![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
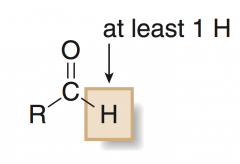
ALDEHYDE
has at least one H atom bonded to the carbonyl group |
|
|
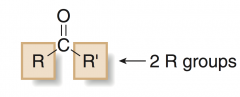
KETONE
has two alkyl or aryl groups bonded to the carbonyl group |
|
|
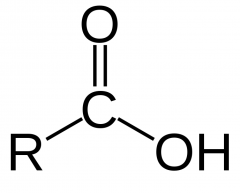
CARBOXYLIC ACID
|
|
|
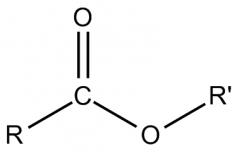
ESTER
|
|
|
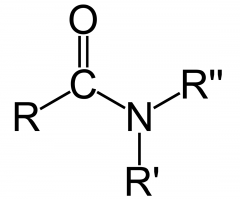
AMIDE
|
|
|
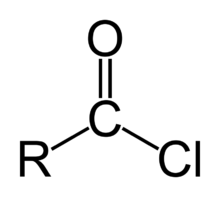
ACID CHLORIDE
|
|
|
What carbonyls undergo nucleophilic addition?
|

Aldehydes and Ketones
|
|
|
What carbonyls undergo nucleophilic substitution?
|
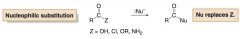
Carbonyl compounds that contain leaving groups
(OH, Cl, OR, NH2) |
|
|
acyl
|
|
|
Oxidation
|
results in an increase in the number of C – Z bonds (usually C – O bonds) or a decrease in the number of C – H bonds
|
|
|
Reduction
|
results in a decrease in the number of C – Z bonds (usually C – O bonds) or an increase in the number of C – H bonds
|
|
|
NaBH₄
|
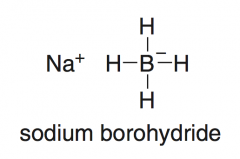
reduces aldehydes and ketones an ADDITION RXN because the elements of H2 are added across the π bond, but it is also a reduction because the product alcohol has fewer C – O bonds than the starting carbonyl compound)
-treating an aldehyde or ketone with NaBH₄ and a proton source (Water, ROH) will give an alcohol. |
|
|
LiAlH₄
|
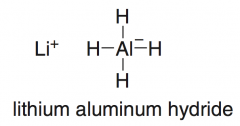
reduces aldehydes and ketones (an ADDITION RXN because the elements of H2 are added across the π bond, but it is also a reduction because the product alcohol has fewer C – O bonds than the starting carbonyl compound)
-stronger reducing agent than NaBH4, because the Al – H bond is more polar than the B – H bond -treating an aldehyde or ketone with LiAlH₄ and a proton source (Water, ROH) will give an alcohol. |
|
|
Metal Hydride Reduction
|
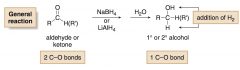
Reduces aldehydes and ketones to alcohols
|

