![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Organism that makes its own food using energy from the environment and carbon from inorganic molecules such as CO2 |
Autotroph |
|
|
|
Main photosynthetic pigment in plants |
Chlorophyll a |
|
|
|
Organism that obtains carbon from organic compounds assembled by other organisms. |
Heterotroph |
|
|
|
An organic molecule that can absorb light of certain wavelengths |
Pigment |
Hair is colored because of.... |
|
|
Distance between the crests of two successive waves, measured in nanometers. Photons travel along these. |
Wavelengths |
|
|
|
Packets of energy in which light is organized. |
Photons |
|
|
|
First stage of photosynthesis; convert light energy into chemical energy. |
Light dependent reactions |
|
|
|
Second stage of photosynthesis; use ATP and NADPH to assemble sugars from water and CO2 |
Light-independent reactions |
|
|
|
The cytoplasm-like fluid between the thylakoid membrane and the two outer membranes of the chloroplast. |
Stroma |
Second stage (The Calving Benson cycle) of photosynthesis happens here. |
|
|
A chloroplast's highly folded inner membrane system; forms a continuous compartment in the stroma. First stage of photosynthesis occurs here. |
Thylakoid Membrane |
|
|
|
Process in which electrons flow through electron transfer chains sets up a hydrogen ion gradient that drives ATP formation. |
Electron Transfer Chain (ETC) |
|
|
|
Process by which light energy breaks down a molecule. |
Photolysis |
In the thylakoid compartment of plants, water is broken down to hydrogen ions and oxygen gas to replace electrons lost from photosystem 2 |
|
|
Cluster of pigments and proteins that converts light energy to chemical energy in photosynthesis. |
Photosystem |
|
|
|
Type of plant that uses only the Calvin-Benson cycle to fix carbon. |
C3 plant |
|
|
|
Type of plant that fixes carbon twice, in two cell types. |
C4 Plant |
|
|
|
Cyclic carbon-fixing pathway that builds sugars from CO2; the light independent reactions of photosynthesis. |
Calvin-Benson Cycle |
|
|
|
type of plant that conserves water by fixing carbon twice at different times of day. |
CAM Plant |
|
|
|
Process by which carbon from an inorganic source such as carbon dioxide gets incorporated into an organic molecule. |
Carbon Fixation |
|
|
|
Reaction in which rubisco attaches oxygen instead of carbon dioxide to ribulose biphosphate (RuBP). |
Photorespiration |
|
|
|
Ribulose Biphosphate carboxylase. Carbon fixing enzyme of the Calvin-Benson cycle. |
Rubisco |
The most abundant protein on Earth |
|
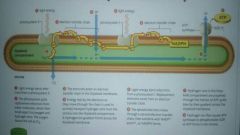
What is the name of this process? What organism does it occur in and in what organelles of its cells? What metabolic process is this part of? |
The light-dependent reaction in photosynthetic organisms. It occurs within the thylakoid membrane found within the chloroplasts. This is the first step of the process of photosynthesis. |
|
|
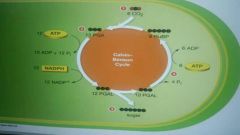
Explain the steps of this cycle. |

|
|

