![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a Global Firm? |
Operates in more than one country Gains marketing, production, R&D, and financial advantages not available to purely domestic competitors Sees the world as one market Minimizes the importance of national boundaries and develops global brands Raises capital, obtains materials and components, and manufactures and markets its goods wherever it can do the best job |
|
|
What are the Major Decisions in International Marketing? |

|
|
|
What are some questions Global Firms should ask themselves? |
What market position should we try to establish in our own country, in our economic region, and globally? Who will our global competitors be, and what are their strategies and resources? Where should we produce or source our product? What strategic alliances should we form with other firms around the world? |
|
|
Talk about Restrictions in the International Trade System. |
Tariffs are taxes on certain imported products designed to raise revenue or to protect domestic firms. Quotas are limits on the amount of foreign imports a country will accept in certain product categories to conserve on foreign exchange and protect domestic industry and employment. Exchange controls are a limit on the amount of foreign exchange and the exchange rate against other currencies. Nontariff trade barriers are biases against bids, restrictive product standards, or excessive regulations. |
|
|
Talk About World Trade Organization and GATT. |
-World Trade Organization -> Enforces GATT rules -> Mediates disputes -> Imposes Trade Sanctions
General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT): A 61-year-old treaty Designed to promote world trade Reduces tariffs and other international trade barriers |
|
|
Talk about Regional Free Trade Zones in relation to Economic Communities. |
Economic communities are free trade zones. – European Union (EU) – North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) – European Free Trade Association (EFTA) |
|
|
Talk about Economic Environment |
• Economic factors reflect a country’s attractiveness as a market: – Industrial structure – Income distribution |
|
|
Talk about Industrial Structure. |
• In subsistence economies, the vast majority of people engage in simple agriculture. – Offer few market opportunities
• Raw material exporting economies are rich in one or more natural resources but poor in other ways. – Good markets for large equipment, tools and supplies, and trucks
• Inindustrializingeconomies,manufacturing accounts for 10 to 20 percent of the country’s economy.
• Industrial economies are major exporters of manufactured goods, services, and investment funds. – Rich markets for all sorts of goods |
|
|
Talk about Income Distribution. |
• Low-income households • High-income households |
|
|
Talk About Political-Legal Environment. |
• Country’s attitude toward international buying • Government bureaucracy
Countertrade is international trade involving the direct or indirect exchange of goods for other goods instead of cash. Barter involves the direct exchange of goods or services. Compensation or buyback is the sale of a plant, equipment, or technology and payment is in the resulting products. Counterpurchase is when the seller receives payment in cash and agrees to spend some of the money in the other country. |
|
|
Talk About Cultural Environment and its Impact on Marketing Strategies. |
• Business norms • Cultural preferences, traditions, behaviours
North American companies have learned that to succeed abroad they must adapt to local cultural values and traditions rather than trying to force their own.
|
|
|
How Does a Company know if it should go Global? |
Can the company learn to understand the preferences and buyer behaviour of consumers in other countries? Can it offer competitively attractive products? Will it be able to adapt to other countries’ business cultures and deal effectively with foreign nationals? Do the company’s managers have the necessary international experience? Has management considered the impact of regulations and the political environments of other countries? |
|
|
How should a company decide whether or not to go global? |
• Define international marketing objectives and policies. • Determine foreign sales volume. • Decide how many countries to market to. • Determine types of countries to market to based on: – Geography – Political climate Rank potential global markets based on: – Market size – Market growth – Cost of doing business – Competitive advantage – Risk level |
|
|
Discuss Deciding How (strategies) a Company should enter a marketplace. |
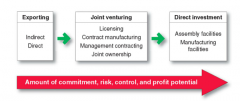
|
|
|
Discuss Exporting. |
- Exporting is when the company produces its goods in the home country and sells them in a foreign market. It is the simplest means involving the least change in the company’s product lines, organization, investments, or mission.
- Indirect exporting involves working through independent international marketing intermediaries. ->Less involvement, less risk
-Direct exporting is when the firm handles its own exports. ->Greater involvement, greater risk, greater potential return -> Can be done BY:: Setting up a domestic export department |
|
|
Discuss Joint Venturing. |
-Joint venturing is when a firm joins with foreign companies to produce or market products or services. –>Licensing -Joint venturing differs from exporting in that the company joins with a host country partner to sell or market abroad.
-Licensing is when a firm enters into an agreement with a licensee in a foreign market. For a fee or royalty, the licensee buys the right to use the company’s process, trademark, patent, trade secret, or other item of value.
|
|
|
What is Contract Managing (Joint Venturing cont'd)? |
-Contract manufacturing is when a firm contracts with manufacturers in the foreign market to produce its product or provide its service. Benefits include faster startup, less risk, and the opportunity to form a partnership or to buy out the local manufacturer.
|
|
|
What is Management Contracting (Joint Venturing cont'd)? |
- When the domestic firm supplies management skill to a foreign company that supplies capital. The domestic firm is exporting management services rather than products. |
|
|
What is Joint Ownership (Joint Venturing cont'd)? |
- When one company joins forces with foreign investors to create a local business in which they share joint ownership and control. Joint ownership is sometimes required for economic or political reasons. |
|
|
What is Direct Investment? |
-Direct investment is the development of foreign-based assembly or manufacturing facilities and offers a number of advantages including: – Labour – Logistics – Control – Lower costs |
|
|
Talk about Deciding on the Global Marketing Program. |
Standardized global marketing is an international marketing strategy for using basically the same marketing strategy and mix in all of the company’s international markets. Adapted global marketing involves adjusting the marketing strategy and mix elements to each international target market, bearing more costs but hoping for a larger market share and return. |
|
|
Talk about Product in the Global Market Place. |
Straight product extension means marketing a product in a foreign market without any change. Product adaptation involves adapting the product to meet local conditions or wants in foreign markets. Product invention consists of creating something new for a specific foreign market. – Maintain or reintroduce earlier product forms. – Create new products. |
|
|
Product in the Global Marketing Place cont'd |
• Communication adaptation is a global communication strategy of fully adapting advertising messages to local markets. • Dual adaptation involves adapting both the product and the advertising messages to the targeted foreign market. |
|
|
Discuss the Relationship between Product and Promotion in the Global Market. |

|
|
|
Discuss Price in the Global Market. |
• Technological forces impact global pricing as the Internet is making global price differences more obvious, forcing a more standardized international pricing. * |
|
|
Discuss Distribution Channels in the Global Market. |
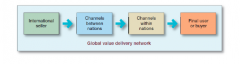
Whole-channel view involves designing international channels that take into account the entire global supply chain and marketing channel, forging an effective global value delivery network.
Channels between nations move company products from points of production to the borders of countries within which they are sold. Channels within nations move the products from their market entry points to the final consumers.
|
|
|
What comprises Management of International Marketing? |
– Organizing an exporting department with a sales manager and a few assistants – Creating an international division organized by geography, products, or operating units – Becoming a complete global organization |

