![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are formed elements?
|
* Formed elements – living blood "cells" suspended in plasma(non-living fluid matrix)
• Erythrocytes (red blood cells, or RBCs) • Leukocytes (white blood cells, or WBCs) • Platelets |
|
|
what are % of formed elements from least to most dense?
|
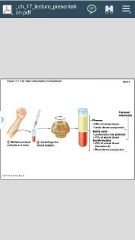
Plasma
• 55% of whole blood Formed elements • Least dense component Buffy coat • Leukocytes and platelets • <1% of whole blood Erythrocytes • 45% of whole blood (hematocrit) • Most dense component |
|
|
what are the functions of blood?
|
Functions include
– Distributing substances – Regulating blood levels of substances – Protection |
|
|
what are the distributing functions?
|
Delivering O2 and nutrients to body cells
• Transporting metabolic wastes to lungs and kidneys for elimination • Transporting hormones from endocrine organs to target organs |
|
|
what is the regulating function?
|
Maintaining body temperature by
absorbing and distributing heat • Maintaining normal pH using buffers; alkaline reserve of bicarbonate ions • Maintaining adequate fluid volume in circulatory system |
|
|
what is the protection function?
|
*MAKES SCARES
Preventing blood loss – Plasma proteins and platelets initiate clot formation • Preventing infection – Antibodies – Complement proteins – WBCs |
|
|
what is the % water in plasma?
|
90%
|
|
|
what are RBCs and its characteristics?
|
**most abundant
-no nuclie (anucleate) -filled with hemoglobin (Hb) *binds reversibly with oxygen -contains protein spectrin for flexibility -contributes to blood viscosity -dedicated to respiratory gas transport. |
|
|
what formes red bone marrow?
|
Hematopiesis
|
|
|
What name is given to the formation of red blood cells?
|
erythropoiesis
|
|
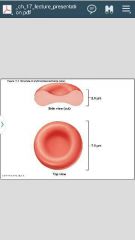
What is this? Name some important characteristics-
|
-Its a red blood cell (RBC) erythrocyte
- has no nuclei or other organelles "anucleated" -biconcave -filled with hemoglobin (hb) for gas transport. -has spectrin for flexibility -lifespan 100-120 days |
|
|
to few (RBC's): to many:
|
hypoxia;viscosity
|
|
|
What is released by kidneys some from liver in response to hypoxia?
|
The hormone Erythropoietin (EPO)
-rapid maturation of committed marrow cells |
|
|
Anemia |
has abnormally low O2 carrying capacity. |
|
|
what are causes of anemia?
|
-blood loss
-low RBC's production -high RBC distribution |
|
|
what disease is caused by single amino acid change in the bata chain? and what amino acid?
|
disease: sickle-cell anemia.
amino acid: hemoglobin. |
|
|
A blood disorder involving less than normal amounts of an oxygen-carrying protein. |
thalassemias |
|
|
what is another name for WBC's"white blood cells"?
|
leukocytes
|
|
|
what are leukocytes functions & characteristics ?
|
• Make up <1% of total blood volume
• Function in defense against disease – Can leave capillaries via diapedesis |
|
|
Leukocytosis: |
WBC count over 11,000/
mm3 – Normal response to infection |
|
|
what leukocytes are granucytes?
|
neutrophils,eosinophils, basophils.
|
|
|
what leukocytes are agranulocytes?
|
lymphocytes, monocytes
|
|
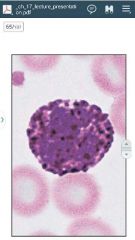
|
basophil
|
|
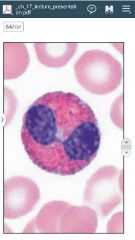
|
eosinophil
|
|
|
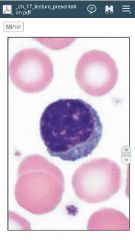
small lymphocyte
|
|
|
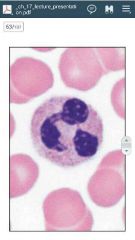
neutrophil
|
|
|
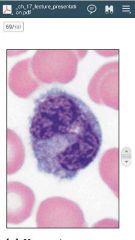
monocyte
|
|
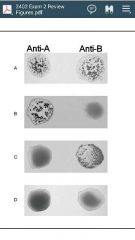
name the blood type? |
a.(AB) b.(B) c.(A) d.(O) |
|
|
most numerous leukocyte
|
neutrophil
|
|
|
increases in numbers during prolonged infections
|
monocyte
|
|
|
primarily water,noncellular; the matrix of blood
|
plasma
|
|
|
many formed in lymphoid tissue
|
lymphocyte
|
|
|
releases histamine promotes inflammation
|
basophil
|
|
|
number rises during infections
|
eosinophil
|
|
|
precursor cell of platelets
|
megakaryote
|
|
|
average blood volume of a
male female |
5.6 ; 4.5
|

