![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Evolution |
The process of biological change by which descendants come to differ from their ancestors. |
|
|
Species |
Group of organisms so similar to one another that they can breed. |
|
|
Fossil |
Trace of an organism from the past. |
|
|
Variation |
Differences in physical traits of an individual from the group to which it belongs. |
|
|
Adapatation |
An inherited trait that is selected over time because it allows organisms to better survive in their environment. |
|
|
Artificial Selection |
Process by which humans modify a species by breeding for its certain traits. |
|
|
Natural Selection |
Mechanism by which individuals that have inherited good adaptation make offspring a lot and quickly. |
|
|
Adaptive Radiation |
Process by which which one species evolves and gives rise to many descendant species that occupy different ecological niches. |
|
|
Population |
Number of all of the same organisms in the same location. |
|
|
Fittness |
The measure of an organism's ability to survive and produce offspring. |
|
|
Homologous Structures |
Body parts that do the same thing, but have different ways of working on different organisms. Example: Bee and Bat wings
|
|
|
Vestigal Structures: |
Remnants of an organ or structure that functioned in an earlier species. Example: Ostrich wings, human tail bone, human appendix |
|
|
Analogous Structure |
Body part that is similar in function as a body part of another organism. Example: Chimps and humans eyeballs. |
|
|
Extinction |
When an organism no longer exists.
|
|
|
Different Ways of Evidence For Evolution |
Anatomy Molecular Biology Palentology
|
|
|
Gene Pool |
Collection of alleles found in all of the individuals of a population. |
|
|
Allele Frequency |
Proportion of one allele, compare with all the alleles for that trait, in the gene pool. |
|
|
Normal Distribution |
Distribution in a population in which allele frequency is highest near mean value. |
|
|
Directional Selection |
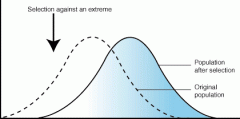
Pathway of natural selection in which 2 opposite, but equally uncommon, phenotypes are selected over more common phenotypes.
|
|
|
Disruptive Selection |
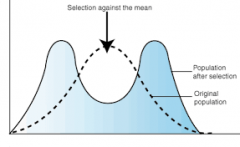
Pathway of natural selection, in which 2 opposite, but equally common, phenotypes are selected over most common phenotypes. |
|
|
Stabilizing Selection |
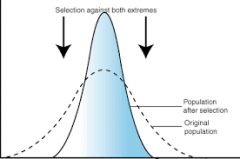
Pathway of natural selection where intermediate phenotypes are selected over phenotypes at both extremes. |
|
|
Handy Weinberg Equilibrium |
Where a population allele frequencies do not change in generations. |
|
|
Reproductive Isolation: |
Members of isolated populations are either no longer to mate or make good offspring. |
|
|
Speciation |
Evolution of 2 or more species from one ancestral species. |
|
|
Behavioral Isolation |
Occurs when members of different populations no longer mate successfully without one another. |
|
|
Geographic Isolation |
Involves physical barriers that divide population into 2 or more groups. |
|
|
Temporal Isolation |
Exists when timing prevents reproduction between population. |
|
|
5 Ways To Maintain Genetic Equilibrium |
1. Large Population 2. Random Mating 3. No Mutation 4. No Migration 5. No Natural Selection
|
|
|
Bottleneck Effect: |
Genetic drift that occurs after an event greatly reduces the size of the population. |

