![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sensory Tracts |
Ascending Tracts |
|
|
Motor Tracts |
Descending Tracts |
|
|
Sensation |
Information passed to the CNS when a receptor is stimulated. Arrives in the form of action potentials in an afferent fiber. |
|
|
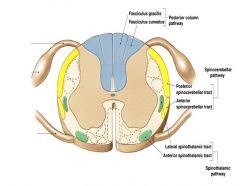
Principle Somatosensory or Ascending Tracts |
1) Posterior columns 2) Spinothalamic Tracts - Anterior & Lateral 3) Spinocerebellar Tracts |
|
|
Posterior Columns |
Proprioception, fine touch, pressure and vibration sensations. (what, where and when) Dorsal white columns. X-over @ medulla |
|
|
Spinothalamic Tracts |
Lateral Spinothalamic Tract: pain and temp - lateral white column - x-over @ spinal cord Anterior Spinothalamic Tract: crude touch and pressure - anterior white column - x-over @ spinal cord |
|
|
Spinocerebellar Tracts |
Proprioception of golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles and jt. capsules Posterior Spinocerebellar Tract - x-over: none Anterior Spincerebellar Tract - x-over @ spinal cord |
|
|
|
|
|
Sensory Homunculus |
Sensory map of the primary sensory cortex. Proportions very different from human because area of sensory cortex devoted to regions not proportional to size but # of receptors region contains. Grtr amounts devoted to hand (especially index) and face |
|
|
Motor Homunculus |
Motor map of the primary motor cortex. Proportions very different from human because area of motor cortex devoted to regions not proportional to size but # of motor units involved in region's control. |
|
|
Motor Descending Tracts |
1) Corticospinal tracts 2) Medial and Lateral pathways |
|
|
Corticospinal Tracts |
Pyramidal Tracts Provide conscious, voluntary control over skeletal muscle. - Corticobulbar tracts (x-over: cerebral peduncle) - Lateral Corticospinal tracts (x-over: medulla) - Anterior Corticospinal tracts (x-over: spinal cord, lower level) |
|
|
Corticobulbar Tracts |
Location: primary motor cortex Destination: Lower motor neurons of cranial nerve nuclei in brain X-Over: Brain stem Action: Conscious motor control of skeletal muscle |
|
|
Lateral Corticospinal tracts |
Location: primary motor cortex Destination: Lower motor neurons of anterior gray horns X-Over: Pyramids of medulla Action: Conscious motor control of skeletal muscle |
|
|
Anterior Corticospinal tracts |
Location: primary motor cortex
Destination: Lower motor neurons of anterior gray horns in C and upper T sections X-Over: Level of lower motor neurons Action: Conscious motor control of skeletal muscle |
|
|
Medial and Lateral Pathways (extrapyramidal) |
Subconscious motor pathways Coordination of motor activity, posture and tone 1) Vestibulospinal 2) Tectospinal 3) Reticulospinal 4) Rubrospinal |
|
|
Ascending Tract Neurons |
1st order: sensory neuron delivering sensation to CNS 2nd order: carries info from spinal cord/brain stem to thalamus 3rd order: carries info from thalamus to cortex |
|
|
Descending Tract Neurons |
1) Upper motor neurons: deliver motor commands from cortex to motor nuclei in brain stem or spinal cord 2) Lower motor neurons: relay motor commands from CNS motor nuclei to skeletal muscle |

