![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Solid |
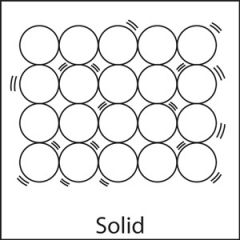
A solid is a substance that has a fixed volume and a fixed shape. In a solid, the particles are close together and usually form a regular pattern. Particles in a solid can vibrate but are fixed in one place. Because each particle is attached to several others, individual particles cannot move from one location to another, and the solid is rigid. |
|
|
Liquid |
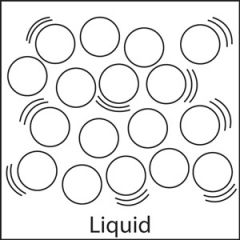
A liquid has a fixed volume but does not have a fixed shape. Liquids take on the shape of the container they are in. The particles in a liquid are attached to one another and are close together. However, particles in a liquid are not fixed in place and can move from one place to another. |
|
|
Gas |
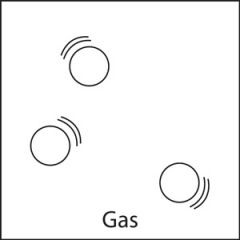
A gas has no fixed volume or shape. A gas can take on both the shape and the volume of a container. Gas particles are not close to one another and can move easily in any direction. There is much more space between gas particles than there is between particles in a liquid or a solid. The space between gas particles can increase or decrease with changes in temperature and pressure. |
|
|
Define sublimation and give an example. |

Sublimation is the process in which solid changes directly to a gas. Example: dry ice changes directly to gas. |
|
|
Define melting and melting point. Give an example. |
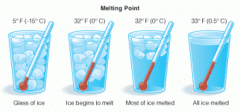
Melting is when something becomes a liquid by heat. The melting point is the temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid. Example: Ice melts at 0 degrees celsius (32 degrees Fahrenheit). |
|
|
Define freezing and freezing point. Give an example. |
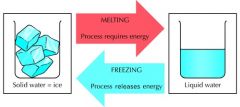
Freezing is when liquid changes into a solid and heat and pressure are released. Freezing point is the temperature at which a liquid becomes a solid. Example: Water freezes at 0 degrees celsius (32 degrees Fahrenheit). |
|
|
Define boiling and boiling point. Give an example. |
Boiling is boiling a liquid to the temperature at which it forms bubbles and turns into water vapor. Boiling point is the temperature in which a solid changes to a gas. Example: heated water forms bubbles of water vapor inside it. |
|
|
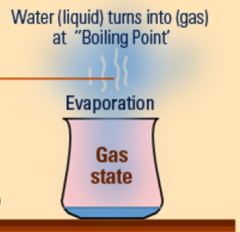
Define evaporation. Give 2 examples. |
Evaporation is the process in which a liquid changes to a gas phase. Example: Grass wet with dew slowly dries in the morning sunshine. Also, a glass of water left out on a table for a long amount of time will slowly decrease and evaporate because of the heat. |
|
|
Define condensation. Give 2 examples. |

Condensation is the process by which a gas changes into a liquid. Example: A cold glass of water forms water drops on the outside. Water droplets form on a window when humid air comes into contact with a cold surface. |
|
|
What is a chemical change? Give 2 examples. |
A chemical change is the change of one substance into another substance; something NEW is made. Example: rust forms on a bike chain or mixing vinegar with baking soda to create a new substance. Also baking a cake or brownies in an oven. |
|
|
What is a physical change? Give 2 examples. |
A physical change is a change in a substance that changes the property; it does NOT create something new. Example: stretching a rubber band and iced water melting in a cup. |

