![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
anastomosis |
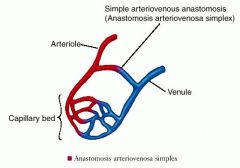
a communication between two blood vessels without any intervening capillary network
|
|
|
aneurysm
|
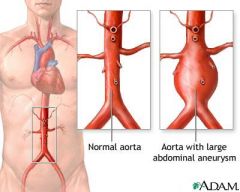
permanent localized dilation of an artery, with an increase in diameter of 1.5 times its normal diameter
|
|
|
arteriosclerosis
|
a disease of the arterial vessels marked by thickening, hardening, and loss of elasticity in the arterial walls
|
|
|
arteriovenous fistula
|
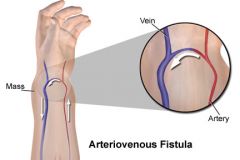
communication between an artery and a vein
|
|
|
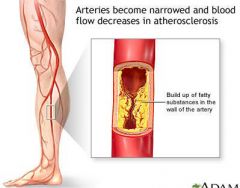
atherosclerosis
|
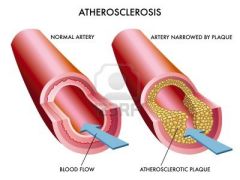
condition in which the aortic wall becomes irregular from plaque formation
|
|
|
Budd-Chiari syndrome
|
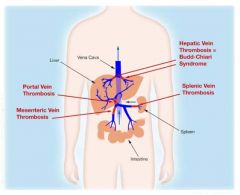
thrombosis of the hepatic veins
|
|
|
cavernous transformation of the portal vein
|
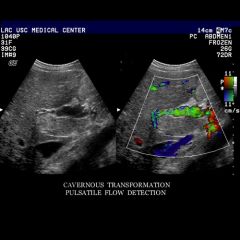
periportal collateral channels in patients with chronic portal vein obstruction
|
|
|
cystic medial necrosis
|
weakening of the arterial wall
|
|
|
dissecting aneurysm
|
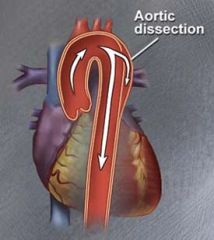
tear in the intima and/or media of the abdominal aorta
|
|
|
Doppler sample volume
|
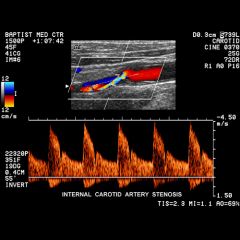
the sonographer selects the exact site to record Doppler signals and sets the sample volume (gate) at this site
|
|
|
fusiform aneurysm
|
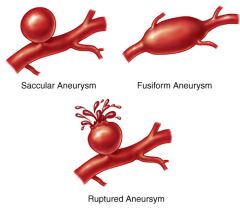
circumferential enlargement of a vessel with tapering at both ends
|
|
|
inferior mesenteric artery (IMA)
|
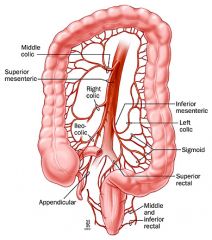
arises from the anterior aortic wall at the level of the third or fourth lumbar vertebra to supply the left transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum
|
|
|
inferior mesenteric vein (IMV)
|
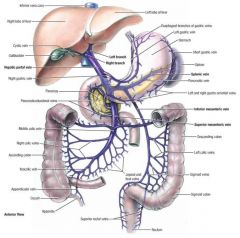
drains the left third of the colon and upper colon and joins the splenic vein
|
|
|
left gastric artery (LGA)
|
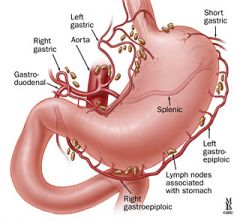
arises from the celiac axis to supply the stomach and lower third of the esophagus
|
|
|
left hepatic artery (LHA)
|
small branch supplying the caudate and left lobes of the liver
|
|
|
left renal artery (LRA)
|
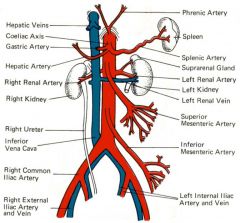
arises from the posterolateral wall of the aorta directly into the hilus of the kidney
|
|
|
left renal vein
|
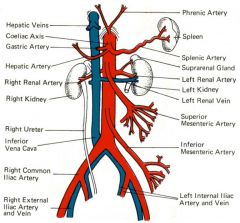
leaves the renal hilum and travels anterior to the aorta and posterior to the superior mesenteric artery to enter the lateral wall of the inferior vena cava
|
|
|
Marfan’s syndrome
|
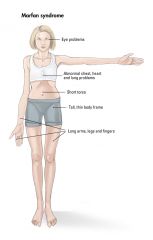
hereditary disorder of connective tissue, bones, muscles, ligaments, and skeletal structures
|
|
|
nonresistive
|
vessels that have a high diastolic component and supply organs that need constant perfusion (i.e., internal carotid artery, hepatic artery, and renal artery)
|
|
|
portal vein (PV)
|
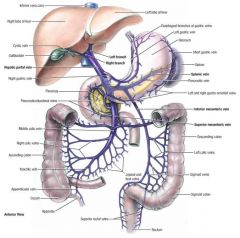
formed by the union of the superior mesenteric vein and the splenic vein near the porta hepatis of the liver
|
|
|
portal venous hypertension
|
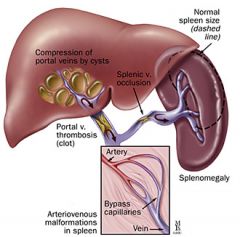
