![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Conscious nerves involve which part of the brain? Autonomic nerves involve which part of the bran?
|
cerebrum; brainstem and spinal cord
|
|
|
What is another name for autonomic nervous system?
|
Visceral nervous system
|
|
|
What is another name for the visceral nervous system?
|
autonomic nervous system
|
|
|
What is the function of the ANS?
|
To maintain homeostasis
|
|
|
What two kinds of neurotransmitter are released from ganglionic neurons?
|
ACh or norepinepherine NE
|
|
|
Are ganglionic neurons myelinated?
|
No
|
|
|
Where are the cell bodies of preganglionic neurons?
|
brain or spinal cord
|
|
|
Where are the cell bodies of ganglionic neurons?
|
autonomic ganglion
|
|
|
How many neurons are in the ANS chain?
|
Two
|
|
|
Why does neuronal convergence occur?
|
because axons from numerous preganglionic neurons synapse with and influence a single ganglionic cell.
|
|
|
Why does neuronal divergence occur?
|
because axons from one preganglionic cell synapse with and influence numerous ganglionic cells
|
|
|
The motor component of the ANS is divided into two subdivisions:
|
sympathetic nervous system
parasympathetic nervous system |
|
|
What is the function of the parasympathetic nervous system?
|
functions to maintain homeostasis when we are at rest. Conserned with conserving energy and replenishing nutrient stores
|
|
|
What is the function of the sympathetic nervous system?
|
preparing the body for emergencies
|
|
|
Which division of the nervous system responds to stressful or frightening situations?
|
sympathetic
|
|
|
Do both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems use a preganglionic neuron and a ganglionic neuron?
|
yes
|
|
|
Where are ganglion housed?
|
autonomic ganglia
|
|
|
Where are the neuron cell bodies of the parasympathetic nervous system housed in the CNS?
|
either the brainstem or the lateral gray matter of the S2-S4 spinal cord
|
|
|
What is the craniosacral division?
|
parasympathetic division
|
|
|
Where do the cell bodies of the sympathetic nervous system reside?
|
lateral horns of the T1-L2 spinal cord segments
|
|
|
What is the thoracolumbar division?
|
sympathetic division
|
|
|
Which cranial nerves are associated with the parasympathetic division?
|
CNIII, CNXII, CNIX, CNX
|
|
|
Where is the autonomic ganglion of the parasympathetic nervous system?
|
on or near the effector organ
|
|
|
Where is the autonomic ganglion of the sympathetic nervous system?
|
Near the spinal cord
|
|
|
Which part of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems are myelinated?
|
preganglionic
|
|
|
are ganglionic neurons myelinated?
|
No
|
|
|
____ is especially important in response to stress, when it is necessary to coordinate rapid changes in activity with numerous structures at once
|
Mass activation
|
|
|
Where are terminal ganglia located
|
close to the effector
|
|
|
Where are intramural ganglia located
|
within the wall of the target organ
|
|
|
What are the two types of ganglia associated with the parasympathetic division?
|
terminal or intramural
|
|
|
What two muscles do the postganglionic axons of CNIII innervate? What do these muscles do?
|
ciliary m.
control of focusing the lense to see close-up objects. pupillary sphincter m. allow more or less light into the pupil. |
|
|
What is CNIII?
|
oculomotor nerve
|
|
|
What division of the ANS controls CNIII?
|
Parasympathetic
|
|
|
Where do the preganglionic cell bodies start for CNIII? (parasympathetic)
|
midbrain nuclei
|
|
|
Where do the preganglionic cell bodies start for CNVII? (parasympathetic)
|
pons
|
|
|
What are the two branches of the parasympathetic preganglionic CNVII? What do they control?
|
pterygopalatine ganglion
(greater petrosal nerve) increase secretion of the lacrimal gland, small glands of the nasal cavity, oral cavity, and palate to increase secretion by these glands submandibular ganglion (chorda tympani) supply the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands in the floor of the mouth, causing an increase in salivary gland secretions. |
|
|
Does CNVII control muscles or glands? (parasympathetic)
|
glands
|
|
|
Does CNIII control muscles or glands? (parasympathetic)
|
muscles (2)
|
|
|
What is the name of the branch of CNVII that innervates submandibular and sublingual glands? (parasympathetic)
|
chorda tympani
|
|
|
What is the name of the barnch of CNVII that innervates the lacrimal gland?
|
greater petrosal nerve
|
|
|
What is CNVII?
|
facial nerve
|
|
|
What is CNIX?
|
glossopharyngeal nerve
|
|
|
Where is the preganglionic cell body of pterygopalatine ganglion located?
|
pons
|
|
|
where is the preganglionic cell body of submandibular ganglion located?
|
pons
|
|
|
Where is the preganglionic cell body of the greater petrosal nerve located?
|
pons
|
|
|
Where is the preganglionic cell body of the chorda tympani located?
|
pons
|
|
|
What is CNIX?
|
glossopharyngeal nerve
|
|
|
Which CN is glossopharyngeal?
|
CNIX
|
|
|
Which CN innervates the parotid salivary gland?
|
CNIX
|
|
|
Where does the preganglionic cell body for the parotid salivary gland start? (parasympathetic)
|
brain stem
|
|
|
What is the ganglionic neuron called that innervates the parotid salivary gland? (parasympathetic)
|
otic ganglion
|
|
|
what does the otic ganglion innervate?
(parasympathetic) |
parotid salivary gland
|
|
|
what is the ganglion for the parotid salivary gland? (parasympathetic)
|
otic ganglion
|
|
|
Which CN is is the origination for the otic ganglion? (parasympathetic)
|
CNIX glossopharyngeal n.
|
|
|
Where is the lacrimal gland?
|
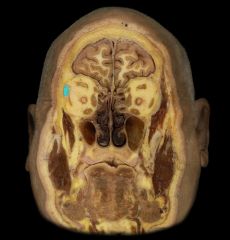
|
|
|
What gland is this?
|
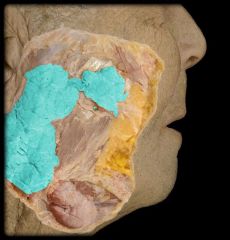
Parotid salivary gland
|
|
|
What is CNX?
|
vagus nerve
|
|
|
Which CN is the vagus nerve?
|
CNX
|
|
|
What does the CNX supply parasympathetic innervation to?
|
thoracic organs, most of the abdominal organs, and gonads
|
|
|
Which CN supplies parasympathetic innervation to the thoracic organs, most of the abdominal organs and the gonads?
|
CNX vagus nerve
|
|
|
Which cranial nerves have a parasympathetic component? What organs are innervated by each?
|
CNIII oculomotor n. innervates the pupillary constrictor m., ciliary m. of the eye
CNVII facial n. innervates the lacrimal gland, glands of the nasal cavity, oral cavity, and palate to increase secretion CNIX glossopharyngeal n. innervates the parotid salivary glands CNX vagus n. innervates thoracic, most abdominal, and gonads. |
|
|
What organs are innervated by the pelvic spanchnic nerves?
|
digestive tract, bladder wall, erection of female clitoris and male penis
|

