![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Number of protons in the atomic nucleus; determines the element. |
Atomic Number |
|
|
|
Electrical property. Opposites of these attract and the same repel. |
Charge |
|
|
|
Negatively charged subatomic particle. |
Electron |
|
|
|
A pure substance that consists only of atoms with the same number of protons. |
Element |
|
|
|
Forms of an element that differ in the number of neutrons their atoms carry |
Isotopes |
Carbon 13, Carbon 14, Carbon 12 are examples of these. |
|
|
Of an isotope, the total number of protons and neutrons in the atomic necleus |
Mass Number |
|
|
|
Uncharted subatomic particle in the atomic nucleus. |
Neutron |
|
|
|
Core of an atom; occupied by protons and neutrons. |
Nucleus |
|
|
|
Tabular arrangement of all known elements bt their atomic number |
Periodic Table |
|
|
|
Positively charged subatomic particle that occurs in the nucleus of all atoms. |
Proton |
|
|
|
Process by which atoms of a radioisotope emit energy and/or subatomic particles when their nucleus spontaneously breaks up. |
Radioactive Decay |
|
|
|
Isotope with an unstable nucleus |
Radioisotope |
Can be used as tracers for medical research/discovery or to carbon date |
|
|
A molecule with a detectable component |
Tracer |
Used in medical research |
|
|
Atom with an unpaired electron |
Free Radical |
No, not the 90s band |
|
|
Charged atom. Have an unequal number o protons and electrons. |
Ion |
|
|
|
Model of electron distribution in an atom. |
Shell Model |
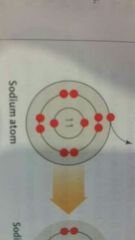
This is an example of one. |
|
|
An attractive force that arises between two atoms when their electrons interact. |
Chemical Bond |
|
|
|
Molecule that has atoms of more than one element |
Compound |
|
|
|
Chemical Bond in which two atoms share a pair of electrons |
Covalent Bond |
Water is an example of this bond. |
|
|
Measure of the ability of an atom to pull electrons away from other atoms. |
Electronegativity |
|
|
|
Type of chemical Bond in which a strong mutual attraction links ions of opposite charge. One atom will take an electron from another with less charge. These bonds are typically polar. |
Ionic Bond |
Sodium Chloride (NaCl) is an example of this chemical bond |
|
|
Separation of charge into positive and negative regions |
Polarity |
|
|
|
Property of a substance that arises from the tendency of its molecules to resist separating from one another. |
Cohesion |
Water is distinctive in this property |
|
|
Transition from a liquid to a vapor |
Evaporation |
|
|
|
Attraction between a covalently bonded hydrogen and another atom taking part in a separate covalent bond |
Hydrogen Bond |
Most visible in water |
|
|
Describes a substance that dissolves easily in water. "Water loving" |
Hydrophillic |
|
|
|
Describes a substance that resists dissolving in water. |
Hydrophobic |
Water repelling |
|
|
Compound that releases ions others than H+ or OH- when it dissolves in water |
Salt |
Americans love it on their food |
|
|
A dissolved substance. Something you add to to solvent to dissolve. |
Solute |
|
|
|
Uniform mixture of solute completely dissolved in solvent. |
Solution |
The opposite of a problem |
|
|
Liquid that can dissolve other substances |
Solvent |
|
|
|
Measure of molecular motion. |
Temperature |
Protein Slayer |
|
|
Substance that releases hydrogen ions in water |
Acid |
|
|
|
Substance that accepts hydrogen ions in water |
Base |
|
|
|
Set of chemicals that can keep the pH of a solution stable by alternately donating and accepting ions that contribute to pH. |
Buffer |
|
|
|
Amount of solute per unit volume of solution |
Concentration |
What we need to learn BIO1 |
|
|
Measure of the number of hydrogen ions in a fluid |
pH |
|

