![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
6 symptoms of LMN lesions
|
1. flaccid paralysis
2. atrophy 3. areflexia 4. hypotonia 5. fasiculations 6. fibrillations |
|
|
Poliomyelitis
1. prototypic disease of what? 2. caused by a... 3. results in.. |
1. LMNs (alpha MNs in ventral horn, esp for lower limbs)
2. enterovirus 3. flaccid paralysis |
|
|
3 examples of LMN diseases
|
1. poliomyelitis
2. Werdnig-Hoffmann disease 3. Kugelberg-Welander |
|
|
2 examples of UMN lesion locations
|
1. cortical neurons that give rise to corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts
2. pyramidal tract lesions (corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts) |
|
|
3 ipsilateral motor deficits of a lateral corticospinal tract lesion
|
UMN
1. spastic hemiparesis w/ mm weakness 2. hyperreflexia 3. clasp-knife spasticity |
|
|
Dorsal column syndrome
1. 2 causes 2. ipsilateral senosry deficits |
1. subacute combined degeneration (B12) and tabes dorsalis (neurosyphilis)
2. tactile discrimination, proprioception, vibration, asteregonosis, dystaxia, Romberg sign |
|
|
Lesions to which tracts cause leg dystaxia...
1. ipsilateral 2. contralateral 3. what test is difficult to perform |
1. dorsal spinocerebellar
2. ventral spinocerebellar 3. heel to shin |
|
|
Lateral spinothalamic tract lesion
1. loss off.. 2. on which side 3. at what level |
1. pain and temp
2. contralateral (crosses in V. commissure) 3. 1 level below lesion |
|
|
Herpes Zoster
1. what is it? 2. where does it occur? 3. limited to... 4. symptoms |
1. viral infaction causing an acute inflammatory rxn
2. dorsal root or CN ganglia 3. one dermatome 4. pain, itching, burning |
|
|
Guillan Barre (acute idiopathic polyneuritis)
1. usually follow... 2. results from... 3. causes... 4. symptoms 5. effect on CSF |
1. infectious illness
2. cell-mediated immunologic rxn directed at peripheral nn. 3. mostly motor fiber demyelination and wallerian degeneration 4. ascending LMN symmptoms: weakness, flaccid paralysis, areflexia 5. increases protein, but no impact on cell count |
|
|
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS; Lou Gehrig's)
1. prototypic disease for 2. causes |
1. combined UMN and LMN
2. progressive bulbar palsy/muscular atrophy (LMN) and pseudobulbar palsy/primary lateral sclerosis (UMN) |
|
|
Ventral spinothalamic tract lesion
-loss of.. -which side? -starting at what level |
1. crude touch
2. contralateral 3. 3-4 levels below lesion |
|
|
Epiconus syndrome
1. which segments? 2. damages... 3. causes loss of.. 4. what is absent? |
1. L4-S2
2. ventral horns and long tracts 3. voluntary bladder control, lower limb motor function (thigh rotation) 4. Achilles reflex |
|
|
Cauda equina syndrome
1. involves which spinal roots? 2. causes... 3. may result from.. 4. often produces.. |
1. L3-Co
2. paralytic bladder, saddle anesthesia, motor disability, and loss of Achillies reflex (conus medullaris + epiconus) 3. intervertebral disk herniation 4. severe spontaneous radicular pain |
|
|
Filum terminale (tethered cord) syndrome
1. results from 2. 3 symptoms |
1. thickened, shortened filum terminale adering to sacrum (puts traction on conus medullaris)
2. sphicter dysfunciton, gait disorders, feet deformities |
|
|
Subacute combined degeneration
1. also known as 2. associated w/ 3. affects what 3 tracts (what losses?) 4. what does it do to them? |
1. Vit B12 neuropathy
