![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define activity (units) |
Number of nucle decaying per second (1 Becquerel (bq) = 1 decay per second) |
|
|
Define Half life |
Time required for the number of nuclei in a sample to fall half of the original |
|
|
Why is half life a prediction |
Because nuclear decay is random |
|
|
Decay constant |
The fixes probability a nucleus has of decaying |
|
|
Why using negatives in decay equations |
To indicate their is now less orginal nuclei |
|
|
What type of change is equation rate of activity proportional to activity |
Exponential |
|
|
Problem with the iterative model of decay |
It assumes activity is constant inbetween time intervals making the lines straight |
|
|
An electrical component that shows exponential decay |
Capacitor |
|
|
What is a capacitor made of |
2 plates (sheets of thin metal foil) with an insulator in the middle |
|
|
Symbol for a capacitor |
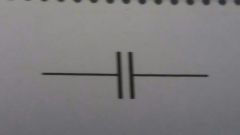
|
|
|
How to charge a capacitor |
Run a potential difference through it. Negative charge will go into one plate and out of the other |
|
|
Use of a capacitor |
Store of energy for use in a circuit |

