![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Most foods are used by the body as metabolic fuels. They are oxidized and transformed into... |
ATP, the chemical energy form needed by body cells to drive their many activities.
|
|
|
The energy value of foods is measured in units called...
|
calories
|
|
|
A nutrient is a...
|
substance in food that is used by the body to promote normal growth, maintenance, and repair.
|
|
|
The nutrients divide neatly into six categories. The major nutrients are...
|
carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins.
Water is also considered to be a major nutrient. |
|
|
Minor nutrients are...
|
vitamins and minerals and are required in minute amounts.
|
|
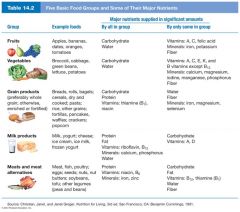
A diet consisting of foods selected from each of the five food groups:
|
grains, fruits, vegetables, meats and meat alternatives, and milk products normally guarantees adequate amounts of all the needed nutrients.
|
|
|
Except for milk, sugar, and small amounts of glycogen in meats, all ingested _____________________ are derived from plants. Sugars come mainly from fruits, sugar cane, and milk.
|
carbohydrates (sugars and starches)
|
|
|
Most dietary __________ are _________________ (neutral fats).
|
lipids
triglycerides |
|
|
Saturated fats are found in...
|
animal products such as meat and dairy foods and in a few plant products, such as coconut.
|
|
|
Unsaturated fats are present in...
|
seeds, nuts, and most vegetable oils. Major sources of cholesterol are egg yolk, meats, and milk products.
|
|
|
Animal products contain the highest-quality...
|
proteins.
|
|
|
Eggs, milk, fish, and most meat proteins are...
|
complete proteins that meet all of the body's amino acid requirements for tissue maintenance and growth.
Legumes (beans and peas), nuts, and cereals are also protein-rich, but their proteins are nutritionally incomplete because they are low in one or more of the essential amino acids. |
|
|
The essential amino acids are...
|
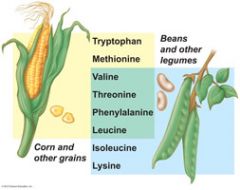
the eight amino acids that the body cannot make.
These amino acids must be obtained through diet. When ingested together, cereal grains and legumes provide all needed amino acids. |
|
|
Vitamins
|
are organic nutrients of various forms that the body requires in small amounts.
Although vitamins are found in all major food groups, no one food contains all the required vitamins. A balanced diet is the best way to ensure a full vitamin complement. |
|
|
The body also requires adequate supplies of seven minerals including...
|
calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, sodium, chloride, magnesium, and trace amounts of about a dozen others.
The most mineral rich foods are vegetables, legumes, milk, and some meats. |
|
|
Metabolism
|
is a broad term referring to all chemical reactions that are necessary to maintain life.
|
|
|
catabolism
|
in which substances are broken down to simpler substances
|
|
|
anabolism
|
in which larger molecules or structures are built from smaller ones.
|
|
|
Glucose
|
also known as blood sugar, is the major breakdown product of carbohydrate digestion.
|
|
|
___________ is the major fuel for making ATP, and homeostasis of _______________ is critically important.
|
Glucose, blood glucose levels .
|
|
|
If the blood glucose levels are excessively high...
|
hyperglycemia
some of the excess is stored in body cells (particularly the liver and muscle cells) as glycogen. If blood glucose levels are still too high, excesses are converted to fat. |
|
|
When blood glucose levels are too low
|
hypoglycemia
the liver breaks down stored glycogen and releases glucose to the blood for cellular use. |
|
|
Fats are used to make...
|
cell membranes and myelin sheaths, and insulate the body with a fatty cushion.
