![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
4 properties of water |
Cohesive, temp stabilizer, polar, pH neutral |
|
|
Mole |
Tells weight& #molecules. 1 mole = 6.02x10^23 molecules |
|
|
Acid |
Adds Hydrogen ions (1-7) |
|
|
Base |
Adds hydroxide ions or binds hydrogen ions |
|
|
Dissociate |
Fall apart into hydrogen&hydroxide ions. Weaks =falls apart a little. strong = a lot |
|
|
Organic molecules |
Contain carbon |
|
|
Hydrocarbons |
Only carbon &hydrogen |
|
|
Functional groups |
Combinations of atoms most commonly found in chemical reactions. Hydroxyl/alcohol, carboxyl, amino, ketone & phosphate group |
|
|
Hydroxyl |

Polar &water soluable |
|
|
Carboxyl |
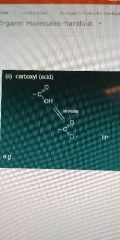
Acid |
|
|
Amino |
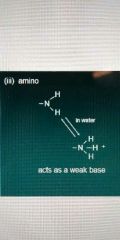
Weak base |
|
|
Phosphate group |

Acid |
|
|
Ketone |
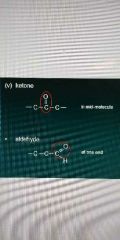
|
|
|
Organic macromolecules |
Big molecules (mostly polymers) that make up most of life excluding h2o. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids |
|
|
Monomers |
Subunits of of polymers. Usually repeating. Dehydration synthesis joins them & hydrolysis breaks them |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Monomers=saccharides/simple sugar. Polar. (CH2O)n. Source of E & building blocks(cell walls). 4 types polysaccharides: starch, glucose, cellulose & chitin |
|
|
Lipids |
Chemically diverse but all hydrophobic (mostly H&C). 3 types. Triacylglycerol E storage (fats). Steroids cell membrane components & hormones. Phospholipids major component of cell membranes. |
|
|
Triacylglycerol |
Amimal fat &vegetable oil. 2 subunits (glycerol(head/polar)&fatty acid(tails/nonpolar)) saturated or unsaturated w hydrogen. |
|
|
Phospholipids |
3 subunits. (1 glyercol 2 fatty acids &1 molecule w a phosphate group(head, v hydrophilic)) tails v hydrophobic & form bilayer |
|
|
Protein |
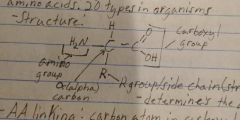
Amino acid=monomer. Many functions: enzymes and cell membrane |
|
|
Protein conformation |
Determines function(shape affects what it can bond to). 1: aa sequence 2: backbone atom H-bonds 3: r-group bonds to backbone/sidechain 4: 1+ polypeptide chain. Denatured by temp salts or pH |
|
|
Nucleic acids |
Carry genetic info. DNA &RNA (monomers=nucleotides) sugar phosphate backbone |
|
|
DNA |
Specifies AA sequence. Sugar=deoxyribose. 2 strand double helix. Has nucleus. N-bases: A=T & G÷C |
|
|
RNA |
mRNA(carries info from DNA to ribosome), tRNA (brings AA for translation) & rRNA(aids ribosomes in translation). Ribose sugar. Single stand. No nucleus. N-bases: A=U & C÷G |
|
|
Nucleotides |
5 carbon sugar, nitrogen base & 1+ phosphate group. Single ring (pyrimidine (C,T&U))and double ring (purine (A&G)) shape |
|
|
ATP |
Adenosine triphosphate |

