform sized stationary particles. Concentrated mixture is placed at the top and washed down through the stationary phase with the mobile phase. The parts spread out, hence becoming collectible. |
|
|
How does thin layer chromatography work? (TLC) |
Thin layer of finely powdered alumina or silica applied evenly across a thin glass as the stationary phase. Capillary action tube is placed near bottom of sheet and the sheet is set in shallow solvent. As the compounds move up, they separate. UV light required for some substances as to illuminate organic materials. |