They are also used as the body's main energy fuel for making ATP when carbohydrates in the diet are inadequate. |
|
|
The ________ controls most lipid or fat metabolism that goes on in the body.
|
liver
|
|
|
Excess fats are stored in fat depots such as the...
|
hips, abdomen, breasts, and subcutaneous tissues.
|
|
|
Proteins make up the bulk of ______________ and are carefully conserved by body cells.
|
cellular structures
|
|
|
Ingested proteins are broken down to ________________.
|
amino acids
|
|
|
Cells cannot build their proteins unless all the needed _______________ are present.
|
amino acids (about 20)
|
|
|
The ____________ is the body's major metabolic organ.
|
liver
Nutrients take a detour through the liver to ensure that the liver's needs are met first. |
|
|
As blood circulates slowly through the liver, liver cells remove ______________________ from the blood.
|
amino acids, fatty acids, and glucose
|
|
|
The liver's ______________ remove and destroy bacteria that have managed to get through the walls of the digestive tract and into the blood.
|
phagocytic cells
|
|
|
After a carbohydrate-rich meal, thousands of glucose molecules are removed from the blood and combined to form the large polysaccharide molecules called__________.
|
glycogen, which are then stored in the liver.
|
|
|
Nutrients that are not needed by the liver cells, as well as the products of liver metabolism, are released into the blood and drain from the liver in the...
|
hepatic vein to enter the systemic circulation, where they become available to other body cells.
|
|
|
The liver cells then release glucose little by little into the blood to...
|
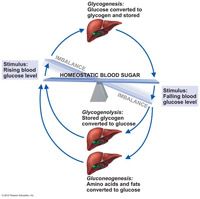
maintain homeostasis of the blood glucose levels.
|
|
|
Cholesterol
|
serves as the structural basis of steroid hormones and vitamin D, and is a major building block of plasma membranes.
|
|
|
Only about _____ of blood cholesterol comes from the diet, the other ____ is made by the liver.
|
15%
85% |
|
|
Fatty acids, fats, and cholesterol are insoluble in water, so they cannot circulate freely in the bloodstream. They are transported bound to the small lipid-protein complexes called...
|
lipoproteins
|
|
|
Low-density lipoproteins, or LDLs
|
transport and move cholesterol and other lipids to body cells, where they are used in various ways.
If large amounts of LDLs are circulating, the chance that fatty substances will be deposited in arterial walls is high. |
|
|
The lipoproteins that transport cholesterol from the tissue cells (or arteries) to the liver for disposal in bile are...
|
high-density lipoproteins, or HDLs.
|
|
|
Energy intake
|
is the energy liberated during food oxidation.
|
|
|
Energy output
|
includes the energy immediately lost as heat or used to do work, plus energy that is stored in the form of fat of glycogen.
When energy intake and energy output are balanced, body weight remains stable. When they are not, weight is lost or gained. |
|
|
When nutrients are broken down to produce ATP, they yield varying amounts of energy. The energy value of foods is measured in a unit called the ___________.
|
kilocalorie
|
|
|
In general, carbohydrates and proteins yield ______, and fats yield ______ when they are broken down for energy production.
|
4 kcal/gram
9 kcal/gram The amount of energy used by the body is also measured in kilocalories. |
|
|
basal metabolic rate (BMR)
|
is the amount of heat produced by the body per unit of time when it is at rest.
It reflects the energy supply a person's body needs to perform essential life activities such as breathing, maintaining the heartbeat, and kidney function. |
|
|
When active, the body must...
|
oxidize more glucose to provide energy for the additional activities
|
|
|
Total metabolic rate (TMR)
|
refers to the total amount of kilocalories the body must consume to fuel all ongoing activities.
Muscular work is the major body activity that increases the TMR. When the total number of kilocalories consumed is equal to the TMR, homeostasis is maintained, and weight remains constant. |
|
|
Most energy that is released as foods are...
|
oxidized escapes as heat.
Less than 40% of available food energy is actually captured to form ATP. |
|
|
Body temperature reflects the balance between _______________and____________.
|
heat production
heat loss |
|
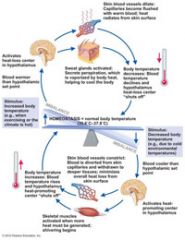
They body's thermostat is...
|
in the hypothalamus of the brain.
Through autonomic nervous system pathways, the hypothalamus continuously regulates body temperature. |
|
|
If the temperature of the circulating blood falls, body heat must be conserved and more heat generated to restore normal body temperature. Short-term means of accomplishing this are...
|
vasoconstriction of blood vessels of the skin and shivering.
|
|
|
Most heat loss occurs through the skin via...
|
radiation or evaporation.
|

