![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Atomic number |
# protons |
|
|
|
Mass Number |
# protons and neutrons |
|
|
|
Atomic weight |
Weighted average of all the isotopes of an element's mass numbers |
|
|
|
Mixtures |
Physical |
|
|
|
Solution |
Particles are tiny, don't settle or scatter light |
|
|
|
Colloid/emulsion |
Solute particles are larger than in sol'n and scatter light, but don't settle |
|
|
|
Suspension |
Solute particles are very large, scatter light, and settle out |
|
|
|
Sol-gel transformation |
Fluid-> solid An ability colloids have |
|
|
|
Rank the three bonds in terms of strength |
Covalent>Ionic>H bonds |
|
|
|
Name the types of reactions |
Synthesis/combination, decomposition, Exchange/displacement, oxidation-reduction/redox, neutralization |
There are 5 |
|
|
Anabolic |
Constructive |
|
|
|
Catabolic |
Degradative |
|
|
|
Exergonic reaction |
Release energy |
|
|
|
Endergonic reaction |
Absorb energy |
|
|
|
Electrolyte |
All ions; conduct an electrical current in sol'n |
|
|
|
Carbonic acid-bicarbonate system |
H2CO3 dissociates reversibly to HCO3- and H+ resists changes in blood pH as a buffer |
|
|
|
Polymers are made up of |
Monomers |
|
|
|
Dehydration synthesis |
Removal of H2O to create bonds |
|
|
|
Hydrolysis |
Addition of water to break bonds |
|
|
|
Monosaccharides |
Simple sugars of structure (CH2O)n where n is the #C; Glucose, Fructose, Galactose, Deoxyribose, and Ribose |
|
|
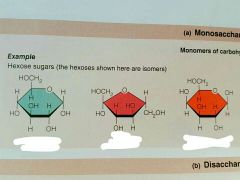
|
From left to right: Glucose, Fructose, Galactose |
|
|
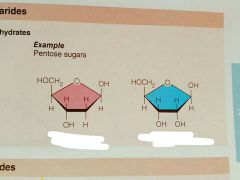
|
From left to right: Deoxyribose and Ribose |
|
|
|
Sucrose |
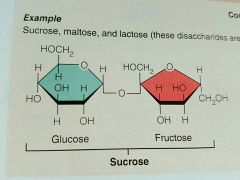
|
|
|
|
Maltose |
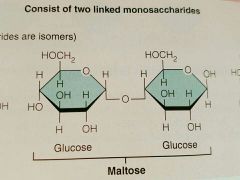
|
|
|
|
Lactose |

|
|
|
|
Disaccharide |
Two monosaccharides joined through dehydration synthesis; Sucrose, Maltose, Lactose |
|
|
|
Polysaccharides |
Polymers of monosaccharides linked by dehydration synthesis; Glycogen |
|
|
|
The polysaccharides of linked glucose |
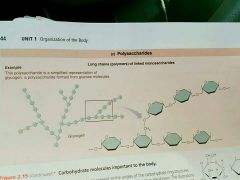
|
|
|
|
Carbohydrates main function is |
To provide ready, easily accessible energy for cellular fuel; releasing bond energy stored in glucose gives ATP. Small amounts of carbohydrates are used for structural purposes. |
|
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Include sugars and starches |
|
|
|
Lipids |
Insoluble in water but dissolve in other lipids and organic solvents such as alcohol and ether; fats and steroids |
|

