![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
125 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Optical density |
Overall blackening of film |
|
|
|
Brightness of displayed image |
Equivalent term for optical density in digital imaging |
|
|
|
Contrast/contrast resolution |
Primarily controlled by bit depth in digital radiography
Controlled by kVp in screen film |
|
|
|
Spatial resolution |
Ability to visualize Small structures |
|
|
|
Spatial resolution controlled by |
IP phosphor DEL size Geometry Distance Focal spot size Motion Film Intensifying screen |
|
|
|
Distortion |
Misrepresentation of the shape or size of a structure
Ex if a bone is projected longer or shorter than it actually is on the radiographicimage it is caused by distortion |
|
|
|
Magnification |
Size distortion
Controlled by;
•OID (object to image receptor distance)
•SID (Source to image receptor distance) |
|
|
|
Radiographer |
Radiologic. Teknowledge he just who administers ionizing radiation to perform a radiographic procedures |
|
|
|
Radiologist extender |
Known as as a radiologist assistant (RA) or a radiology practitioner assistant (RPA) |
|
|
|
Radiologist |
Physician who is board-certified to read, or interpret x-ray examinations |
|
|
|
Sterilization |
Accomplishes total destruction of micro organisms |
|
|
|
Infection control |
Blood and body fluid's recommendations are issued by the centers for disease control (CDC)
|
|
|
|
Infection control |
The tabletop or upright Bucky must be cleaned after every patient |
|
|
|
Motion |
Three types; Involuntary voluntary equipment |
|
|
|
Involuntary motion |
Caused by; • heartbeat •chills •peristalsis •tremor •spasm •pain |
|
|
|
Voluntary motion |
Normally caused by;
•Nervousness •discomfort •excitability •mental illness •fear •Age •breathing |
|
|
|
How to avoid Voluntary motion |
You can avoid voluntary motion by,
•Given clear instructions •providing patient comfort •adjusting support devices •applying immobilization •decreasing exposure time |
|
|
|
Image always requires |
•Date •patients name or ID number •right or left side marker •institution identity |
|
|
|
Three general IR positions |
Lengthwise – longitudinal Crosswise- Horizontal Diagonal – corner to corner |
|
|
|
Central ray (CR) |
The central or principal beam of rays |
|
|
|
X-ray tube shall not be closer than? |
12 inches from the patient |
|
|
|
SID standardize for examinations must be indicated on technique charts |
40 inches ( 102cm) traditionally used on most examinations.
72 inches (183cm) used on examinations with increased OID to reduce magnification. |
|
|
|
Collimation |
Restriction of the x-ray beam to only anatomy of interest |
|
|
|
Collimation serves two purposes... |
•Minimizes patient exposure •reduces scatter radiation |
|
|
|
Collimation will also increase? |
Radiographic contrast |
|
|
|
Shielding guidelines |
•Gonads lie within or close to (about 5cm from) primary x-ray field
•clinical objectives is not compromised
•patient has reasonable reproductive potential |
|
|
|
Highest gonad dose in a male is when... |
A pelvis (3mGy) is performed |
|
|
|
It is the responsibility of the radiographer to |
Ensure that each radiation exposure upholds the ALARA(as low as reasonable achievable)concept |
|
|
|
Final contrast and brightness adjustments radiographic Image are done by using a |
Computer |
|
|
|
Final contrast and brightness adjustments radiographic Image are done by using a |
Computer |
|
|
|
Exposure numbers are used to determine |
Whether a image is within quality range |
|
|
|
IP phosphors are more sensitive to |
Scatter radiation |
|
|
|
IR could be open for a few minutes without causing stored image to be destroyed |
|
|
|
|
Technique chart should be in every room and on mobile machines |
|
|
|
|
Primary factors in exposure technique |
•mAs
•KVP
• automatic exposure control (AEC)
•SID
•Patient (part) thickness
•Grid
•CR exposure indicators or other digital exposure value estimates
•IR or collimated field dimensions
•screen film speed number
•electrical supply |
|
|
|
Primary factors in exposure technique |
•mAs
•KVP
• automatic exposure control (AEC)
•SID
•Patient (part) thickness
•Grid
•CR exposure indicators or other digital exposure value estimates
