![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
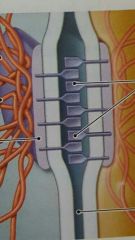
tight junction |
A tight Junction is formed by the fusion of the outer layers of two plasma membranes |
|
|
Hemidesmosomes |
Attach a cell to exteacellular structures such as the protein fibers in the basement membrane |
|
|
Gap Junctions |
Permit the free diffusion of ions and small molecules between two cells |
|
|
Stop desmosome |
ties adjacent cells together |
|
|
Functions of the Epithelial Tissue |
provide physical protection control permeability provide sensatiob produce specialized secretionsa |
|
|
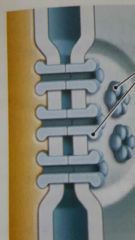
stop desmosome |
|

|
hemidesmosomes |
|
|
Gap junction |
|

|
Tight junction |
|
|
types of tissue |
ephithelial connective muscle neural |
|
|
characteristics of the epithelia |
cellularity polarity attachment avascularity regeneration |
|
|
germinative cells |
divide continually to produce bew epithelial cells |
|
|
ephithelial cells that have to absorb have what on their surface |
microvilli |
|

|
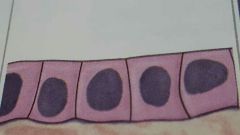
simple columnar epithelium |
|
|
simple cuboidal epithelium |
|

|
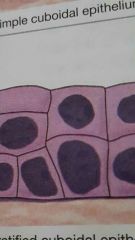
stratified columnar epithelium |
|
|
stratified cuboidal |
|
|
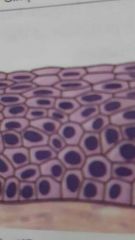
stratified squamous |
|
|
simple squamous epithelium function & where located |
reduce friction,controls vessel permeability, absorption & secretion pleural , pericardial, peritoneal cavities |
|
|
Stratified squamous epithelium function and where at |
Surface of skin, lining of mouth, throat, esophagus, rectum anus vagina Provide physical protection against abrasion, pathogens and chemical attack |
|
|
Simple cuboidal epithelium functions location |
glands, ducts, portion of kidnet tubules, thyroid gland limited protection, secretion, absorption |
|
|
stratified cuboidal epithelium function location |
lining of some ducts Protection secretion absorption |
|
|
Transitional epithelium function location |
Urinary bladder renal pelvis uterus renal pelvis, ureters permits expansion and recoil after stretching |
|
|
Columnar epithelium function location |
Lining of stomach intestine gallbladder uterine tubes and collecting ducts of kidneys Protection secretion absorption |
|
|
pseudostratified ciliared columnar epithelium |
Lining of nasal cavity, trachea, bronchi , male reproductive tract Protection secretion move mucus with cilia |
|
|
Stratified columnar epithelium |
Small areas of the pharnyx epiglottis anus mammary glands salivary glands urethra protection |
|
|
mucos membrane |
Are coated with the secretions of mucous glands these membranes line the digestive respiratory urinary and reproductive tracts |
|
|
serous membrane |
Line the ventral body cavities the peritoneal, pleural, and pericardial cavities |
|
|
cutaneous membrane |
(skin) covers the outer surface of the body |
|
|
synovial membranes |
line joint cavities and produce the fluid within the joint |
|
|
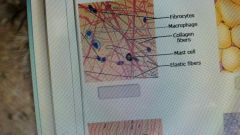
areolar tissue |
|
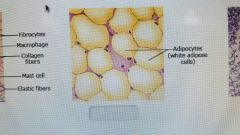
|
adipose tissue |
|
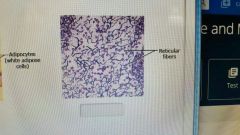
|
reticular tissue |
|

|
elastic tissue |
|

|
dense irregular connective tissue |
|
|
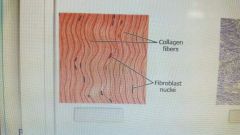
dense regular connective tissue |
|
|
Which cell produces the protein fibers in areolar connective tissue |
fibroblast |
|
|
The framework or stroma of organs such as the spleen liver and lymph nodes is made out of what tissue |
reticular connective |
|
|
The dominant fiber type in dense connective tissue is |
Collagen |
|
|
Which connective tissue cells produces collagen |
fibroblasts |
|
|
The three types of protein fibers in connective tissue are |
Collagen reticular elastic |
|
|
white blood cells |
leukocytes |
|
|
the most common type of cartilage is |
hylaine |
|
|
osseous tissue is called |
bone |
|
|
The permanent replacement of normal tissue by fibrosis tissue is called |
fibrosis |