caused by increased resistance to venous flow through the liver; sonographic findings include dilation of the portal and splenic and mesenteric veins, reversal of portal venous blood flow, and the development of collateral vessels
|
|
|
pseudoaneurysm
|
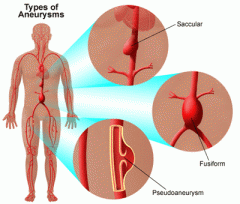
pulsatile hematoma that results from leakage of blood into soft tissues abutting the punctured artery with fibrous encapsulation and failure of the vessel wall to heal
|
|
|
resistive
|
vessels that have little or reversed flow in diastole and that supply organs that do not need a constant blood supply (e.g., external carotid artery, brachial arteries)
|
|
|
resistive index
|
peak systole minus peak diastole divided by peak systole (S − D/S = RI)
|
|
|
What resistive index means good perfusion? Bad perfusion?
|
An RI of 0.7 or less indicates good perfusion; an RI of 0.7 or higher indicates decreased perfusion
|
|
|
right gastric artery (RGA)
|
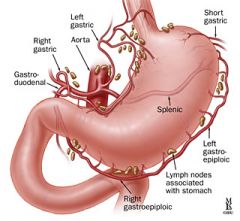
supplies the stomach
|
|
|
right hepatic artery (RHA)
|
supplies the gallbladder via the cystic artery
|
|
|
right renal artery (RRA)
|
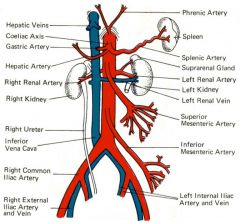
arises from the posterolateral wall of the aorta and travels posterior to the inferior vena cava to supply the kidney
|
|
|
right renal vein (RRV)
|
leaves the renal hilum to enter the lateral wall of the inferior vena cava
|
|
|
saccular aneurysm
|
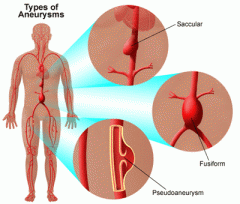
localized dilation of the vessel
|
|
|
spectral broadening
|
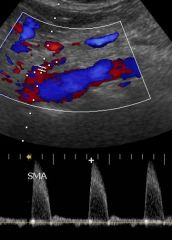
change in spectral width that increases with flow disturbance
|
|
|
splenic artery (SA)
|
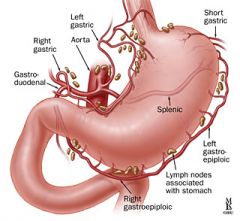
one of the three vessels that arise from the celiac axis to supply the spleen, pancreas, stomach, and greater omentum
|
|
|
splenic vein (SV)
|
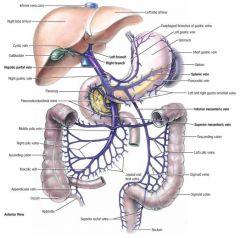
drains the spleen; travels horizontally across the abdomen (posterior to the pancreas) to join the superior mesenteric vein to form the portal vein
|
|
|
superior mesenteric artery (SMA)
|
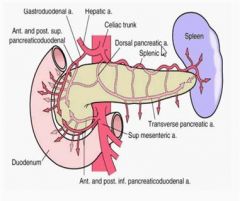
arises inferior to the celiac axis to supply the proximal half of the colon and the small intestine
|
|
|
superior mesenteric vein (SMV)
|
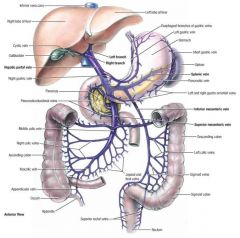
drains the proximal half of the colon and small intestine; travels vertically (anterior to the inferior vena cava) to join the splenic vein to form the portal veins
|
|
|
TIPS
|
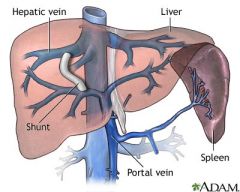
transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt
|
|
|
true aneurysm
|
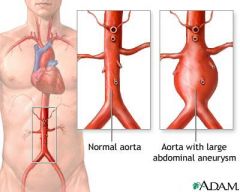
permanent dilation of an artery that forms when tensile strength of the arterial wall decreases
|
|
|
tunica adventitia
|
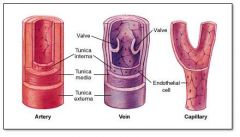
outer layer of the vascular system; contains the vasa vasorum
|
|
|
tunica intima
|
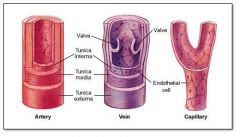
inner layer of the vascular system
|
|
|
tunica media
|
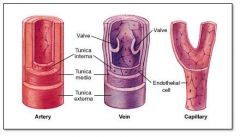
middle layer of the vascular system; veins have thinner tunica media than arteries
|
|
|
vasa vasorum
|
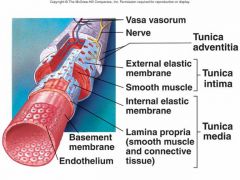
tiny arteries and veins that supply the walls of blood vessels
|
|
|
What are the Doppler Flow patterns for the Renal Vein?