2. pernicious anemia 3. dorsal columns (prop, vib); spinocerebellar (limb ataxia); corticospinal (UMN spasticity) 4. demyelinates |
|
|
Friedreich hereditary ataxia
1. how do you get it? 2. similar to subacute combined degeneration how? 3. what else is involved? (symptom) 4. commonly leads to... |
1. autosomal recessive inheritance
2. degenerates dorsal columns, spinocerebellar, and corticospinal tracts 3. Cerebellum/purkinje fibers (ataxia) 4. cardiomyopathy, pes cavus, kyphoscoliosis |
|
|
Syringomyelia
1. destroys.. 2. interrupts (symptoms) 3. what other characteristic symptom? 4. distribution of sensory loss |
1. ventral commissure
2. crossing spinothalamic fibers (bilat pain and temp loss) 3. atrophy of hand muscles 4. cape-like |
|
|
Multiple sclerosis
1. most common what? 2. what kind of lesions? 3. most commonly affects what segments? |
1. demyelinating diseas
2. asymmetrical lesions of white matter 3. cervical segments |
|
|
Charcot-Marie-Tooth
1. aka 2. most common what? 3. affects what two areas? (Symptoms) |
1. peroneal muscular atrophy (stork legs)
2. inherited neuropathy 3. dorsal columns (loss of prop, vib) and ventral horns (atrophy) |
|
|
Intervertebral disk herniation
1. causes what kind symptoms? 2. occurs where 90% of the time? 3. and the other 10%? |
1. spinal root symptoms: parasthesia, pain, sensory loss, hyporeflexia, mm weakness
2. L4-L5 or L5-S1 3. C5-C6 or C6-C7 |
|
|
Cervical spondylosis w/ myelopathy
1. most common what? 2. what causes it? 3. how does it present? |
1. observed myelopathy
2. calcified disk material exuded into spinal canal compressing the spinal cord 3. stiff neck, arm pain and weakness, spastic legs, dystaxia |
|
|
Hypothalamospinal tract
1. results in... 2. if transected above.. |
1. Horner syndrom
2. T2 |
|
|
Dorsal horn destruction
1. symptoms 2. on which side? 3. distributed along? |
1. anesthesia and areflexia
2. ipsi 3. dermatomal distribution |
|
|
Complete transection
1. at C1-C3 2. C4-C5 3. below T1 4. above C5 5. four other symptoms |
1. exitus lethalis
2. quadriplegia 3. paraplegia 4. loss of voluntary breathing (phrenic nucleus) 5. spastic paralysis, anesthesia, anhidrosis, loss of voluntary bladder control |
|
|
Anterior/Ventral spinal artery occlusion
1. 4 tracts it destroys (symptoms?) 2. also causes... 3. usually spares... |
1.V. horn (flaccid paralysis at level); corticospinal (spastic paralysis below level); spinothalamic (loss of pain and temp); spinocerebellar (cerebellar symptoms masked by paralysis)
2. bilateral horner syndrome 3. dorsal columns |
|
|
Conus medullaris syndrome
1. what segments? 2. destroys... 3. causes... 4. absence of... |
1. S3-Co
2. sacral parasymp nucleus 3. paretic bladder, fecal incontinence, impotence 4. lower limb muscle deficits |
|
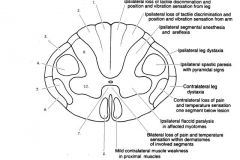
|
1. fasciculus gracilis
2. fasciculus cuneatus 3. dorsal spinocerebellar 4. lateral corticospinal 5. lateral spinothalamic 6. ventral spinocerebellar 7. ventral white commissure 8. ventral corticospinal |
|
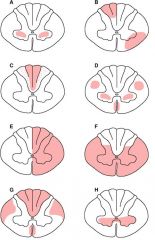
|
A. poliomyelitis
B. multiple sclerosis C. tabes dorsalis D. ALS (Lou Gehrig's) E. Brown Sequard F. ventral spinal artery occlusion G. subacute combined degeneration (Vit B12 neuropathy) H. syringomyelia I. Charcot-Marie-Tooth J. dorsal spinal artery occlusion |
|
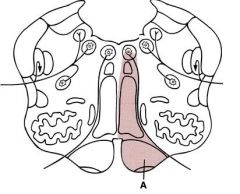
|
Medial medullary syndrome (anterior spinal a.)
