![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the specific name used for bacterial enzymes that are used to cut DNA?
|
Restriction endonucleases (RE)
|
|
|
Restriction enzymes recognize ______ DNA sequences. What exactly are these?
|
palindromic
A sequence of DNA that is read the same way backwards and forwards. For example: GAATTC CTTAAG |
|
|
What are the different types of "cuts" a restriction enzyme can make?
|
1. Straight cuts
2. Staggered cuts |
|
|
What is a "sticky end"?
|
When restriction enzymes make a staggered cut, each fragement carries single stranded "over hang" at the location of the cut.
|
|
|
How do sticky ends combine?
|
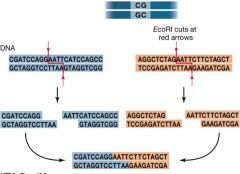
The base pairs of one sticky end combine with the complementary base pairs of another sticky end
|
|
|
It is not possible for fragmented DNA from DIFFERENT organisms to be joined. T or F?
|
False
|
|
|
What catalyzes the formation of covalent bonds between adjacent nucleotides at the ends of the fragements?
|
DNA ligase
This is basically the "glue" that joins them together to form a single larger molecule |
|
|
A DNA molecule that is derived from at least two genetic sources in a labratory is called what?
|
Recombinant DNA
|
|
|
One of the main purposes of recombinant DNA is to make ______ of genes?
|
clones
|
|
|
The cloning of recombinant DNA by inserting it into a host cell OTHER THAN an animal cell is called what?
|
Transformation
|
|
|
The cloning of recombinant DNA by inserting it into an ANIMAL host cell is called what?
|
Transfection
|
|
|
When cloning cells, almost every "host" cell that is injected becomes transformed. T or F?
|
False
Usually only a few are transformed |
|
|
A host cell or organism that contains recombinant DNA is referred to as what?
|
Transgenic
|
|
|
How does a biologist determine which hosts cells contain the newly planted sequence?
|
Through selectable markers.
For example, in our lab, the gfp glowing protien was a selectable marker. It allowed us to easily IDENTIFY that the bacteria we were looking at contained that specific gene |
|
|
How exactly do biologists insert recombinant DNA into a host cell? Give 4 examples.
|
1. Chemically treat the host: making the membrane more permeable so that DNA can diffuse into it
2. Electroporation: short electric shock which creates temporary pores in the membrane for DNA to enter 3. Viruses can carry it into cells 4. Transformed plants 5. Transgenic animals: injecting the DNA into the nuclei of fertilized eggs |
|
|
What happens after DNA is succesfully inserted into a host cell?
|
Host cell divides and new DNA replicates. Clones!
|
|
|
The challenge of inserting DNA is getting it to replicate. For this to happen, the inserted DNA must become part of a segment of DNA with an ORI. What is this called?
|
A replicon
|
|
|
An newly inserted DNA can become part of a replicon in one of two ways. What are they?
|
1. It may be inserted into a host chromosome near its ORI
2. It can enter the host cell as part of a carrier DNA sequence called a vector |
|
|
What makes are really good vector and why?
|
Plasmid
1. Small and easy to manipulate 2. Have one or more restriction enzyme recognition sequences 3. Have a bacterial ORI |
|
|
What is the drawback of plasmids.
|
It can only hold up to 10,000 base pairs. This is fairly small, so therefore cannot hold the large eukaryotic genes with very large base sequences.
|
|
|
A virus can be a vector. T or F?
|
True: these viruses are called bacteriophage
|
|
|
What is a reporter gene?
|
A selectable marker that has an EASILY observable gene expression. For example: the gfp glowing gene from our lab!
|
|
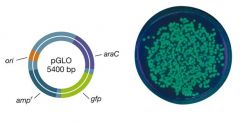
Explain what is happening in this picture.
|
1. This is a plasmid and it is acting as a vector
2. The GFP gene has been spliced into it 3. This plasmid is then inserted into host bacteria 4. The bacteria replicates (clones) 5. Was it succesful in replicating?? 6. Yes! because we can see that each one of the clones who has the spliced-in gene glows under UV light |
|
|
A collection of DNA fragments that together comprise the genome of an organism is called what?
|
A genomic library
|
|
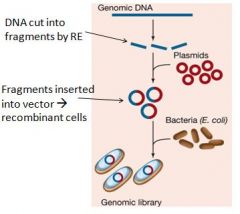
This illustration is describing how a genomic library is constructed. What is happening in this diagram?
|
1. Small fragments of the genome DNA is cut up
2. These fragments are inserted into vectors (plasmids) 3. Plasmids are inserted into a host cell 4. This cell produces a COLONY of recombinant cells |
|
|
A smaller DNA library (as opposed to a genomic library) include only the genes that transcribe a particular tissue. What type of DNA aids in this process?
|
cDNA (complementary DNA)
|
|
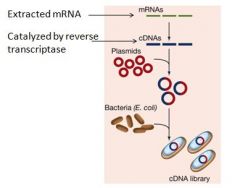
This picture describes how a library is made using cDNA. What is happening in this diagram?
|
1. A strand of mRNA is isolated from a cell
2. Through complementary base pairing, cDNA copies are made (reverse transcriptase) 3. cDNA is spliced into a vector (plasmid) 4. Vector injected into host cell 5. Host cell replicates and cDNA library is created |
|
|
The use of living cells or organisms to produce materials useful to people is called what?
|
Biotechnology
|
|
|
Give several examples of biotechnology.
|
1. Yeasts to brew beer and wine
2. Bacteria to make cheese and yogurt 3. Microbes to produce antibiotics, alcohol, etc |
|
|
The production of pharmaceuticals in farm animal or plants is called what?
|
Pharming
|
|
|
Give an example of pharming (hint: cows).
|

1. A gene that encodes a USEFUL protien can be inserted next to the promoter of the gene in cows that encodes for the protein lactoglobulin (found in milk)
2. Any cow that carries this recombinant DNA will produce large amounts of the USEFUL protein into their milk. 3. This USEFUL protien can then be separated from the milk and used for medical purposes. |
|
|
The use of organisms to remove contaminants from the environment is called what?
|
Bioremediation
|
|
|
Give an example of bioremediation.
|
Composting: Involves the use of bacteria to break down large molecules and proteins in waste products such as wood chips, paper, straw and kitchen scraps.
|
|
|
Transgenic organisms can be used to clean up environmental contaminants such as oil spills. T or F?
|
True
|