•IR or collimated field dimensions
•screen film speed number
•electrical supply |
|
|
|
Certain pathological conditions are required a... |
Decrease in technique |
|
|
|
Certain pathological conditions that require a decrease in technique are |
Old age pneumothorax Emphysema Emaciation Degenerative arthritis Atrophy |
|
|
|
Certain pathological conditions also require a |
Increase in technique |
|
|
|
Pathological Conditions that require a increase in technique are... |
•Pneumonia •Pleural infusion •Hydrocephalus •Enlarged heart •edema •ascites |
|
|
|
Communication is key and all imaging procedures |
Empathic communication is essential |
|
|
|
Obesity |
Increase in bodyweight by excessive accumulation of fat |
|
|
|
When imaging obese patients what is affected |
•Image quality
•the ability to transfer patient safely
•ability to find landmarks |
|
|
|
When moving patient to table make sure |
Table can be supported by patient weight |
When moving patient to table make sure |
|
|
Localization tips |
Never prod patient unnecessary
Locate jugular notch |
|
|
|
Localization tips |
Never prod patient unnecessary
Locate jugular notch |
|
|
|
Jugular notch is located |
<5feet: 21 inches 5 to 6 feet : 22inches >6 feet: 24 inches |
|
|
|
Anatomy |
The science of the structure of the body |
|
|
|
occlusal |
Plane formed by biting surface of upper and lower teeth (jaws closed) |
|
|
|
Interiliac |
Plane transects the body at the pelvis at the top of iliac crest (level of L4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Body cavities |
Thoracic
Abdominal cavity (lower portion of abdominal cavity is called pelvic cavity) |
|
|
|
Abdominal cavity has no lower portion, but the lower portion is called the pelvic cavity also referred to as |
Abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
|
What is inside thoracic cavity |
Pleural membranes lungs trachea esophagus Pericardium heart and great vessels |
|
|
|
Abdominal cavity contains |
Peritoneum Liver Gallbladder Pancreas Spleen Stomach Kidneys ureters Major blood vessels |
|
|
|
Pelvic cavity portion contains |
Rectum Urinary bladder Part of the reproductive system |
|
|
|
What are the four quadrants |
Right upper quadrant RUQ right lower quadrant RLQ left upper quadrant LUQ left lower quadrant LLQ |
|
|
|
Abdomen is divided into how many regions |
Nine |
|
|
|
Physiology |
Study of the function of the body organs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Superior regions contain |
Right hypochondrium epigastrium Left hypochondrium |
|
|
|
Middle regions |
Right lateral umbilical left lateral |
|
|
|
Inferior regions |
Right inguinal Hypogastrium Left inguinal |
|
|
|
Body habitus |
Defined as the common variations in the shape of the human body |
|
|
|
Why is body habitus important in radiography |
Because habitus determines size, shape,and position of organs in the thoracic and abdominal cavities |
|
|
|
What organs are affected by body habitus |
Heart lungs diaphragm stomach Collon gallbladder |
|
|
|
What are the four major types of body habitus |
Sthenic Anthemic hyposthenic Hypersthenic |
|
|
|
Hypersthenic 5% |
Lungs are short and wide diaphragm very high stomach high |
|
|
|
Sthenic 50% |
Lungs will be moderate length |
|
|
|
Osteology |
Study of the bones |
|
|
|
Hyposthenic 35% |
Organs and characteristics are intermediate between sthenic and asthenic |
|
|
|
Asthenic 10% |
Longest lungs stomach is the lowest |
|
|
|
How many bones are in the body |
206 |
|
|
|
What two groups are the bones divided in |
Axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton |
|
|
|
Axial skeleton has how many bones |
80 and it supports and protects the head and trunk |
|
|
|
How many bones does appendicular skeleton have |
126 and it provides a means for movement, so your extremities |
|
|
|
Compact bone |
Strong dense outer layer of compact boney tissue |
|
|
|
Spongy bone |
Inner less dense layer contains network called Trabuculae |
|
|
|
TRABECULAE is filled with what |
Red and yellow marrow |
|
|
|
Red marrow produces |
Produces red and white blood cells |
|
|
|
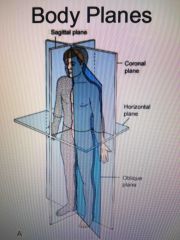
There are four fundamental Planes |
Sagittal coronal horizontal oblique |
|
|
|
Yellow marrow |
Stores fat cells |
|
|
|
Medullary cavity |