1. corticospinal tract (contra hemiparesis) 2. medial lemniscus (contra loss of vib/prop) **3. hypoglossal n. (ipsi flaccid paralysis of tongue) |
|
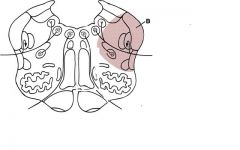
|
Lateral medullary (PICA; Wallenburg) syndrome
1. vestibular nuclei (nystagmus, nausea, vertigo) 2. inf cerebellar peduncle (dystaxia) 3. nucleus ambiguus (larynx/pharynx paralysis; loss of gag reflex) 4. spinothalamic tract (contra body pain/temp) 5. spinal trigeminal tract (ipsi face pain/temp) 6. ipsi Horner syndrome |
|
|
Medial pontine syndrome
1. results from.. 2. affected structures (resultant deficits) |
1. occlusion of paramedian branches of basilar artery
2. **a)abducent nerve (ipsi LR) b) corticobulubar tracts (contra weakness of lower face) c) corticospinal tracts (contra hemiparesis of body) d)middle cerebellar peduncle (ipsi ataxia) e) medial lemniscus (contra prop/vib) |
|
|
Lateral inferior pontine (AICA) syndrome
|
**1. facial nucleus (ipsi facial mm, taste ant 2/3)
2. cohclear nuclei (unilateral deafness) 3. vestibular nuclei (nystagmus, nausea, vertigo) 4. spinal trigmeninal tract (ipsi face pain/temp) 5. middle and inferior cp (dystaxia) 6. spinothalamic tracts (contra body pain and temp) 7. ipsi Horner syndrome |
|
|
Lateral super/mid pontine syndrome (short circumferential branch or SCA)
|
**1. trigeminal motor and main sensory nuclei (mm. of mastication, jaw deviates to paretic side, facial hemianesthesia)
2. cerebral peduncles (ipsi dystaxia) 3. spinothalamic and trigeminothalamic tracts (pain/temp from body and face) 4. ipsi Horner syndrom 5. medial lemniscus (contra loss of prop/vib from lower extremities) |
|
|
Locked in syndrome (pseudocoma)
1. what is it? 2. what does it cause? 3. how do these people communicate? |
1. infarction at base of superior pons
2. infarction of corticobulbar and corticospinal tracts (quadriplegia and loss of lower cranial nerves) 3. by blinking their eyes |
|
|
Dorsal midbrain (Parinaud) syndrome
1. common cause 2. affects what structures (resultant deficits) |
1. pinealoma
2. superior colliculis/pretectal area (paralysis of up & down gaze, pupillary disturbances, no convergence) and cerebral aqueduct (hydrocephalus) |
|
|
Paramedian midbrain (Benedikt) syndrome (paramedia branches of PCA)
|
**1. oculomotor nerve (ipsi eye looks down and out, ptosis, fixed dilated pupil)
2. Red nucleus (contra dystaxia w/ intention tremor) 3. Medial lemniscus (contro prop/vib) |
|
|
Medial midbrain (Weber) Syndrome (PCA and circle of willis aneurisms)
|
1. oculomotor nerve roots (ipsi eye down and out, ptosis, fixed dilated pupil)
2. corticobulbar tracts (contra weakness of lower face, tongue, and palate-7, 9, 10) 3. contra hemiparesis of body |
|
|
Acoustic Neuroma (Scwannoma)
|
**1. CN VIII (cochlear n = deafness; vestibular n = nystagmus, nausea, vertigo)
**2. CN VII (facial weakness) 3. spinal trigeminal tract (CN V; anesthesia of ipsi face) |
|
|
Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia (INO)
1. aka 2. results from... 3. frequent sign of... 4. causes... 5. what else causes these signs? |
1. medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) syndrome
2. lesion of MLF in medial pontine tegmentum 3. multiple sclerosis 4. MR palsy on lateral gaze and nystagmus in abducting eye w/ normal convergence 5. abducent nucleus lesion (+ LR paralysis) |
|
|
Jugular Foramen (Vernet) Syndrome
Affects what three cranial nerves? |
1. glossopharyngeal-CN IX (loss of afferent gag relfex, taste post 1/3)
2. vagal-CN X (laryngeal paralysis w/ dyphagia and hoarseness, paltal paralysis w/ loss of efferent gag reflex 3. accessory-CN XI (SCM and trapezius weakness w/ shoudler drop) |
|
|
Subclavian Steal syndrome
1. results from... 2. what happens to blood flow? 3. what clinical signs? |
1. thrombosis of L subclavian artery proximal to vertebral a.
2. blood is shunted retrograde down the vertebral a. into the L subclavian a. 3. transient weakness and claudication of left arm on exercise and vertigo/dizziness |