|
• Variable flow like IVC
• Evaluate with renal transplants |
|
|
What are the Doppler Flow patterns for the IVC & Hepatic Vein?
|
• Vary with respiration
• Flow above and below baseline • Affected by Rt. atrium contraction |
|
|
What are the Doppler Flow patterns for the Budd-Chiari Syndrome?
|
• Thrombosis of hepatic veins
• Hepatic veins are small and echogenic • Normal flow = No Budd-Chiari |
|
|
What are the Doppler Flow patterns for the Portal Vein?
|
• Hepatopetal flow
• Continuous flow pattern; Varies slightly with respirations |
|
|
What are the Doppler Flow patterns for the Cavernous Transformation of the Portal Vein?
|
• Complication of chronic portal vein obstruction
• No Extrahepatic portal vein visualized • Echogenic porta hepatis • Periportal collaterals |
|
|
What are the Doppler Flow patterns for Portal Venous Hypertension?
|
• Hepatopetal vs Hepatofugal
• Low velocity in Portal Vein • Patent Umbilical Vein (Definitive diagnosis) • No respiratory variation |
|
|
What are the Doppler Flow patterns for Renal Artery Stenosis?
|
• Stenoses difficult to visualize
• Collaterals may form |
|
|
What are the Doppler Flow patterns for the Renal Hydronephrosis?
|
Doppler needed to rule out prominent vessels.
|
|
|
What are the Doppler Flow patterns for Renal Transplants?
|
• Turbulence near anastomosis
• 12% of transplants = renal artery stenosis • Occlusion easier to diagnose in transplant than in native kidney |
|
|
What are the Doppler Flow patterns for the Aorta?
|
• Flow varies at different levels
• Proximal AO has high systolic and low diastolic • Distal has triphasic flow |
|
|
What are the Doppler Flow patterns for the Celiac Axis?
|
• Spectral broadening
• Unchanged after meals |
|
|
What are the Doppler Flow patterns for the Hepatic Artery?
|
• Spectral broadening
• Review after heart transplants |
|
|
What are the Doppler Flow patterns for the Splenic Artery?
|
• Very turbulent flow
• Very prone to aneurysm |
|
|
What are the Doppler Flow patterns for the SMA?
|
• Highly resistive for fasting
• Non resistive for eating |
|
|
What are the Doppler Flow patterns for the Renal Artery?
|
• Nonresistive
• Spectral broadening |
|
|
True or False. Aneurysms smaller than 6 cm have high growth patterns. Those higher than 6 cm has low growth patterns.
|
False. Aneurysms SMALLER than 6 cm have LOW growth patterns. Those HIGHER than 6 cm has HIGH growth patterns.
|
|
|
What is your survival rate with an aneurysm of less than 6 cm?
|
75% chance of 1 year survival.
|
|
|
What is your survival rate with an aneurysm of larger than 6 cm?
|
50% chance of 1 year survival.
|
|
|
What is your survival rate with an aneurysm of larger than 7 cm?
|
25% chance of 1 year survival.
|
|
|
What is your risk of fatal rupture with an aneurysm larger than 7 cm?
|
75%
|
|
|
What percent of aneurisms are smaller than 5 cm?
|
1%
|
|
|
What is the mortality rate of surgery before aneurysm rupture? For surgery after rupture?
|
5% ; 50%
|
|
|
What are some MOST COMMON features of abdominal aortic aneurisms? List 5
|
• Most are TRUE aneurysms
• 95% are INFRARENAL • MURAL thrombus common in large ones • Mycotic (infection) • Atherosclerosis TIMMA ! |
|
|
When should surgery of aneurism be considered?
|
> 5cm
|