Central cavity of long bones |
|
|
|
Endosteum |
Lines the marrow cavity and lines medullary cavity |
|
|
|
Periosteum |
Tough fibrous connective tissue that covers bone, except the articular ends |
|
|
|
Ossification |
Term that applies to the development and formation of bones |
|
|
|
Two processes of ossification |
Intermembranous
Endochondral |
|
|
|
Epiphyseal plate |
Piece of Cartlidge that separates the end of the developing long bone from the central shaft |
|
|
|
When does full ossification occur |
Near the age of 21 |
|
|
|
How are bones classified |
Shape; Long short flat irregular sesamoid |
|
|
|
Where are long bones found |
Limbs |
|
|
|
Mid sagittal plane MSP |
Specific sagittal plane that passes through midline and divides body into equal right and left halves |
|
|
|
What Are short bones |
Many cancellous bones with thin outer layer of compact bone Ex carpal bones |
|
|
|
Flat bones |
They consist of two plates of compact bones
ex sternum and cranium |
|
|
|
Irregular bones |
Peculiarly shaped
ex vertebrae and facial bones |
|
|
|
Sesamoid bones |
Very small and oval they develop inside and beside tendons
ex largest is the patella |
|
|
|
Anthrology |
Study of joints or articulations between bones |
|
|
|
What are the three subdivisions of mobility of joints |
Synarthroses- immovable Amphiaryhoroses- slightly moveable Diarthroses- freely moveable |
|
|
|
Three distinct groups are based on connected tissues |
•Connective tissue •Fibrous cartilaginous •Synovial- contains joints that are freely movable |
|
|
|
How many specific types of joints fall in the three broad categories, fibrous cartilaginous and synovial |
11 specific types of joints fall with in the 3 categories |
|
|
|
How many types of fibrous joints are there |
Three; •Sydesmosis- immovable or slightly movable ex inferior tibiofibular joint • suture – immovable joint only in the skull •gomphosis-immovable joints only in the roots of the teeth
|
|
|
|
What are the six types of synovial joint's |
Gliding hinge Pivot Ellipsoid Saddle ball and socket |
|
|
|
Sagittal planes pass through the body |
Parallel with the mid sagittal plane |
|
|
|
Meniscus |
Thick cushioning pad of fibrocartilage |
|
|
|
Bursae Only saddle joint in the body |
Synovial fluid filled sac outside the main joint cavity |
|
|
|
How many saddle joints are in the body and what is it called |
One, in the hand, carpometacarpal joint between trapezium and first metacarpal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Malleolus |
Club shape process on a bone |
|
|
|
Tubercle |
Small rounded elevated process |
|
|
|
Tuberosity |
Large rounded elevated process
part of bone we're muscle and tendons attach |
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
Foreman |
Hole in bone for transmission of blood vessels |
|
|
|
View |
Used to describe the body part seen by IR |
|
|
|
Coronal plane is Passthrough the body |
Vertically from side to side, dividing the body into anterior and posterior parts |
|
|
|
Method |
Refers to a specific radiographic projection developed by an individual |
|
|
|
Projection |
Defined as the path of the CR as it exits the x-ray tube passing through the patient to the IR |
|
|
|
Position |
Term used to describe the active placing a patient in appropriate position for a radiographic examination |
|
|
|
Trendelenburg position |
Head Lower than feet |
|
|
|
Fowlers position |
Supine with head elevated |
|
|
|
Sims position |
Recovering it with patient lying on left anterior side with legs extended and right knee and thigh particularly flexed
Ex this is how they do enemas |
|
|
|
Tangential |
CR directed along the outer margin of a curve body surface |
|
|
|
How are oblique positions named |
Named according to the side and surface of the body closer to the table or IR |
|
|
|
Mid coronal plane MCP also called mid axillary plane |
Specific plane that passes through the midline and divides the body into equal anterior and posterior halves |
|
|
|
Horizontal plains pass through the body |
Crosswise at right angles to the longitudinal axis
Position that right angle to sagittal and coronal
Also divides body into superior and inferior position |
|
|
|
To specialize planes that are located to specific parts of the body are |
Interiliac
Occlusal |
|

