![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Biochemistry
|
a field of life science; biological chemistry
|
|
|
|
decomposition reaction
|
the bonds of a reactant molecule break to form simpler molecules, atoms, or ions; AB --> A+B
|
|
|
|
exchange reaction
|
(replacement reaction), parts of 2 different types of molecules trade positions as bonds are broken and new bonds are formed; AB+CD --> AD +CB
|
|
|
|
reversible reaction
|
the product or products can change back to the reactant or reactants;
A+B --><-- AB |
|
|
|
catalyst
|
molecules that influence the rates (not the direction) of chemical reactions but are not consumed in the process.
|
|
|
|
electrolyte
|
substances that release ions in water
|
|
|
|
acid
|
electrolytes that dissociate to release hydrogen ions (H+) in water.
|
|
|
|
base
|
substances that combine with hydrogen ions.
|
|
|
|
salt
|
bases can react w/ acids to neutralize them, forming water and electrolytes called salts
|
|
|
|
pH scale
|
Mixing acids and bases can cancel out their extreme effects; much like mixing hot and cold water can even out the water temperature. A substance that is neither acidic nor basic is neutral. The pH scale measures how acidic or basic a substance is. It ranges from 0 to 14.
|
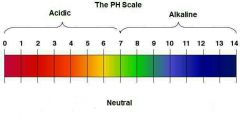
|
|
|
buffer
|
chemicals that resist pH change
|
|
|
|
organic
|
compounds that have carbon and hydrogen
|
|
|
|
inorganic
|
compounds w/out carbon and hydrogen; all other chemicals
|
|
|
|
carbohydrates
|
provide much of the energy that cells require, also supply materials to build certain cellstructures and they often are stored as reserve energy supplies.
|
|
|
|
monosaccharides
|
single sugars
|
|
|
|
disaccharides
|
double sugars
|
|
|
|
polysaccharides
|
complex carbohydrates
|
|
|
|
lipids
|
a group of organic chemicals that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents
|
|
|
|
saturated fatty acid
|
single carbon bonds link all the carbon atoms, each carbon atom binds as many hydrogen atoms as possible and is thus saturated w/ hydrogen atoms
|
|
|
|
unsaturated fatty acids
|
have one or more double bonds between carbon atoms
|
|
|
|
proteins
|
structural materials, energy sources, and chemical messengers (hormones).
|
|
|
|
enzymes
|
they speed specific chemical reactions w/out being consumed.
|
|
|
|
amino acids
|
biologically important organic compounds composed of amine and carboxylic acid functional groups, along with a side-chain specific to each amino acid.
|
|
|
|
nucleic acids
|
polymeric macromolecules, or large biological molecules, essential for all known forms of life, which include DNA (deoxyribonucleicacid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid), are made from monomers known as nucleotides.
|
|
|
|
nucleotides
|
organic molecules that serve as the monomers, or subunits, of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. The building blocks of nucleic acids, nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and at least one phosphate group.
|
|
|
|
RNA
|
Ribonucleic acid; is a polymeric molecule. It's implicated in a varied sort of biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes
|
|
|
|
DNA
|
Deoxyribonucleic acid; is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development andfunctioning of all known living organisms and many viruses.
|
|

