![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Nutrients |
Stuff needed to make molecules he |

|
|
|
Heterotrophs |
heterotrophs get energy and nutrients from from other organisms |
Also known as consumers |
|
|
Autotrophs |
create their own energy by photosynthesis or chomosynthesis
|
Deep sea animals, and plants known as producers |
|
|
Phototrophs |
Organisms that creat their energy from photosynthesis |
Plants and plankton |
|
|
Photosynthesis |
A chemical reaction which she turns carbon dioxide to water with the help of the sun |
Plants and plankton do this |
|
|
Chemoautotrophs |
organisms that get their energy through chemosynthesis |
Deep sea creatures |
|
|
Chemosynthesis |
Chemical reactions that use chemical energy to make organic compounds |
Deep sea creatures do this |
|
|
Producers |
Organisms that produce their own energy |
Plants |
|
|
Consumers |
Organisms that consume producers and or other consumers for energy |
People, dogs, birds, and mice are examples |
|
|
Cellular respiration |
a Chemical reaction that organisms use to take organic compounds and turn them into energy |
C6H12O6 yields 6H2O+6CO2+energy |
|
|
Decomposers |
Organisms that break down dead things for energy |
Worms mushrooms |
|
|
Food web |
A physical representation of the relationship of energy transfer between different organisms |
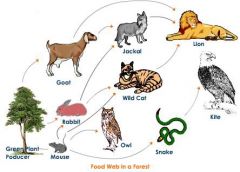
|
|
|
Biotic |
Living organisms |
People, dogs, and cats are examples |
|
|
Abiotic |
Things that aren't biotic |
Rocks and minerals |
|
|
Ecosystem |
Abiotic and biotic things in a certain place |
A coral reef |
|
|
Habitat |
Part of an ecosystem that has certain organisms |
A shallow pool of water |
|
|
Biosphere |
Everywhere stuff is and lives on earth |
The earth |
|
|
Energy |
Energy is the force that allows things to do stuff |
There seer two laws, of thermodynamics, conservation a of energy and disorder |
|
|
Chemical reaction |
The rearrangement of molecules often to creat energy |
Every organism needs this to live and takes part in your body in every second of the day |
|
|
Free energy |
Energy that is around to do work |
Known as entropy |
|
|
Heat energy |
Energy that is released from chemical reactions |
You cannot do anything with this type of energy as it is often released into the atmosphere around you |
|
|
First law of thermodynamics |
Energy cannot by created or destroyed |
Known as the conservation of energy |
|
|
Second law of thermodynamics |
Systems tend to change in a way that increases the entropy of the systems and its surroundings |
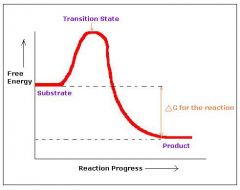
|
|
|
Entropy |
Unavailiability of energy to do work |
Disorder |
|
|
Enzymes |
Proteins that allow chemical reactions to go faster |
They are all catalysts |
|
|
Catalysts |
Chemicals that lower the necessary amount of activation energy for a reaction |
Can be enzymes but not always |
|
|
Active site |
The part of an enzyme that binds a protein to another substance |
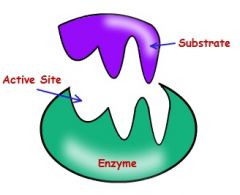
|
|
|
Substrate |
The substrate aligns with the active sight and the enzyme. The enzyme brings the substrate closer to allow products to be formed easily |
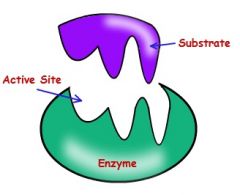
|
|
|
Metabolism |
Chemical reactions that take place inside of organisms to allow the organism to live |
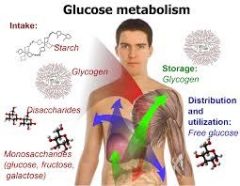
|
|
|
Decomposition |
The pocess of rotting or decaying |
This happens inside of a compost dump |
|
|
Biosynthesis |
The process of creating complex molecules in an organisms |
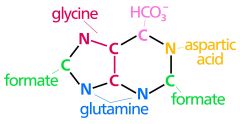
|
|
|
Oxidation |
The action of forming with an atom |
When iron does this it rusts |
|
|
ATP |
Adenosine triosphate |
The action of transporting chemical energy in cell walls |
|
|
ADP |
Adenosine diphosphate |
Essential for the flow of energy in organism |
|
|
Synthesis |
The process of creating compound through chemical reactions |
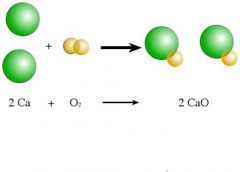
|

