![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Identify whether the following trait is typically found with a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid: Shiny
|
Metal or Metalloid
|
|
|
Identify whether the following trait is typically found with a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid: Generally silvery in color (except gold and copper)
|
Metal
|
|
|
Identify whether the following trait is typically found with a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid: Good conductors of heat and electricity
|
Metal
|
|
|
Identify whether the following trait is typically found with a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid: Malleable
|
Metal
|
|
|
Identify whether the following trait is typically found with a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid: Ductile
|
Metal
|
|
|
Identify whether the following trait is typically found with a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid: To the left of the stairs
|
Metal
|
|
|
Identify whether the following trait is typically found with a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid: Dull
|
Nonmetal
|
|
|
Identify whether the following trait is typically found with a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid: Many colors
|
Nonmetal or Metalloid
|
|
|
Identify whether the following trait is typically found with a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid: Insulators
|
Nonmetal
|
|
|
Identify whether the following trait is typically found with a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid: Brittle
|
Nonmetal or Metalloid
|
|
|
Identify whether the following trait is typically found with a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid: To the right of the stairs
|
Nonmetal
|
|
|
Identify whether the following trait is typically found with a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid: Bridge between metals and nonmetals
|
Metalloids
|
|
|
Identify whether the following trait is typically found with a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid: Semiconductors
|
Metalloids
|
|
|
Identify whether the following trait is typically found with a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid: On the stairs
|
Metalloids
|
|
|
Define malleable.
|

Able to be formed by pressing
|
|
|
Define ductile.
|

Able to be pulled into a wire
|
|
|
Define semiconductor.
|

Depending on the environment, they can be conductors or insulators
|
|
|
Each column on the periodic table makes up a _____ _____.
|
Chemical Family
|
|
|
What two things do elements in the same chemical family have in common?
|
1) They have very similar chemical properties.
2) They have very similar behaviors. |
|
|
What is Group 1 also known as?
|
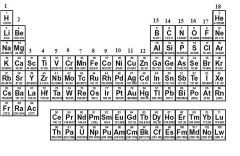
Alkali Metals or Non-radioactive Metals
|
|
|
What is Group 2 also known as?
|
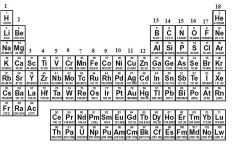
Alkaline Earth Metals
|
|
|
Alkaline Earth Metals create _____ when combined with water.
|
bases
|
|
|
Where are alkaline earth metals typically found?
|

in soil
|
|
|
Alkaline Earth Metals are associated with what common household mixture?
|

Hard water
|
|
|
What family is in group 17?
|
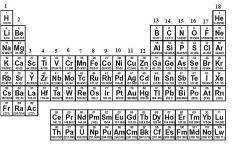
Halogens
|
|
|
What family is in group 18?
|
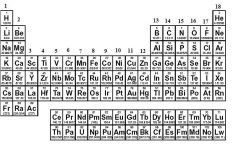
Noble Gases
|
|
|
What family is in groups 3 to 12?
|
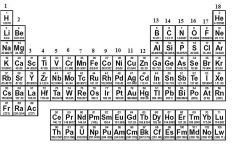
Transition Metals
|
|
|
What family is in groups 1, 2, and 13 to 18?
|
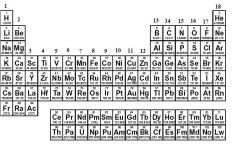
Main Group Elements
|
|
|
For the most part, the elements (in their pure state) exist as individual _____.
|
atoms
|
|
|
Define atom.
|
The smallest particle that retains all properties associated with the element.
|
|
|
There is a group of 7 elements that always exist in nature in pairs. What are these pairings called?
|
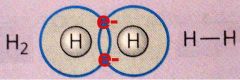
Diatomic Molecules
|
|
|
What are the diatomic molecules?
|

see the picture
|
|
|
Define molecule.
|
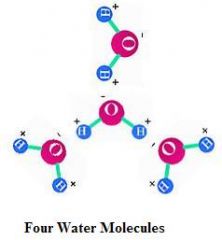
2 or more atoms physically joined by a covalent bond to produce a single entity.
|
|
|
What two characteristics are attributed to physical changes?
|
1) Changes do not produce a new substance.
2) The same substance is simply in a different state/shape/arrangement. |
|
|
What characteristic is always true of a chemical change?
|
They always produce a new substance.
|
|
|
Define melting point.
|
The point where a solid turns into a liquid.
|
|
|
Define freezing point.
|

The point where a liquid turns into a solid.
|
|
|
Define boiling point.
|

The point where a liquid turns into a gas.
|
|
|
Define condensation point.
|

The point where a gas turns into a liquid.
|
|
|
Define sublimation point
|
The point where a solid turns into a gas.
|
|
|
Identify whether the following is a physical or a chemical change: Sugar crystals form on the cup of a syrup bottle.
|
physical
|
|
|
Identify whether the following is a physical or a chemical change: Spilled acid produces a hole in a pair of pants.
|
chemical
|
|
|
Identify whether the following is a physical or a chemical change: Sugar is combined with water to produce "simple sugar".
|
physical
|
|
|
Identify whether the following is a physical or a chemical change: A steak is grilled.
|
chemical
|
|
|
Identify whether the following is a physical or a chemical change: A rubber band is stretched.
|
physical
|
|
|
Identify whether the following is a physical or a chemical change: Orange juice is filtered.
|
physical
|
|
|
Identify whether the following is a physical or a chemical change: Water is distilled.
|
physical
|
|
|
What type of physical separation takes place with physical sorting?
|

Solids are separated from solids.
|
|
|
What type of physical separation takes place with filtration?
|

Solids are separated from liquids.
|
|
|
What 2 types of physical separation takes place with chromatography?
|
1) Gas is separated from gas
or 2) Solid is separated from solid (only if in solution) |
|
|
Define distillation.
|
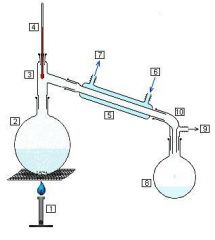
Heating a mixture until a component boils (vapor is then condensed to get purified liquid)
|

