![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Microbial contamination |
Sepsis |
|
|
Absence of significant contamination |
Asepsis |
|
|
Antimicrobial classification: agent inhibits growth, but does not kill organism |
Bacteriostatic |
|
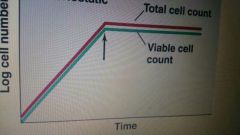
Agent classification |
Bacteriostatic |
|
|
An agent that kills microbes |
Germicides |
|
|
_______ kills bacteria _______ kills viruses _______ kills fungi |
Bactericide Viricide Fungicide |
|
|
Sterilization Killing or removal of _____ _____ Inactives all forms of microbial life, including ________ Not completely effective on ______ |
All organisms Endospores Prions |
|
|
Disinfection: Target the removal of _______ not all ____ Used on ______ ______ surfaces (table) |
Vegetative Endospores Non living |
|
|
Antiseptic Used on ______ surfaces (scrape) Kill or inhibit ______ pathogens, not ______ |
Living Vegetative Endospores |
|

Type of antimicrobial? |
Antiseptic |
|

Type of antimicrobial |
Disinfectant (disinfection) Non living surfaces |
|
|
Decontamination Ruduction of _______ to ______ _____ Mostly removal rather than ______ _____ _______ |
Microbes to safe levels Killing off pathogens |
|

Type of microbial cleaning |
Decontamination |
|
|
Sanitization - cleans _______ surface Degerming - cleans ________ surface |
Non living Living |
|
|
Drugs that have an enhanced effect in combination |
Synergism |
|
|
Drugs that have a decreased effect in combination |
Antagonism |
|
|
Time to reach 100 percent death at a particular concentration |
Death time |
|
|
Decimal Reduction time (D10) - time to achieve one log decrease in populations = |
90 percent dead 10% left alive |
|
|
Factors that influence death rate |
Concentration of treatment Length of exposure How big the population is Type of environment (surface of table or in dog poop) |
|
|
Most resistant microbes Least resistant microbes |
MOST: Prions, endospores, mycobacteria, cysts or protozoa LEAST: viruses w/ lipid envelopes, gram positive bacteria |
|
|
Growth Controls 1. Moist heat, such as |
Boiling for 10 min Autoclave pressure steam Pasteurization decontamination 63 for 30 min |
|
|
Growth Controls Dry heat: |
Flaming - incineration Oven - kills by oxidation Bactericidal treatments |
|
|
Growth Controls Filter sterilization: |
Filtration - doesn't kill, just physically seperate Depth filter from AIR Membrane filter, seperating liquids |
|
|
Growth Sterilization Radiation : can kill by ______ _____, which blocks replication |
DNA Damage |
|
|
Not all wavelengths are strong enough to damage cells, such as: |
Visible light |
|
|
X RAY and Gamma rays are _____ radiation that can penetrate through ______ and into material. _____ wavelength, so high energy. |
Ionizing Surfaces Material |
|
|
UV light is ______ _____ radiation ______ penetrate through solids |
Non ionizing Cannot |
|
|
Microwave radiation ______ wavelengths _____ sterilizing, _______ damage DNA in cells Microwaves heat water, causing . . . |
Long Not Cannot |
|
|
Low temperature _________ - inhibits growth High pressure ________ proteins, but does not harm endospores |
Bacteriostatic Denatures |
|
|
Types of growth controls |
Moist heat Dry heat Filter sterilization Radiation sterilization |
|
|
Non sterilizing physical treatments 1. 2. 3. 4. |
1. Low temp2. High Pressure3. Desiccation 4. Salting |

